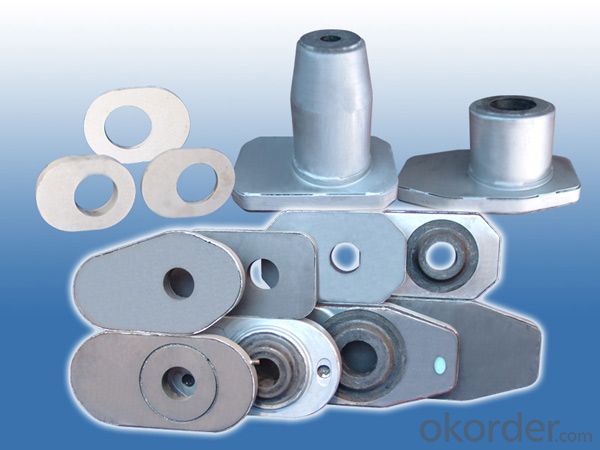
Monolithic Refractories Slide Gate Plates for Ladle & Tundish
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 set
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 set/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specifications
Ladle Sliding Plate
1.Competitive price
2.Manufacture
3.Worldwide customers
4.Long service life
Slide gate plate Information
Alumina-carbon slide gate plate is characterized by high strength, erosion resistance and good thermal shock resistance. They are preferred products for large/middle ladle and continuous casting tundish. They can meet the needs of different steel grades.
Features:
1. Tundish Slide Gate Plate
2. Tundish Slide Gate Plate with good performance
3.long service life
4.fit for tundish
5. original manufacturer with own r&d team
6. good reputation at home & abroad
7. with competitive price
Application
They are preferred products for large/middle ladle and continuous casting tundish. They can meet the needs of different steel grades.
Burned slide plate ladle refractory brick 1. Passed ISOcertified 2.have a good reputation on both domestic and oversea country
Physicochemical indexes :
ITEM | Al-C Slide Plate | Al-Zr-C Slide Plate | ||||||
70 | 75 | 80 | 85 | 86 | 70 | 75 | 77 | |
Al2O3,% | 70 | 75 | 80 | 85 | 86 | 70 | 75 | 77 |
C,% | 7 | 7 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
ZrO2,% | - | - | - | - | - | 6 | 6 | 2.5 |
A.P.,%≤ | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 7 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
B.D.,g/cm3 | 2.8 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 3.0 | 2.95 | 3.00 | 3.05 | 2.90 |
C.C.S., MPa ≥ | 65 | 70 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 110
| 115 | 100 |
- Q: How do monolithic refractories protect lining in ladles and tundishes?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in protecting the lining in ladles and tundishes through their unique properties and characteristics. These refractories are composed of a single, solid piece, as opposed to traditional brick or tile linings, which consist of individual units. One of the key ways in which monolithic refractories protect the lining is through their high density and low porosity. This property ensures that the refractory material acts as an effective barrier against the penetration of molten metal and slag. By preventing the infiltration of these corrosive substances, the monolithic refractory shields the lining from chemical attack, ensuring its longevity and performance. Additionally, monolithic refractories have excellent thermal shock resistance. Ladles and tundishes are subjected to extreme temperature fluctuations during the steelmaking process, as molten metal is poured and then allowed to cool. The ability of monolithic refractories to withstand these rapid temperature changes without cracking or spalling is vital in protecting the lining from thermal damage. Furthermore, monolithic refractories offer superior strength and mechanical properties. Ladles and tundishes are subjected to various mechanical stresses, such as the weight of the molten metal, the movement of the refractory lining during pouring, and the impact of scrap or additives. The robustness of monolithic refractories allows them to withstand these forces, preventing any structural failure or damage to the lining. Another advantage of monolithic refractories is their ease of installation. Unlike brick or tile linings, which require meticulous jointing and careful placement, monolithic refractories can be applied as a single, cohesive layer. This seamless application ensures a uniform protective barrier, eliminating weak points or gaps that could compromise the lining's integrity. In summary, monolithic refractories protect the lining in ladles and tundishes by providing a dense, impermeable barrier against the penetration of molten metal and slag. Their thermal shock resistance, mechanical strength, and easy installation contribute to the overall durability and longevity of the lining, ensuring its effective performance in the demanding steelmaking environment.
- Q: What are the challenges in using monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry?
- One of the major challenges in using monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry is their susceptibility to thermal shock. Monolithic refractories, unlike traditional brick refractories, are made from a single material and do not have the same structural integrity. This makes them more prone to cracking and failure when exposed to rapid temperature changes, which are common in the iron and steel production processes. Another challenge is the difficulty in achieving consistent and uniform application of monolithic refractories. Unlike brick refractories that can be precisely shaped and fitted into the desired areas, monolithic refractories are typically applied as a mortar-like mixture that is poured or sprayed into place. This process can be more complex and requires skilled operators to ensure proper application and adhesion. Additionally, monolithic refractories tend to have a shorter lifespan compared to brick refractories. They are more susceptible to erosion and wear, especially in high-temperature environments and when exposed to harsh chemicals and slag. This means that regular maintenance and replacement of monolithic refractories are necessary, which can result in increased downtime and costs for the iron and steel industry. Furthermore, the selection and customization of monolithic refractories can be challenging. Due to the wide range of operating conditions and requirements in the iron and steel industry, finding the right monolithic refractory composition and design that can withstand the specific demands of each application can be difficult. This requires careful consideration of factors such as temperature, chemical composition, and mechanical stress. Overall, while monolithic refractories offer advantages such as ease of installation and versatility, their susceptibility to thermal shock, difficulty in achieving uniform application, shorter lifespan, and the need for customized selection pose challenges for their effective use in the iron and steel industry.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories resist corrosion from molten metals?
- Due to their unique composition and structural properties, monolithic refractories have the ability to resist corrosion caused by molten metals. Typically made from a single material like alumina, magnesia, or silica, these refractories are specifically designed to withstand harsh chemical environments and high temperatures. A significant contributing factor to their corrosion resistance is their dense and compact structure. Through a specialized manufacturing process, monolithic refractories are created with a tightly bonded material that has minimal porosity. This low porosity prevents molten metals from penetrating the refractory and causing damage. Moreover, monolithic refractories often incorporate additives or binders to enhance their resistance to corrosion. These additives, such as silicon carbide, zirconia, or other chemically stable materials, can endure the corrosive effects of molten metals. Additionally, monolithic refractories possess excellent thermal shock resistance. This means that they can endure sudden temperature changes without cracking or spalling. When in contact with molten metals, the refractory's ability to handle thermal shock prevents the formation of cracks or fractures, which would allow further penetration of the corrosive molten metal. In conclusion, the combination of a dense structure, chemical additives, and high thermal shock resistance enables monolithic refractories to effectively resist corrosion caused by molten metals. These refractories find extensive use in various industrial applications, including steelmaking, foundries, and non-ferrous metal processing, where they offer reliable and durable protection against corrosion.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to energy efficiency in the iron and steel industry?
- Various mechanisms are employed by monolithic refractories to enhance energy efficiency in the iron and steel industry. The first mechanism is their exceptional thermal insulation properties, which minimize heat loss from furnaces and high-temperature equipment. This efficient utilization of heat generated during production leads to significant energy savings. Another important feature of monolithic refractories is their ability to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or spalling, known as thermal shock resistance. This quality is crucial in an industry where extreme temperature variations are common. By maintaining their structural integrity, these refractories prevent heat leakage and ensure effective energy utilization. Furthermore, monolithic refractories contribute to energy efficiency by reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency. Their easy installation and repair result in shorter maintenance cycles, minimizing the time required for furnace maintenance. This allows for continuous operation and uninterrupted energy utilization. Additionally, their high durability reduces the need for frequent replacements, further enhancing energy efficiency by reducing material and energy waste associated with regular repairs. In conclusion, monolithic refractories play a significant role in enhancing energy efficiency in the iron and steel industry. Their properties, such as thermal insulation, thermal shock resistance, and ease of installation and repair, ensure effective energy utilization and substantial energy savings. Improved operational efficiency and reduced downtime further contribute to overall energy efficiency.
- Q: What are the factors affecting the thermal expansion of monolithic refractories?
- There are several factors that influence the thermal expansion of monolithic refractories. 1. Chemical Composition: The chemical composition of the refractory material plays a significant role in its thermal expansion. Different chemical elements and compounds have different coefficients of thermal expansion. For example, materials containing high levels of silica tend to have lower coefficients of thermal expansion compared to materials with higher concentrations of alumina. 2. Particle Size: The particle size distribution of the refractory material can affect its thermal expansion. Smaller particle sizes tend to result in higher thermal expansion due to increased surface area and greater contact between particles. 3. Temperature: The temperature at which the monolithic refractory is exposed can greatly impact its thermal expansion. As the temperature increases, the kinetic energy of the particles increases, causing them to move more vigorously and expand. Different refractory materials have different temperature ranges at which they exhibit significant expansion. 4. Thermal History: The thermal history of the refractory material, including its heating and cooling cycles, can influence its thermal expansion behavior. Repeated heating and cooling cycles can induce microstructural changes in the material, affecting its thermal expansion properties. 5. Porosity: The porosity of the monolithic refractory can affect its thermal expansion. Higher porosity generally leads to higher thermal expansion due to the presence of voids and gaps within the material. 6. Binder Content: Monolithic refractories often contain binders that hold the particles together. The type and amount of binder used can impact the thermal expansion of the refractory. Different binders have different coefficients of thermal expansion, which can influence the overall expansion behavior of the material. 7. Thermal Shock: Rapid temperature changes, such as during quenching or exposure to alternating heating and cooling, can cause thermal shock in the refractory material. This can lead to cracks, spalling, and changes in the thermal expansion behavior. Understanding these factors is crucial in selecting the appropriate monolithic refractory material for specific applications, as the thermal expansion characteristics can directly impact the performance and longevity of the refractory in high-temperature environments.
- Q: What are monolithic refractories and how are they different from other refractory materials?
- Monolithic refractories, unlike bricks or tiles, are refractory materials that are not pre-formed into specific shapes or sizes. Instead, they are composed of a mixture of aggregates, binders, and additives, which are then installed and cured to create a solid and dense structure. One notable difference between monolithic refractories and other refractory materials is their versatility and ease of installation. While traditional bricks or tiles require skilled labor and careful assembly, monolithic refractories can be poured, sprayed, or gunned into place, allowing for a faster and more efficient installation process. This makes them particularly suitable for complex shapes or hard-to-reach areas. Another distinction lies in the physical properties of monolithic refractories. Unlike bricks and tiles, which are known for their mechanical strength and resistance to thermal shock, monolithic refractories can be customized to exhibit a wide range of properties. Depending on the specific application requirements, they can be engineered to have excellent thermal insulation, superior corrosion resistance, or enhanced abrasion resistance. This adaptability makes monolithic refractories suitable for various industries, including steel, cement, glass, and petrochemical. Furthermore, monolithic refractories have the advantage of being able to expand and contract with temperature changes, unlike rigid brick structures. This thermal flexibility helps prevent cracking and damage caused by thermal cycling, thus prolonging the lifespan of the refractory lining. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer better refractory integrity and reduced joint failure since they do not have seams or weak points that are susceptible to thermal stresses. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are a versatile and convenient type of refractory material that can be tailored to meet specific application requirements. Their easy installation, thermal flexibility, and customizable properties distinguish them from other refractory materials like bricks or tiles.
- Q: How are monolithic refractories different from traditional refractory bricks?
- Monolithic refractories, unlike traditional refractory bricks, are composed of a single, homogeneous structure. This structural distinction leads to several differences between the two. Firstly, monolithic refractories provide greater flexibility and versatility in terms of shape and installation. They can be easily molded and shaped to fit specific applications and complex geometries, making them ideal for lining furnaces, kilns, and other high-temperature equipment. Secondly, monolithic refractories have superior thermal shock resistance compared to traditional refractory bricks. Their uniform structure allows for better heat distribution, minimizing the risk of thermal stress and cracking. This makes them suitable for applications with rapid temperature fluctuations or severe thermal cycling. Additionally, monolithic refractories often exhibit better overall performance in terms of strength, mechanical properties, and resistance to chemical attack. The absence of joints and seams eliminates potential weak points, resulting in a more durable and reliable lining. Moreover, the homogeneous structure provides better resistance to corrosive agents, ensuring prolonged service life in harsh environments. Lastly, monolithic refractories offer advantages in terms of installation and maintenance. Their monolithic nature simplifies the installation process, reducing labor and time requirements. Additionally, repairs and maintenance can be carried out more easily and cost-effectively compared to traditional refractory bricks, which may require the replacement of entire sections or bricks. In summary, monolithic refractories differ from traditional refractory bricks in structure, flexibility, thermal shock resistance, performance, and installation characteristics. These differences make monolithic refractories a preferred choice in many high-temperature applications, offering improved efficiency, durability, and ease of use.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories perform in electric arc furnace roof applications?
- Due to their unique properties and characteristics, monolithic refractories are extremely effective when used in electric arc furnace (EAF) roof applications. Comprised of a single, solid material, these refractories offer several advantages specific to this application. To begin with, monolithic refractories provide exceptional thermal insulation, a critical factor in EAF roof applications. Traditional brick refractories can suffer structural damage from the intense heat generated in the furnace. However, monolithic refractories possess a higher resistance to thermal shock, reducing the risk of cracking and spalling. This ensures that they maintain their integrity and insulation properties even under extreme temperature conditions. Furthermore, monolithic refractories exhibit high strength and abrasion resistance, guaranteeing their durability and longevity in EAF roof applications. The roof of an electric arc furnace is subjected to harsh conditions, including the impact of scrap materials and the erosive effects of molten metal and slag. Monolithic refractories are specifically designed to withstand these challenges, offering superior resistance to mechanical wear and erosion. Another advantage of monolithic refractories lies in their ease of installation. Unlike traditional brick refractories, which necessitate time-consuming and complex installation processes, monolithic refractories can be applied rapidly and efficiently. They can be cast, gunned, or sprayed onto the roof surface, adapting to any shape or contour. Consequently, installation or repair downtime is reduced significantly. Moreover, monolithic refractories contribute to increased energy efficiency in EAF roof applications. Their superior insulation properties minimize heat loss, resulting in reduced energy consumption and cost savings. This is particularly crucial for electric arc furnaces, as their efficiency and productivity heavily rely on maintaining high temperatures for metal melting and processing. Any heat loss can have a significant impact on these factors. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are highly suitable for electric arc furnace roof applications due to their exceptional thermal insulation, strength, abrasion resistance, ease of installation, and energy efficiency. These refractories offer significant advantages over traditional brick refractories, ensuring optimal performance and extended service life in the demanding environment of an electric arc furnace.
- Q: What are the recommended curing times for monolithic refractories?
- The recommended curing times for monolithic refractories vary depending on the specific type and manufacturer's instructions. However, in general, it is recommended to allow monolithic refractories to cure for at least 24 to 48 hours before subjecting them to any heat or thermal stress. It is important to follow the specific curing guidelines provided by the manufacturer to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the refractory material.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories provide thermal insulation in the iron and steel industry?
- The iron and steel industry heavily relies on monolithic refractories for thermal insulation. These refractories are extensively used to line furnaces and other high-temperature equipment involved in the production processes. Monolithic refractories excel in thermal insulation due to their ability to withstand extreme temperatures without degradation or melting. They are specifically designed to resist high heat, enabling their usage in environments with temperatures reaching several thousand degrees Celsius. By enduring such extreme conditions, these refractories effectively prevent heat transfer to the surrounding structure, thereby ensuring insulation. Another key aspect of monolithic refractories' thermal insulation is their low thermal conductivity. These materials possess a low thermal conductivity, rendering them inefficient in conducting heat. Instead, they trap heat within their structure and minimize its transfer to the surrounding equipment or environment. This characteristic is instrumental in maintaining optimal temperatures inside furnaces and other high-temperature equipment, enabling efficient and controlled metal production. Moreover, monolithic refractories can be applied as a thick lining layer, further establishing an additional barrier between the high-temperature environment and the surrounding equipment. The thickness of the refractory lining acts as a buffer, reducing heat transfer and mitigating the impact of high temperatures on the structural integrity of the equipment. In addition to providing thermal insulation, monolithic refractories also exhibit exceptional resistance to chemical attack and mechanical wear, which are common challenges in the iron and steel industry. This resistance ensures the longevity of the refractory lining, guaranteeing consistent and reliable insulation over time. In summary, monolithic refractories contribute to thermal insulation in the iron and steel industry through their high-temperature resistance, low thermal conductivity, thick lining layer, and resistance to chemical attack and mechanical wear. These properties effectively maintain the desired temperature inside equipment and safeguard the surrounding structure from the intense heat generated during metal production processes.
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories Slide Gate Plates for Ladle & Tundish
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 set
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 set/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products

Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry - Acid Ramming Mass for Induction Furnace Lining
Hot Searches
Related keywords