Triax Tx160 Geogrid
Triax Tx160 Geogrid Related Searches
Triax Geogrid Tx160 Tensar Triax Tx160 Geogrid Tensar Triax Geogrid Tx160 Tx160 Triaxial Geogrid Geogrid Tx160 Tensar Tx160 Geogrid Triax 160 Geogrid Tensar Triax 160 Geogrid Tensar Triax Tx170 Geogrid Tensar Triax Tx140 Geogrid Triax Tx Geogrid Tensar Triax Tx 140 Geogrid Tensar Triax Tx130s Geogrid Tx160 Geogrid Price Tensar Tx160 Geogrid Price Geogrid Tx150 Tx150 Geogrid Tx170 Geogrid Tensar Tx140 Geogrid Triax Geogrid Tensar Triax 160 Geogrid Price Geogrid Tx140 Tensar Triax Tx7 Geogrid Tensar Geogrid Tx140 Geogrid Triax Tensar Triax Tx5 Geogrid Tx 140 Geogrid Tensar Tx 130 Geogrid Tensar Triax Geogrid Tx 130 GeogridTriax Tx160 Geogrid Supplier & Manufacturer from China
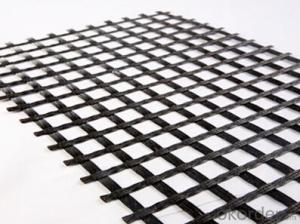
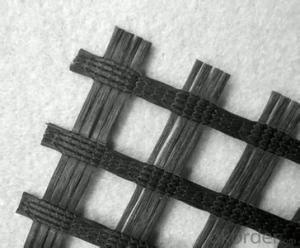
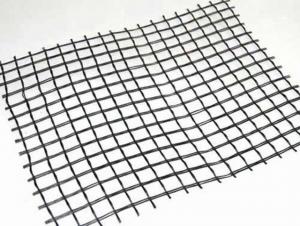
Triax Tx160 Geogrid is a high-performance geosynthetic product designed to enhance the stability and load-bearing capacity of soil structures. It is manufactured using high-quality, durable materials that provide excellent tensile strength and dimensional stability, making it ideal for various civil engineering applications. This innovative product is specifically engineered to offer superior performance in reinforcing soil, improving slope stability, and reducing the overall cost of construction projects.The Triax Tx160 Geogrid is widely used in a range of applications, including road construction, embankments, retaining walls, and other earthworks. Its unique design allows for efficient distribution of stresses across the soil, thereby increasing the overall stability and load-bearing capacity of the structure. This product is particularly beneficial in situations where soil conditions are poor or where additional reinforcement is required to support heavy loads. By incorporating Triax Tx160 Geogrid into your construction project, you can ensure a more robust and reliable foundation, ultimately leading to a longer-lasting and safer structure.
Okorder.com is a leading wholesale supplier of Triax Tx160 Geogrid, offering a vast inventory of this high-quality product at competitive prices. As a trusted distributor, we are committed to providing our customers with the best possible service and support, ensuring that they have access to the materials they need to complete their projects successfully. Our extensive inventory of Triax Tx160 Geogrid allows us to cater to the needs of both small and large-scale construction projects, making us the ideal choice for contractors and engineers seeking a reliable source for this essential geosynthetic material.
Hot Products