Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry - Ladle Shroud Long Nozzle Chinese Steelmaking
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 set
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 set/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Description:
Steelmaking long nozzle /refractory materials/refractory nozzles
steelmaking zircon nozzle Zr content 94-95% , and nozzle with metal shell ,
can protect nozzle burst.the casting temperature normally at 1520-1580 ℃.
our zirconia cores temperature resistance up to 2000℃, density is 4.2g/cm3 .
Steelmaking tundish nozzle zircon core contact face made a little big than other,effectively protect the nozzle using life.
tundish zirconia nozzles materials is alumina-zirconia-carbon .composed by Alumina-Carbon Shell, and zirconia core.
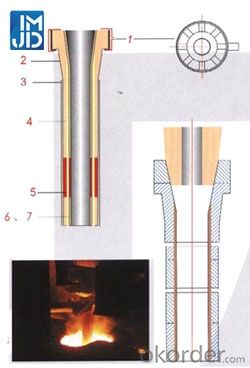
Graphic illustration:
1.Argon injection structure depending on customer specifications.
2.Ceramic glaze layer to prevent the material oxidation effectively.
3.Ceramic fiber blanket to prevent heat lost during casting.
4.High quality Al-C materials having high corrosion and thermal shock resistance.
5.High quality Zr-based composite to provide high corrosion resistance at the slag line.
6.Non-graphite based mased materials to meet the requirements of producing low carbon steel,silicon steel and high purity steel.
Manufacturing and QC
1.Raw materials blending
Independent raw materials blending center to assurestrict control of materials quality.
2.Shaping
Isostatic pressing technoloty,with as 1000 tons of pressure to assure the homogenous bulk density of each product.
3.Machining
To assure the uniform shape,dimension and dimension tolerance of each product.
4.X-ray defect inspection
To assure all products supplied to our customers without any defect and to prevent the un-countable feconomic loss for our customers.
5.Physical and chemistry analysis
To assure all products meet the physical and chemistry characteristics.
6.Packaging
The world-class for packaging to assure the safety transportation.
- Q: How are monolithic refractories different from traditional brick refractories?
- Monolithic refractories differ from traditional brick refractories in several ways. Firstly, monolithic refractories are made from a single, homogeneous material, while traditional brick refractories are made from individual bricks that are assembled together. This difference in construction allows monolithic refractories to have a more uniform and consistent structure, which can enhance their performance and durability. Secondly, monolithic refractories are typically easier to install compared to traditional brick refractories. Since they are made from a single material, they can be poured or sprayed into place, eliminating the need for precise bricklaying and mortar application. This ease of installation saves time and labor during construction or repair projects. Additionally, monolithic refractories often have superior thermal shock resistance compared to traditional brick refractories. The homogeneous structure of monolithic refractories allows them to expand and contract more uniformly under thermal stress, reducing the risk of cracking and failure. This makes monolithic refractories more suitable for applications where rapid temperature changes occur, such as in furnaces or kilns. Furthermore, monolithic refractories can offer better resistance to chemical attacks and erosion. Traditional brick refractories may have joints and gaps between bricks, which can become vulnerable to chemical reactions or erosion over time. Monolithic refractories, on the other hand, have a seamless structure that minimizes the risk of chemical penetration and erosion, enhancing their longevity and performance. Overall, monolithic refractories offer advantages in terms of uniformity, ease of installation, thermal shock resistance, and chemical resistance compared to traditional brick refractories. These differences make monolithic refractories a preferred choice for many industrial applications where high temperatures and harsh environments are present.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories perform in rotary hearth furnace applications?
- Monolithic refractories are known for their excellent performance in rotary hearth furnace applications. These refractories are designed to withstand the extreme temperatures and harsh conditions found in rotary hearth furnaces, making them an ideal choice for this specific application. One of the main advantages of monolithic refractories is their ability to resist thermal shock. In a rotary hearth furnace, the material being processed is subjected to rapid heating and cooling cycles, which can cause significant thermal stress on the refractory lining. Monolithic refractories have high thermal conductivity and low thermal expansion, allowing them to withstand these temperature fluctuations without cracking or spalling. Another key characteristic of monolithic refractories is their excellent abrasion resistance. In a rotary hearth furnace, the material being processed can contain abrasive particles that can erode the refractory lining over time. Monolithic refractories are formulated with high-quality aggregates and binders that offer superior resistance to abrasion, ensuring a longer service life for the lining. Furthermore, monolithic refractories have good chemical resistance, making them suitable for a wide range of applications in rotary hearth furnaces. They can withstand exposure to various chemical substances, such as molten metals, slags, and gases, without undergoing significant chemical reactions or degradation. This chemical stability ensures that the refractory lining remains intact and maintains its performance in the demanding environment of a rotary hearth furnace. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer excellent installation flexibility. Unlike traditional brick or tile refractories, which require complex installation procedures, monolithic refractories can be easily shaped and applied in-situ using various methods, such as gunning, casting, or ramming. This flexibility allows for quicker and more efficient lining repairs or replacements, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are highly reliable and efficient in rotary hearth furnace applications. Their ability to resist thermal shock, abrasion, and chemical attack, coupled with their easy installation, make them the preferred choice for lining materials in these demanding environments.
- Q: What are the main types of monolithic refractories used in the iron and steel industry?
- The main types of monolithic refractories used in the iron and steel industry are castables, plastic refractories, and ramming mixes.
- Q: What are the recommended drying procedures for monolithic refractories?
- Drying methods for monolithic refractories differ based on the specific type and composition of the material. Nevertheless, there exist general guidelines that can be adhered to. Initially, it is crucial to eliminate any excess moisture from the refractory material prior to drying. This can be achieved by storing the refractory in a dry environment or utilizing a dehumidifier if necessary. Once the refractory material has been adequately dried, the drying process can commence. It is advisable to initiate the process with a low drying temperature in order to prevent cracking or spalling. Gradually raising the temperature over time will allow for the gradual release of moisture. This can be accomplished by employing a controlled drying oven or furnace. The duration of the drying process will differ depending on the thickness and composition of the refractory. It is imperative to adhere to the manufacturer's guidelines for the specific refractory material being utilized, as they will provide the recommended drying duration and temperature range. Throughout the drying process, it is important to closely monitor the refractory for any indications of cracking or spalling. Should any cracks or damage occur, the drying process should be immediately halted to prevent further harm. It may be necessary to repair or replace the damaged areas before proceeding with the drying process. Once the refractory material has been fully dried, it is crucial to gradually cool it down to avoid thermal shock. This can be achieved by gradually reducing the temperature over time or allowing the refractory to naturally cool in a controlled environment. In conclusion, the recommended drying procedures for monolithic refractories involve gradually increasing the temperature over time, closely monitoring for any signs of damage, and slowly cooling down the refractory to prevent thermal shock. It is essential to adhere to the manufacturer's guidelines and recommendations for the specific refractory material being utilized to ensure proper drying and optimal performance.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand mechanical stress in the iron and steel industry?
- Monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry withstand mechanical stress primarily due to their composition and installation techniques. These refractories are made from a single, solid material, which provides them with excellent strength and resistance to mechanical pressure. Additionally, they are typically installed using specialized techniques, such as gunning or ramming, which ensure proper bonding and densification. These factors collectively enable monolithic refractories to effectively withstand the intense mechanical stress encountered in the iron and steel industry.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand the mechanical impacts in furnace door applications?
- Monolithic refractories are designed to withstand mechanical impacts in furnace door applications due to their unique properties and composition. These refractories are made from a single piece of material, which eliminates the need for joints or seams that are prone to cracking or failure under mechanical stress. One important characteristic of monolithic refractories is their high density, which provides them with excellent strength and resistance to mechanical impacts. Their dense structure makes them less susceptible to cracking or breaking when subjected to sudden or repeated impacts, such as when a furnace door is opened or closed. In addition to their density, monolithic refractories also possess high tensile strength and toughness. These properties allow them to absorb and distribute the energy from mechanical impacts, reducing the risk of damage or failure. This is particularly important in furnace door applications, where the refractories are constantly exposed to the stress of opening and closing the door. Furthermore, monolithic refractories often contain additives or bonding agents that enhance their mechanical properties. These additives can include fibers or aggregates that reinforce the structure and improve resistance to impacts. They can also improve the refractory's ability to withstand thermal cycling, which is common in furnace door applications. Overall, monolithic refractories are specifically engineered to withstand the mechanical impacts encountered in furnace door applications. Their dense, high-strength composition, combined with the use of additives and bonding agents, ensures their durability and longevity in these demanding environments.
- Q: What are the factors affecting the thermal expansion of monolithic refractories?
- The thermal expansion of monolithic refractories is influenced by several factors. These factors include the chemical composition of the refractory material, particle size, temperature, thermal history, porosity, binder content, and thermal shock. 1. The thermal expansion of the refractory material is significantly influenced by its chemical composition. Different chemical elements and compounds have varying coefficients of thermal expansion. For instance, materials with high levels of silica generally have lower coefficients of thermal expansion compared to those with higher concentrations of alumina. 2. The particle size distribution of the refractory material can also impact its thermal expansion. Smaller particle sizes result in higher thermal expansion due to increased surface area and greater particle contact. 3. The temperature at which the monolithic refractory is exposed plays a crucial role in its thermal expansion. As the temperature increases, the particles gain more kinetic energy, leading to increased movement and expansion. Different refractory materials exhibit significant expansion within specific temperature ranges. 4. The thermal history of the refractory material, including its heating and cooling cycles, can influence its thermal expansion behavior. Repeated heating and cooling cycles can induce microstructural changes in the material, affecting its thermal expansion properties. 5. The porosity of the monolithic refractory also affects its thermal expansion. Higher porosity generally results in higher thermal expansion due to the presence of voids and gaps within the material. 6. The type and amount of binder used in monolithic refractories impact their thermal expansion. Different binders have different coefficients of thermal expansion, which can influence the overall expansion behavior of the material. 7. Rapid temperature changes, such as quenching or exposure to alternating heating and cooling, can cause thermal shock in the refractory material. This can lead to cracks, spalling, and changes in thermal expansion behavior. Understanding these factors is essential when selecting the appropriate monolithic refractory material for specific applications. The thermal expansion characteristics directly affect the performance and longevity of the refractory in high-temperature environments.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the reduction of downtime in iron and steel plants?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in reducing downtime in iron and steel plants due to their unique properties and applications. These refractories are composed of a single, uniform material, making them highly versatile and easier to install compared to traditional brick refractories. Firstly, monolithic refractories offer excellent thermal insulation, which helps to prevent heat loss and maintain high temperatures in various areas of the plant. This insulation capability reduces the need for frequent repairs and replacements, as it minimizes thermal stress and prolongs the lifespan of equipment and furnaces. This, in turn, results in less downtime required for maintenance and repair work. Secondly, monolithic refractories exhibit superior resistance to thermal shock. The extreme temperatures experienced in iron and steel plants can cause rapid and significant temperature changes, leading to the cracking and failure of refractory linings. However, monolithic refractories have better thermal shock resistance, enabling them to withstand sudden temperature fluctuations without sustaining damage. This property enhances their durability and contributes to the reduction of downtime. Moreover, monolithic refractories offer enhanced mechanical strength and chemical resistance, making them suitable for the harsh operating conditions in iron and steel plants. These refractories can withstand the erosive effects of molten metal, slag, and other corrosive materials, ensuring the longevity of equipment and reducing the frequency of maintenance interventions. Additionally, the installation process of monolithic refractories is faster and more efficient compared to brick refractories. They can be easily applied using various techniques, such as shotcreting or gunning, allowing for quick repairs or renovations during planned shutdowns or even emergency situations. The reduced installation time results in shorter downtime periods, enabling the plant to resume operations promptly. In conclusion, monolithic refractories significantly contribute to the reduction of downtime in iron and steel plants through their excellent thermal insulation, resistance to thermal shock, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance. Their ease of installation and quick repair capabilities further enhance their role in minimizing downtime and ensuring uninterrupted production in these critical industries.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand chemical attack from molten metals and slag?
- Monolithic refractories are highly resistant to chemical attack from molten metals and slag due to their unique composition and structure. These refractories are typically made from a single, solid piece with no joints or seams, which minimizes the opportunity for chemical penetration. One of the key factors that enables monolithic refractories to withstand chemical attack is their high melting point. These materials are designed to have a melting point significantly higher than the temperature of the molten metal or slag they are exposed to. This prevents the refractory from melting or deforming when in contact with the hot molten substances. In addition to their high melting point, monolithic refractories are formulated with materials that have excellent chemical resistance. They are often composed of a combination of oxides, such as alumina, magnesia, and zirconia, which have a strong affinity for oxygen and form stable compounds. This allows the refractory to form a protective oxide layer on its surface when exposed to molten metals and slag, effectively shielding it from chemical attack. Furthermore, the dense and compact structure of monolithic refractories plays a crucial role in their resistance to chemical attack. The absence of joints and seams minimizes the chances of molten metals and slag infiltrating the refractory and causing chemical reactions. This dense structure also reduces the porosity of the material, making it less permeable to aggressive substances. Moreover, manufacturers often add specialized additives to monolithic refractories to enhance their chemical resistance. These additives can include fibers, binders, and corrosion inhibitors, which further improve the refractory's ability to withstand chemical attack. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are designed to withstand chemical attack from molten metals and slag through their high melting point, chemical-resistant composition, dense structure, and specialized additives. These properties allow them to maintain their integrity and performance even in the harshest environments, making them an ideal choice for applications involving high-temperature and corrosive substances.
- Q: How does the choice of monolithic refractory impact the overall cost of iron and steel production?
- The choice of monolithic refractory can have a significant impact on the overall cost of iron and steel production. Monolithic refractory refers to a type of refractory material that is installed in a continuous manner, as opposed to traditional brick or tile refractories. One key factor that affects the cost of iron and steel production is the lifespan of the refractory. Monolithic refractories generally have a longer lifespan compared to traditional brick or tile refractories. This means that they require less frequent maintenance and replacement, resulting in lower overall costs over time. Additionally, monolithic refractories have a higher resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress, which further extends their lifespan and reduces the need for repairs and replacements. Another important consideration is the energy efficiency of the monolithic refractory. These refractories have better insulation properties, which leads to reduced heat loss during the iron and steel production process. This helps to lower energy consumption and, consequently, the overall cost of production. The improved insulation also contributes to a more stable and controlled temperature profile within the furnace, resulting in better product quality and reduced scrap rates. Furthermore, monolithic refractories offer greater flexibility in terms of installation and repair. They can be easily applied to complex shapes and structures, allowing for more efficient use of refractory materials. This reduces waste and lowers material costs. The ease of installation also saves time and labor, further contributing to cost savings. Additionally, monolithic refractories are known for their superior performance in high-temperature environments. They exhibit excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to chemical attacks, ensuring optimal furnace operation and reducing the likelihood of downtime and production delays. This, in turn, minimizes the impact of unexpected maintenance, repairs, and shutdowns on the overall cost of iron and steel production. In conclusion, the choice of monolithic refractory can have a significant impact on the overall cost of iron and steel production. Its longer lifespan, improved energy efficiency, ease of installation and repair, and superior performance in high-temperature environments all contribute to cost savings in various aspects of the production process. Thus, careful consideration of the type of monolithic refractory used can result in significant cost reductions and improved overall efficiency in iron and steel production.
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry - Ladle Shroud Long Nozzle Chinese Steelmaking
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 set
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 set/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords

























