Prime square alloy steel billet 90mm Q235
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Prime square alloy steel billet 90mm Q235
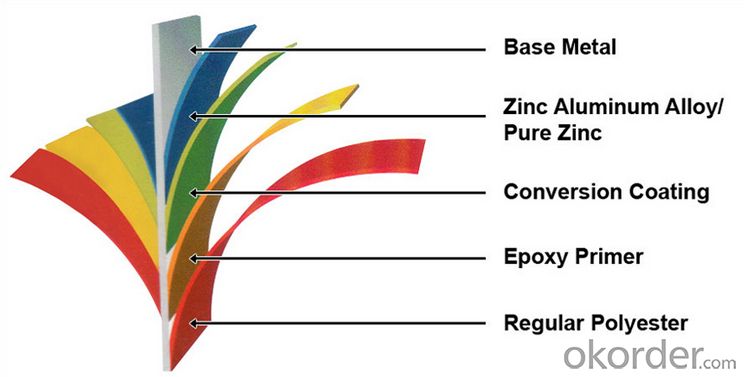
Description of Prime square alloy steel billet 90mm Q235
1. Prepainted steel coil is coated with organic layer, which provides higher anti-corrosion property and a longer lifespan than that of galvanized or galvalume steel sheets.
2. The base metals for prepainted steel coil consist of cold rolled, HDGI Steel, electro-galvanized and hot-dip alu-zinc coated steel. The finish coats of prepainted steel coil can be classified into groups as follows: polyester, silicon modified polyesters, polyvinylidene fluoride, high-durability polyester, etc.
3. The production process has evolved from one-coating-and-one-baking to double-coating-and-double-baking, and even three-coating-and-three-baking.
4. The color of the prepainted steel coil has a very wide selection, like orange, cream-colored, dark sky blue, sea blue, bright red, brick red, ivory white, porcelain blue, etc.
5. The prepainted steel coils can also be classified into groups by their surface textures, namely regular prepainted sheets, embossed sheets and printed sheets.
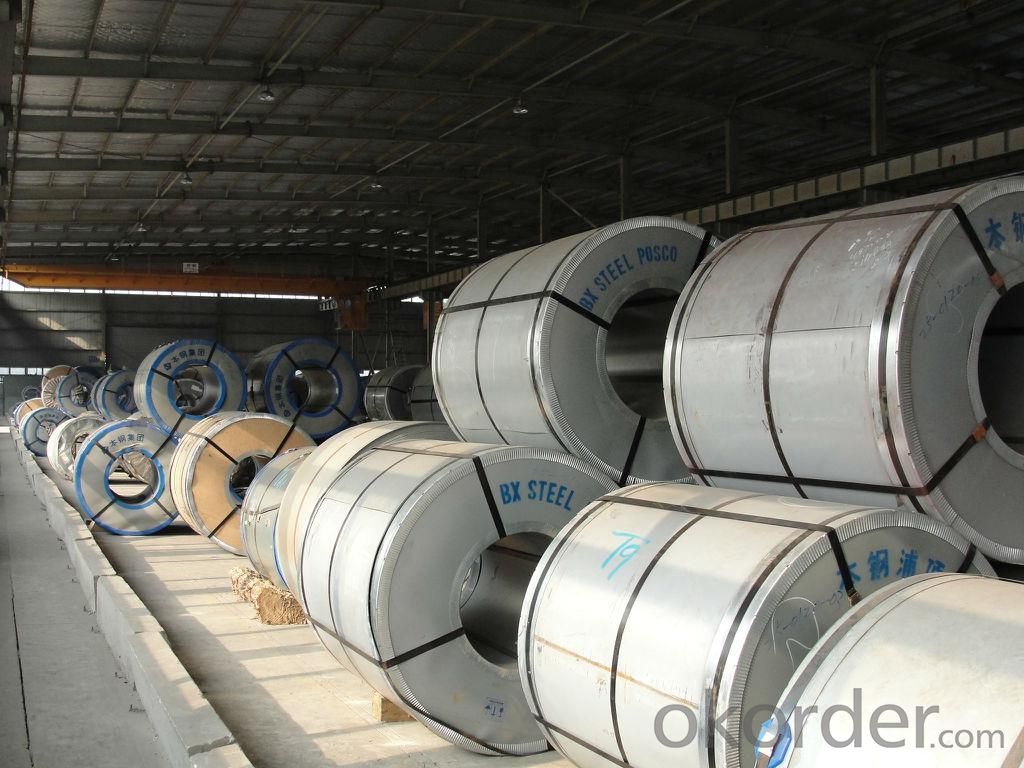

Main Feature of Prime square alloy steel billet 90mm Q235
1. Thickness: ≥20μm
2. Pencil Hardness: 2H
3. 60° specular glossiness of coating: >60
4. 180°bend: ≤3T
5. Impact: ≥9J
6. Salt Fog Resistant: ≥500h
7. Color difference:<0.8δe< span="">
Applications of Prime square alloy steel billet 90mm Q235
Manufacture Progress:HRC-CRC-GALVANIZED-COLOR COATED
Application : Construction, electrical, transportation, steel plant, composite board plant, steel tile factory
Payment & Shipping Terms:T/T ,L/C, and FOB CHINA
Minimum Order Quantity: 25Tons
Packge Type: Moisture-proof paper inner,Steel outside,Bundle by steel rope.
Package in Container : Wood as a foot pad, wire rope reinforcement,PPGI steel coil tied together by steel rope.
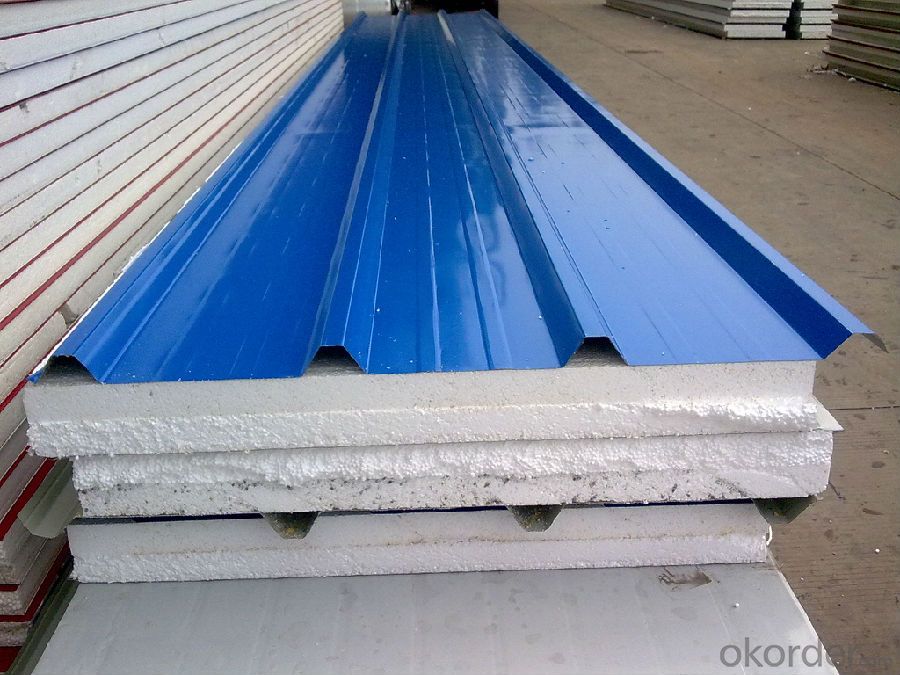

Specifications of Prime square alloy steel billet 90mm Q235
Product | Billet |
Material Grade | SGCC / SGCH / DX51D+AZ, etc |
Thickness | 0.6-3.0mm |
Width | 500-1500mm |
Tolerance | Thickness: +/-0.02mm , Width:+/-2mm |
Zinc-coating | Z30-150g/m2 |
Technique | Raw material: Hot rolled steel coil --> Cold rolled_>hot dipped galvalume |
Surface | Dried, Chromated, Unoiled |
Spangle | Regular spangle , small spangle, zero spangle |
ID | 508MM 610MM |
Coil weight | 1-25MT |
Export package | Cardboard inner sleeves, Waterproof paper, galvanized steel covered and steel strip packed |
FAQ of Prime square alloy steel billet 90mm Q235
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1. How Can I Visit There?
Our company is located in Tianjin City, China, near Beijing. You can fly to Tianjin Airport Directly. All our clients, from home or aboard, are warmly welcome to visit us!
2. How Can I Get Some Sample?
We are honored to offer you sample.
3. Why choose CNBM?
we always fix steel produce in container well to make it safe arrive at destination port
we always provide best and professional forward service for our buyer
we always apply 14days free detention for our buyers container in destination
we provide one set After-sales service for our buyer
we provide China inland steel market price report
we help our buyer become number one in local market .
- Q: How are steel billets labeled for identification purposes?
- Steel billets are labeled for identification purposes using a combination of alphanumeric codes and markings. These labels provide crucial information about the steel billet's composition, size, and other important details. The most common method of labeling steel billets involves stamping or engraving the required information directly onto the surface of the billet. This can include details such as the grade of steel, heat number, lot number, and the manufacturer's symbol or logo. These markings are typically made using industrial-grade ink or through a process called electrochemical etching, which ensures durability and legibility even in harsh environments. Additionally, steel billets may also have identification tags or labels attached to them, providing further information that cannot be easily engraved or stamped. These tags or labels may include barcodes, QR codes, or RFID tags, which can be scanned or read using specialized equipment to quickly access the relevant information. By using these labeling methods, steel billets can be easily identified, tracked, and traced throughout their lifecycle, ensuring quality control, inventory management, and efficient production processes in the steel industry.
- Q: Can steel billets be forged into complex shapes?
- Yes, steel billets can be forged into complex shapes using various forging techniques such as open die forging, closed die forging, or impression die forging. These processes involve heating the billet and applying pressure to shape it into the desired form.
- Q: Can steel billets be used in the production of railway infrastructure?
- Yes, steel billets can be used in the production of railway infrastructure. Steel billets are semi-finished steel products that can be further processed into various railway components such as rails, sleepers, and fasteners. Due to their high strength, durability, and ability to withstand heavy loads and harsh environmental conditions, steel billets are commonly used in the manufacturing of railway infrastructure to ensure the safety and efficiency of train operations.
- Q: How are steel billets cleaned before further processing?
- Steel billets are cleaned before further processing through a series of steps to remove any impurities or contaminants. The cleaning process starts with the billets being subjected to a high-pressure water jet to remove any loose scale or dirt on the surface. This water jetting helps in removing most of the loose particles and provides a clean surface for further cleaning. After the initial water jetting, the billets are then immersed in an acid bath. The acid bath can be a mixture of different chemicals like hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, or a combination of both. The acid bath helps in removing any remaining scale or oxide layers on the surface of the billets. The acid reacts with these impurities, dissolving them and leaving a clean surface behind. Once the acid cleaning is complete, the billets are rinsed thoroughly with water to remove any traces of the acid. This rinsing process is crucial to ensure that no acid residue remains on the surface, as it could potentially affect the quality of the final product. After rinsing, the billets are then dried using hot air or in a furnace to remove any moisture. This drying process is necessary to prevent any rusting or corrosion from occurring on the surface of the billets. Overall, the cleaning of steel billets before further processing is a crucial step in ensuring the quality and integrity of the final product. It helps in removing impurities, scale, and oxide layers from the surface, providing a clean and uniform surface for subsequent processing operations.
- Q: How are steel billets stored and transported?
- Steel billets, which are used for further processing, are carefully stored and transported to maintain their quality and safety. In terms of storage, steel billets are kept in designated areas within steel plants or warehouses, equipped with proper ventilation, drainage, and protection from the elements. They are organized in stacks with enough space between them for easy accessibility and inspection. To maximize space, steel billets are often stored vertically in racks or on specially designed shelves. This allows for easy handling and transportation. When it comes to transportation, heavy-duty equipment such as cranes or forklifts are used to move the billets safely, minimizing the risk of damage or injury. Chains or straps are used to secure the billets and prevent movement during transit. For longer distance transportation, steel billets are loaded onto trucks, trains, or ships. Containers or trailers are chosen based on the size and weight of the billets to ensure stability and safety. Proper weight distribution is crucial to maintain balance and prevent accidents. During transportation, it is important to protect the billets from moisture, extreme temperatures, and other external factors that could affect their quality. This may involve covering them with tarpaulins or using specialized containers. In conclusion, steel billets are stored and transported with great care to maintain their integrity and quality. Proper storage methods and suitable environmental conditions prevent damage and deterioration. Heavy-duty equipment and secure transportation minimize the risk of accidents. By following these practices, steel billets can be safely stored and transported, ready for further processing in the steel industry.
- Q: How do steel billets compare to other steel products?
- Steel billets are raw steel products that are formed into a specific shape, typically a square or rectangular cross-section. They are often used as a starting material for further processing and manufacturing of various steel products. Compared to other steel products, steel billets offer flexibility in terms of size and shape, allowing manufacturers to produce a wide range of end products. Additionally, steel billets possess superior strength and durability, making them an excellent choice for structural and construction applications.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of wire products?
- Wire products rely on steel billets as a crucial element in their production. These billets serve as the initial material for the wire manufacturing process. Typically, steel billets are semi-finished items that take the form of rectangular or square shapes. Molten steel is solidified to create these billets, which then undergo various shaping techniques to achieve the desired dimensions. The first step in using steel billets for wire production involves heating them to a specific temperature in a furnace. This procedure, known as annealing, serves to soften the steel and increase its malleability. Consequently, it becomes easier to mold the billets into wire shapes. Once the billets have been heated and softened, they are subjected to a series of rollers and drawing dies. These machines gradually decrease the cross-sectional area of the billets, elongating them into the desired wire diameter. Wire drawing is the term used to describe the process of reducing the billets' diameter. Throughout the wire drawing process, the steel billets undergo multiple passes through the rollers and drawing dies. Each pass further reduces the diameter of the billets until they reach the desired wire size. This continuous reduction in diameter also enhances the mechanical properties of the wire, such as tensile strength and ductility. Following the wire drawing process, the steel wire is typically wound onto spools or reels for additional processing or distribution. Depending on its intended use, the wire may undergo further treatments, such as heat treatment or surface coating, to enhance its properties or provide protection against corrosion. In conclusion, steel billets are utilized in wire product manufacturing through a series of steps involving heating, shaping, and drawing through rollers and dies to reduce their diameter and transform them into wire shapes. This process enables the production of wires with varying dimensions and properties, making them suitable for a wide array of applications in industries such as construction, automotive, electrical, and manufacturing.
- Q: How are steel billets inspected before they are used in production?
- Steel billets are inspected thoroughly before they are used in production to ensure their quality and adherence to the required specifications. The inspection process typically involves several key steps. Firstly, visual inspection is conducted to examine the surface of the billets for any surface defects such as cracks, seams, or deformities. Any irregularities can indicate potential weaknesses or problems in the billet that may affect its performance during production. Secondly, dimensional inspection is performed to verify the billet's size, length, width, and other critical dimensions. This is crucial to ensure that the billets meet the precise requirements of the production process and can be seamlessly integrated into the manufacturing operations. Thirdly, ultrasonic testing is often employed to detect any internal defects or discontinuities within the billets. Ultrasonic waves are passed through the billet, and any reflections or echoes are analyzed to identify any flaws such as voids, inclusions, or cracks that may compromise the structural integrity of the billets. Additionally, magnetic particle inspection may be carried out to identify surface or near-surface defects that may not be visible to the naked eye. This technique involves applying magnetic particles to the surface of the billet and detecting any magnetic leakage caused by defects through the use of magnetic fields. Furthermore, chemical analysis is frequently performed to ensure that the steel billets have the desired chemical composition. This involves taking samples from the billets and subjecting them to various tests to determine the percentages of different elements present. This analysis guarantees that the billets possess the necessary chemical properties for the intended application. Overall, steel billets undergo a comprehensive inspection process that encompasses visual examination, dimensional verification, ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle inspection, and chemical analysis. This multi-faceted approach ensures that the billets meet the required quality standards and are suitable for use in production, thus minimizing the risk of any performance issues or failures during manufacturing processes.
- Q: What are the properties and characteristics of steel billets?
- Steel billets are semi-finished products that possess several key properties and characteristics. Firstly, they have a rectangular or square cross-section with a relatively large size, typically ranging from 100x100mm to 200x200mm. They are manufactured through the process of continuous casting, which ensures their uniform composition and high quality. Steel billets exhibit excellent strength and hardness, making them suitable for various applications in the manufacturing industry. They have a high resistance to deformation, enabling them to withstand heavy loads and pressures. Additionally, they have good ductility and can be easily shaped or formed into desired products through processes like rolling or forging. Another important characteristic of steel billets is their excellent thermal conductivity, enabling efficient heat transfer during processing. They also have a good resistance to corrosion, which makes them suitable for outdoor applications and in environments with high humidity or exposure to chemicals. Overall, steel billets are versatile and robust materials with a wide range of applications in the construction, automotive, and machinery industries, among others. Their distinctive properties make them a preferred choice for various manufacturing processes, enabling the production of durable and reliable end products.
- Q: What are the different surface treatments for steel billets?
- Steel billets can undergo various surface treatments to enhance their performance and safeguard them against corrosion. Hot-dip galvanizing is a popular method, which involves immersing the billets in molten zinc to create a protective coating that acts as a barrier against moisture and corrosive elements. Electroplating offers another option, where a thin layer of metal like chromium or nickel is deposited onto the billet surface using an electric current. This not only provides corrosion resistance but also enhances the appearance of the billets. Painting or powder coating is a third approach, wherein a layer of paint or dry powder is applied to the billet surface. This forms a protective barrier, preventing moisture and corrosive substances from reaching the steel. Shot blasting or sandblasting can also be utilized for surface treatment. This technique involves propelling abrasive particles at high speeds onto the billet surface to eliminate impurities and scale, resulting in a clean and smooth finish. Lastly, chemical treatments like phosphating are available. Phosphating involves immersing the steel in a phosphoric acid solution, forming a protective phosphate coating that improves corrosion resistance and promotes paint adhesion. Ultimately, the choice of surface treatment for steel billets depends on the specific requirements of the application and the desired level of protection against corrosion and environmental factors.
Send your message to us
Prime square alloy steel billet 90mm Q235
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords






























