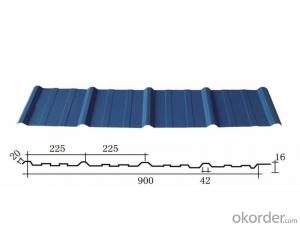
22 Gauge Sheet Metal 4X8
22 Gauge Sheet Metal 4X8 Related Searches
4X8 Galvanized Sheet Metal Galvanized Sheet Metal 4X8 Sheet Metal 4X8 4X8 Metal Sheets 4X8 Sheet Aluminum Sheet Metal Sheets 4X8 Galvanized Steel Sheet 4x8 4x8 Sheet Of Stainless Steel 4x8 Stainless Steel Sheet Stainless Steel 4x8 Sheet 4 X 8 Sheet Of Stainless Steel Stainless Steel 4x8 Sheets 28 Gauge Galvanized Sheet Metal Stainless Steel Sheets 4x8 19 Gauge Sheet Metal 30 Gauge Sheet Metal 18 Gauge Galvanized Sheet Metal 4x8 Sheet Diamond Plate Aluminum Diamond Plate Aluminum Sheets 4X8 Sheet Metal 20 Gauge 4x8 Sheet Aluminum Diamond Plate 4x8 Stainless Steel Sheet Price Aluminum Diamond Plate 4x8 Sheet Hard Plastic Sheets 4X8 1 8 Stainless Steel Sheet 16 Gauge Sheet Steel 4X8 Tin Sheets Plastic Sheets 4X8 18 Gauge Aluminum Sheet Aluminum Tread Plate Sheet 4x822 Gauge Sheet Metal 4X8 Supplier & Manufacturer from China
22 Gauge Sheet Metal 4X8 is a versatile product that comes in the form of a thin, flat sheet made from metal, specifically with a thickness of 22 gauge. This type of sheet metal is widely used across various industries due to its durability and ease of manipulation.The 22 Gauge Sheet Metal 4X8 is commonly utilized in construction, automotive, and manufacturing sectors. It is ideal for creating custom parts, brackets, and enclosures, as well as for use in various DIY projects and repairs. Its lightweight nature and malleability make it a popular choice for those seeking a sturdy yet flexible material.
Okorder.com is a reputable wholesale supplier of 22 Gauge Sheet Metal 4X8, offering a vast inventory to cater to the diverse needs of customers. With their extensive stock, they ensure that clients have access to this product in various quantities and specifications, making it a go-to source for businesses and individuals alike.
Hot Products