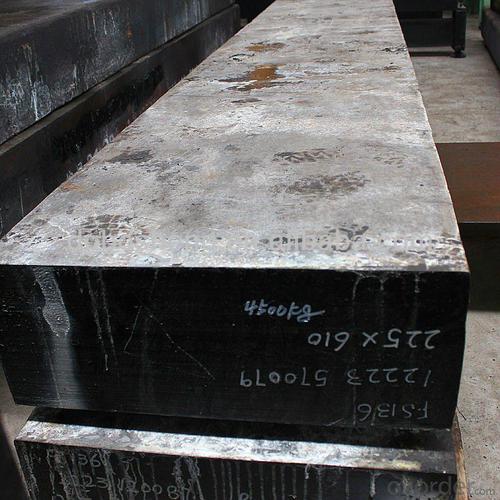
Prime square alloy steel billet 135mm Q235
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Prime square alloy steel billet 135mm Q235
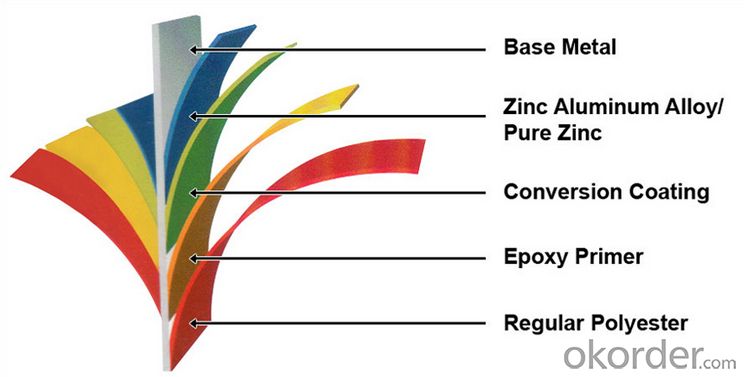
Description of Prime square alloy steel billet 135mm Q235
Manufacture Progress:HRC-CRC-GALVANIZED-COLOR COATED
Application : Construction, electrical, transportation, steel plant, composite board plant, steel tile factory
Payment & Shipping Terms:T/T ,L/C, and FOB CHINA
Minimum Order Quantity: 25Tons
Packge Type: Moisture-proof paper inner,Steel outside,Bundle by steel rope.
Package in Container : Wood as a foot pad, wire rope reinforcement,PPGI steel coil tied together by steel rope.

Main Feature of Prime square alloy steel billet 135mm Q235
Uncoated CR steel sheet
With the features of in line with the international highest standards in demension and shape, excellent surface finish and properties, the products are mainly used in home appliance and automobile industries.
Galvanized steel sheet(include HDG and EG)
With the features of good corrosion resistance, the products are mainly used in automobile, home appliance, electronics, building and machinery manufacture industries, etc.
Precoated steel sheet
With the features of enviromental protection and good processablility, long lasting surface durability, rich in colors, the products are maily used in building, home appliance and furniture industries, etc.
Applications of Prime square alloy steel billet 135mm Q235
1) Excellent corrosion resistance: The zinc layer provides a good protection of Pre-painted Galvanizeed Steel Sheet.
2) High heat resistance: The reflective surface of the material aids in efficiently reflecting the sunlight away and in turn reducing the amount of heat transmitted. The thermal reflectivity converts into energy savings.
3) Aesthetics: Pre-Painted Galvanized steel sheet is available in plethora of patterns and multiple sizes as per the requirements that given by our customers.
4) Versatility: can be used in the various areas.

Specifications of Prime square alloy steel billet 135mm Q235
Product | Billet |
Material Grade | SGCC / SGCH / DX51D+AZ, etc |
Thickness | 0.6-3.0mm |
Width | 500-1500mm |
Tolerance | Thickness: +/-0.02mm , Width:+/-2mm |
Zinc-coating | Z30-150g/m2 |
Technique | Raw material: Hot rolled steel coil --> Cold rolled_>hot dipped galvalume |
Surface | Dried, Chromated, Unoiled |
Spangle | Regular spangle , small spangle, zero spangle |
ID | 508MM 610MM |
Coil weight | 1-25MT |
Export package | Cardboard inner sleeves, Waterproof paper, galvanized steel covered and steel strip packed |
FAQ of Prime square alloy steel billet 135mm Q235
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1. How Can I Visit There?
Our company is located in Tianjin City, China, near Beijing. You can fly to Tianjin Airport Directly. All our clients, from home or aboard, are warmly welcome to visit us!
2. How Can I Get Some Sample?
We are honored to offer you sample.
3. Why choose CNBM?
we always fix steel produce in container well to make it safe arrive at destination port
we always provide best and professional forward service for our buyer
we always apply 14days free detention for our buyers container in destination
we provide one set After-sales service for our buyer
we provide China inland steel market price report
we help our buyer become number one in local market .
- Q: What are the common defects in steel billets during hot rolling?
- Some common defects in steel billets during hot rolling include surface cracks, internal cracks, surface scales, segregation, and surface defects such as pits, scars, and scratches. These defects can affect the quality and integrity of the final product and may require further processing or rejection of the billets.
- Q: How long do steel billets last?
- The lifespan of steel billets can vary depending on various factors such as the quality of the steel, storage conditions, and usage. Generally, steel billets can last for decades if stored properly and used within their recommended lifespan.
- Q: What are the different types of steel billet inspection techniques?
- In the industry, various techniques are utilized for inspecting steel billets to ensure their quality and integrity before further processing or utilization in manufacturing. Some commonly employed inspection techniques comprise: 1. Visual Inspection: Inspectors visually examine the steel billets for surface defects like cracks, pits, or deformities, making it a quick and effective method for detecting obvious visual defects. 2. Dimensional Inspection: This technique involves measuring the dimensions of the steel billet using tools like Vernier calipers or micrometers, ensuring that the billets meet the required dimensional specifications. 3. Ultrasonic Testing: High-frequency sound waves are used in ultrasonic testing to detect internal defects or inconsistencies in the steel billets. This technique can identify defects like cracks, voids, or inclusions that may not be visible to the naked eye. 4. Magnetic Particle Inspection: By applying magnetic fields to the steel billets and utilizing iron particles or magnetic ink, this technique identifies surface and near-surface defects, particularly cracks or discontinuities. 5. Eddy Current Testing: Eddy current testing utilizes electromagnetic induction to detect surface defects and measure the conductivity or thickness of the steel billets. It is a non-destructive technique that can identify defects like cracks, corrosion, or variations in material thickness. 6. Radiographic Testing: X-rays or gamma rays are employed in this technique to inspect the internal structure of the steel billets, enabling the detection of defects like inclusions, voids, or improper internal structure. 7. Dye Penetrant Inspection: By applying a dye or fluorescent liquid to the steel billets, dye penetrant inspection detects surface defects. The dye seeps into cracks or discontinuities, and excess dye is wiped off, leaving only the dye trapped in the defects, which can be easily identified under UV light. These techniques are commonly used for inspecting steel billets, with each having its own advantages and limitations. The choice of technique depends on factors such as the type and size of the billets, the level of defect detection required, and budget constraints.
- Q: What are the main factors affecting the metallurgical properties of steel billets?
- The main factors affecting the metallurgical properties of steel billets include the chemical composition of the steel, the cooling rate during solidification, the presence of impurities or alloying elements, the microstructure, and the heat treatment processes applied.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of bars and rods?
- Steel billets are an integral component in the manufacturing process of bars and rods. These billets, which are cylindrical in shape, serve as the starting point for producing various types of bars and rods. To begin with, steel billets are often made through a process called continuous casting. This involves pouring molten steel into a mold, which then solidifies and forms a billet. The billets are typically heated to a specific temperature to improve their workability and reduce the risk of cracking during subsequent processes. Once the billets are prepared, they are sent to rolling mills where they are subjected to intense pressure and high temperatures. This process, known as hot rolling, involves passing the billet through a series of rollers to gradually shape it into the desired form. The rolling mills can be equipped with different types of rolls, such as flat rolls or grooved rolls, depending on the specific requirements of the bar or rod being produced. During the hot rolling process, the billet is elongated and reduced in cross-sectional area, resulting in a longer and thinner product. This transformation allows for the production of bars and rods with consistent dimensions and improved mechanical properties. The hot rolling process also refines the grain structure of the steel, enhancing its strength and toughness. After hot rolling, the bars or rods may undergo further processes to achieve specific characteristics. These additional processes may include quenching and tempering, which aim to optimize the mechanical properties of the final product, such as hardness and ductility. In summary, steel billets play a crucial role in the manufacturing of bars and rods. They are transformed through the hot rolling process to achieve the desired shape, dimensions, and mechanical properties. The versatility of steel billets allows for the production of a wide range of bars and rods used in various industries, including construction, automotive, and manufacturing.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of power transmission equipment?
- Steel billets are used in the manufacturing of power transmission equipment as they serve as the raw material for various components such as gears, shafts, and housings. These billets are forged, machined, and shaped into the required sizes and shapes to create strong and durable parts that can withstand the high loads and pressures involved in power transmission. Overall, steel billets play a vital role in ensuring the reliability and performance of power transmission equipment.
- Q: What are the different surface finishes available for steel billets?
- There are several different surface finishes available for steel billets, depending on the specific requirements and applications. Some of the commonly used surface finishes include: 1. Hot Rolled: This is the most basic surface finish obtained by rolling the steel billets at high temperatures. It results in a rough and scaled surface, which is suitable for applications where aesthetics are not a concern. 2. Cold Rolled: In this process, the steel billets are rolled at room temperature to achieve a smoother and more polished surface finish. Cold rolling helps to improve the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of the billets. 3. Pickled and Oiled: This surface finish involves the removal of scale and rust from the steel billets by using an acid solution, followed by an oil coating to prevent corrosion. It provides a clean and rust-free surface, commonly used in the automotive and construction industries. 4. Galvanized: Galvanizing involves the application of a zinc coating to the steel billets to protect them from corrosion. This surface finish provides excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for outdoor applications, such as fencing, roofing, and structural components. 5. Passivated: Passivation is a chemical process that removes free iron from the steel surface, enhancing its corrosion resistance. This surface finish is commonly used in the production of stainless steel billets to improve their resistance to rust and other forms of corrosion. 6. Shot Blasting: Shot blasting involves the projection of small abrasive particles onto the steel billets' surface to remove scale, rust, and other impurities. This process results in a textured and uniform surface finish, ideal for applications where improved adhesion is required, such as painting or coating. 7. Polished: Polishing is a mechanical process that involves the use of abrasive materials to smoothen the surface of steel billets and achieve a high-gloss finish. This surface finish is often used in decorative applications, such as furniture, architectural components, and jewelry. It is important to note that the choice of surface finish for steel billets depends on various factors, including the intended application, desired aesthetics, and the level of corrosion resistance required.
- Q: What are the main factors affecting the mechanical properties of steel billets?
- There are several main factors that can affect the mechanical properties of steel billets. 1. Chemical Composition: The chemical composition of steel, specifically the amounts of carbon, alloying elements, and impurities, plays a significant role in determining its mechanical properties. Higher carbon content usually leads to increased strength but reduced ductility. Alloying elements such as manganese, nickel, and chromium can enhance specific properties like hardness, toughness, or corrosion resistance. 2. Heat Treatment: The heat treatment process, which involves heating and cooling the steel billets under controlled conditions, can greatly influence their mechanical properties. Different heat treatment methods, such as annealing, quenching, and tempering, can alter the microstructure and consequently the hardness, strength, and toughness of the steel. 3. Microstructure: The microstructure of steel, which is determined by the cooling rate during solidification or heat treatment, is another crucial factor. The presence of different phases, grain size, and distribution of alloying elements within the microstructure can significantly affect the steel's mechanical properties. 4. Manufacturing Process: The manufacturing process used to produce steel billets can also impact their mechanical properties. Factors such as casting method, rolling or forging techniques, and the presence of any defects or impurities introduced during production can influence the final properties of the billets. 5. Temperature: Temperature has a considerable influence on the mechanical properties of steel. It can affect the strength, ductility, and toughness of the material. For instance, as temperature decreases, steel tends to become more brittle, whereas at elevated temperatures, it may exhibit reduced strength and increased ductility. 6. Strain Rate: The rate at which a load is applied to the steel billets, known as strain rate, can affect their mechanical properties. High strain rates, such as those experienced during rapid impact or dynamic loading, can result in different behavior and failure mechanisms compared to slower or static loading conditions. It is important to note that these factors are interrelated, and changes in one factor can influence others, leading to a complex interaction and a wide range of possible mechanical properties for steel billets.
- Q: What are the main factors affecting the thermal expansion of steel billets?
- The main factors affecting the thermal expansion of steel billets include temperature, composition of the steel, and the grain structure of the material.
- Q: What are the potential applications of steel billets in the defense sector?
- Steel billets have a range of potential applications in the defense sector, including the manufacturing of armored vehicles, tanks, and naval vessels. They can also be used for constructing military infrastructure, such as bunkers, fortifications, and barriers. Additionally, steel billets can be utilized in the production of various weapons and ammunition, such as artillery shells and components for firearms. The strength, durability, and versatility of steel make it an essential material for various defense applications.
Send your message to us
Prime square alloy steel billet 135mm Q235
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords

































