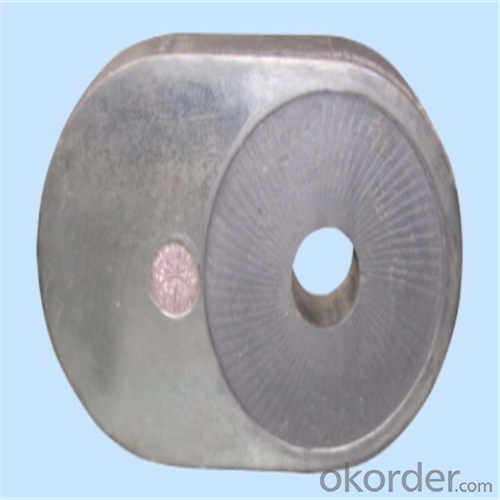
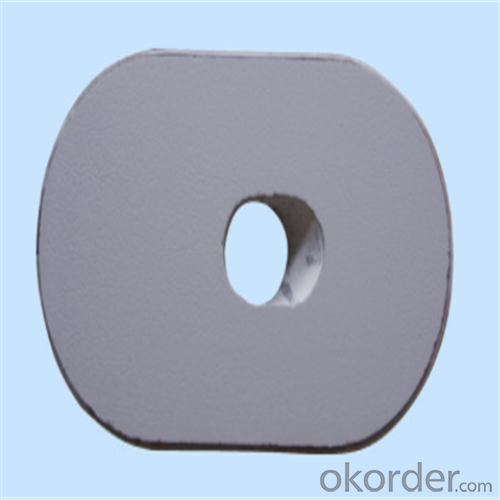
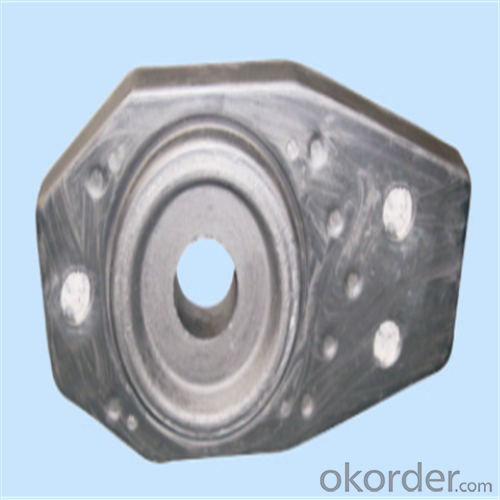
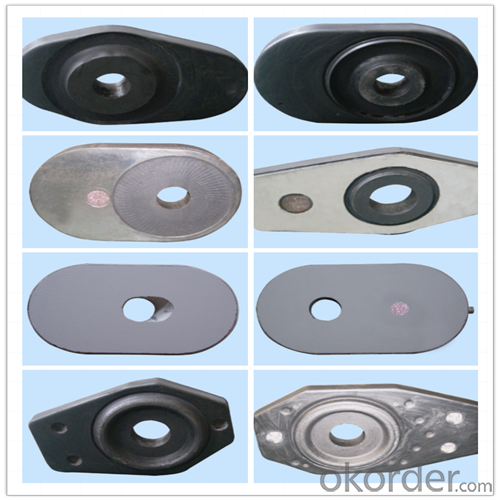
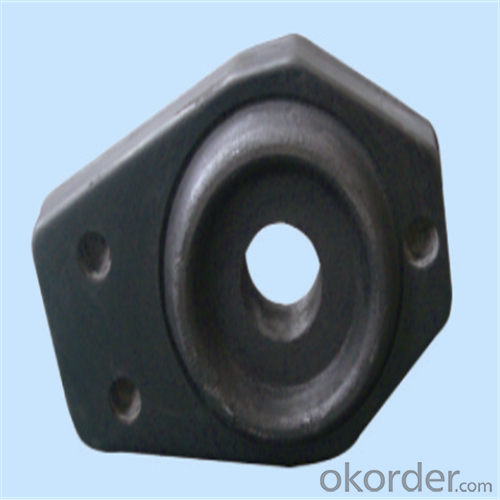
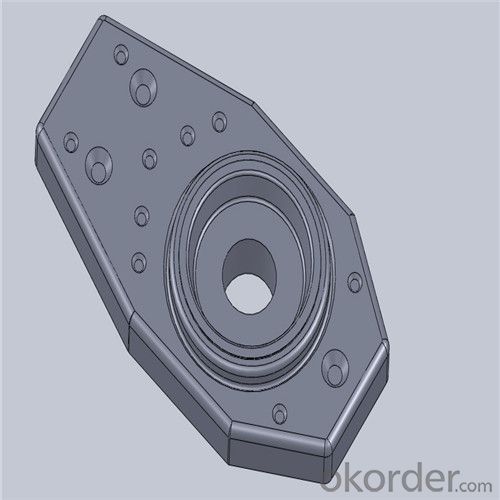
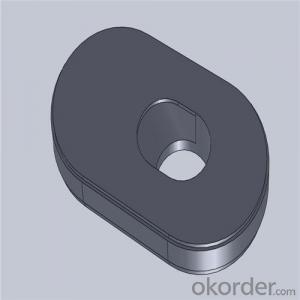
Monolithic Refractories High Performance Ladle Slide Gate for Iron and Steel Industry
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for High Performance Refractory Ladle Slide Gate
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Shape: | Plate | Material: | Alumina Block |
| SiO2 Content (%): | N/A | Al2O3 Content (%): | 80-90% | MgO Content (%): | N/A |
| CaO Content (%): | N/A | Refractoriness (Degree): | 1770°< Refractoriness< 2000° | CrO Content (%): | N/A |
| SiC Content (%): | N/A | Model Number: | CS80 | Brand Name: | |
| Product name: | High performance refractory ladle slide gate | Model No.: | cs80 | Brand name: | CMAX |
| Quality: | Al-C or Al-Zr-C | Service life: | 4-6 heats | Apparent porosity: | 7% Max |
| Bulk density:: | 3.1 MIN | C.C.S: | 120MPA | MOQ: | 100 pcs for trial |
| Delivery time: | 60 working days upon receipt of deposit |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Inner carton packing, outer wooden case suitable for long term sea shipping |
| Delivery Detail: | three months working days upon receipt of deposit |
Specifications
Surface flatness less than 0.05mm
High mechanical strength
Erosion resistance
Oxidation resistance
Thermal shock stability
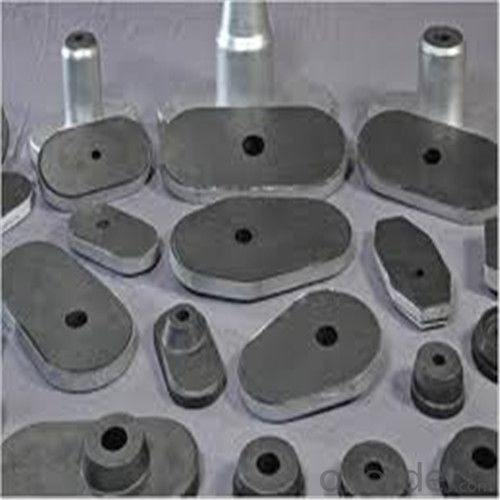
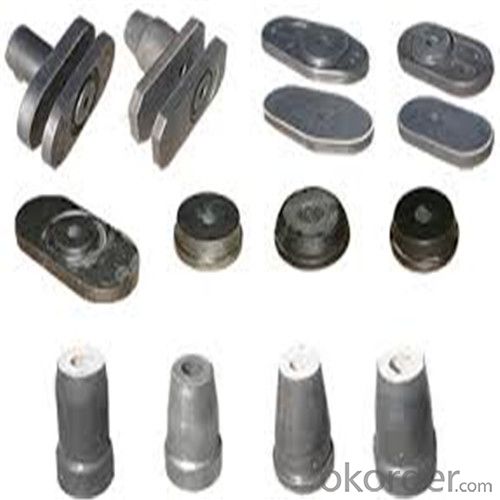
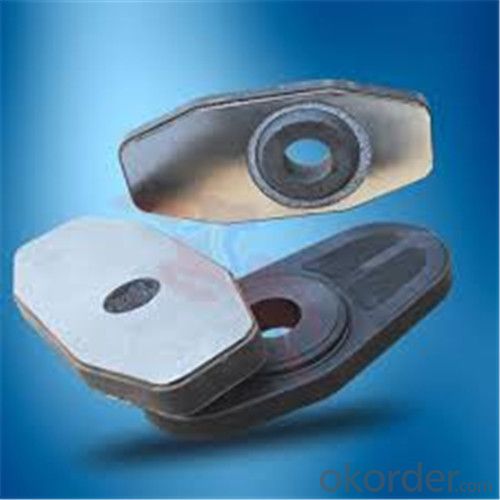


General Chemical Analysis for refractory ladle slide gate :
slide gate plate widely including Alumina carbon and Alumina Zirconia Carbon slide gate plate, MgO and MgO-spinel slide gate plate,nonoxides bonding slide gate plateand unburned slide gate plate.
Alumina -Zirconia-Carbon material
| Al-Zr-C Material | |||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) |
| 85 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
Composite type: Al-Zr-C for working line, outer Al-C material
| Al-Zr-C & Al-C Material | ||||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S | |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) | |
| Inner side (Working face) | 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| Outside | 90 | 3 | 0 | 9 | 3 | |

About us


Sample is on your request.
Welcome to visit our factory~
- Q: How are monolithic refractories applied in the hot face and cold face of furnace linings?
- Monolithic refractories are applied in the hot face and cold face of furnace linings through different methods. For the hot face, monolithic refractories are typically sprayed or troweled onto the surface, forming a dense and heat-resistant layer. This layer protects the furnace from high temperatures and thermal shocks. In contrast, for the cold face, monolithic refractories are usually cast or gunned into place, creating a more insulating layer. This layer helps to maintain a lower temperature on the outer surface of the furnace lining. Overall, the application of monolithic refractories in both the hot face and cold face ensures optimal performance and durability of furnace linings.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the overall efficiency of ladle transfer processes?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in enhancing the overall efficiency of ladle transfer processes. These refractories are made of a single, homogeneous material, which allows for easy installation and maintenance. This feature significantly reduces downtime during the ladle transfer process, resulting in increased productivity. One way monolithic refractories contribute to efficiency is through their high thermal conductivity. Ladle transfer processes involve the transfer of molten metal, which generates immense heat. Monolithic refractories have excellent heat resistance, ensuring that they can withstand the extreme temperatures of the molten metal. This property prevents refractory failure and prolongs the lifespan of the ladle, leading to more efficient and uninterrupted ladle transfer operations. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer superior corrosion resistance. The corrosive nature of molten metal can cause significant damage to ladles over time. However, monolithic refractories are designed to withstand chemical attacks from molten metal, preventing the degradation of the ladle's integrity. As a result, ladles lined with monolithic refractories have a longer lifespan and require less frequent replacement, leading to cost savings and improved efficiency. Furthermore, the ability of monolithic refractories to conform to complex shapes and designs is another contributing factor to the efficiency of ladle transfer processes. Ladles come in various sizes and shapes, and the use of monolithic refractories allows for customized linings that perfectly fit the ladle's dimensions. This precise fit minimizes heat loss and maximizes energy efficiency during ladle transfer processes. Moreover, monolithic refractories offer excellent mechanical strength and resistance to thermal shock. Ladle transfer processes involve the handling and movement of ladles, which can subject refractories to mechanical stresses. The outstanding mechanical properties of monolithic refractories ensure their durability and prevent cracking or spalling, reducing the risk of refractory failure and improving the efficiency of ladle transfer operations. In summary, monolithic refractories contribute to the overall efficiency of ladle transfer processes by providing high thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, precise lining fit, and excellent mechanical properties. These refractories enhance the ladle's durability, reduce downtime, and improve energy efficiency, resulting in cost savings and increased productivity in the steelmaking industry.
- Q: What are the advantages of using insulating castables in the iron and steel industry?
- The advantages of using insulating castables in the iron and steel industry are numerous. Firstly, insulating castables have excellent thermal insulation properties, which help to reduce heat loss during the manufacturing process. This leads to increased energy efficiency and cost savings for the industry. Additionally, insulating castables have a low thermal conductivity, meaning they can withstand high temperatures without transferring excessive heat. This is crucial in the iron and steel industry, where temperatures can reach extremely high levels. By using insulating castables, the industry can ensure the longevity and durability of its equipment and structures. Furthermore, insulating castables have good resistance to thermal shock, meaning they can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or breaking. This is particularly beneficial in the iron and steel industry, where the heating and cooling processes are frequent and intense. Lastly, insulating castables have a low density, making them lightweight and easier to handle and install. This not only saves time and effort during installation but also reduces the structural load on equipment and structures. Overall, the use of insulating castables in the iron and steel industry offers advantages such as improved energy efficiency, enhanced durability, resistance to thermal shock, and ease of installation.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand the thermal cycling in coke oven applications?
- Monolithic refractories are able to withstand the thermal cycling in coke oven applications due to their high thermal shock resistance and low thermal conductivity. They have a unique composition and structure that allows them to expand and contract without cracking or spalling under extreme temperature fluctuations. Additionally, their dense and homogeneous structure minimizes heat transfer, allowing them to maintain their integrity and strength even in the harsh conditions of coke oven operations.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories perform in reheating furnace roof applications?
- Monolithic refractories perform exceptionally well in reheating furnace roof applications due to their superior thermal shock resistance, high strength, and excellent resistance to chemical attack at high temperatures. These refractories provide a reliable and durable lining that can withstand the extreme conditions of reheating furnaces, ensuring efficient heat transfer, reduced maintenance, and prolonged furnace life.
- Q: What are monolithic refractories?
- Monolithic refractories, in contrast to individual bricks or precast shapes, are refractory materials that are manufactured as a single unit. They can be shaped and installed without the need for joints or mortar, making them convenient for lining furnaces, boilers, kilns, and other high-temperature industrial equipment. These refractories consist of a carefully selected mixture of refractory aggregates, binders, and additives. This combination provides desired properties such as high temperature resistance, thermal shock resistance, and chemical durability. Aggregates like alumina, magnesia, zirconia, and silica are used, while binders such as clay, cement, or phosphate hold the aggregates together. One advantage of monolithic refractories is their ability to adapt to complex shapes and designs, allowing for customized linings that meet specific equipment requirements. They can be applied through pouring, gunning, ramming, or spraying onto the surface to be lined, leading to quick and efficient installation. This eliminates the need for time-consuming bricklaying and jointing, reducing installation time and labor costs. Monolithic refractories also possess superior thermal conductivity, enabling them to withstand high temperatures and sudden temperature changes. They offer excellent insulation properties, preventing heat loss and improving energy efficiency in industrial processes. Additionally, these refractories exhibit good resistance to chemical attack from molten metals, slags, gases, and other corrosive substances found in various industrial environments. This makes them highly suitable for applications in steel, cement, glass, petrochemical, and non-ferrous metals industries. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are a versatile and efficient solution for high-temperature applications. Their ability to be shaped and installed without joints or mortar, combined with their excellent thermal conductivity and chemical resistance, make them a valuable choice for lining industrial equipment operating under extreme conditions.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories enhance the performance of ladle and tundish purging systems?
- Monolithic refractories enhance the performance of ladle and tundish purging systems by providing high thermal insulation, excellent erosion resistance, and increased durability. These refractories help maintain the desired temperature in the ladle and tundish, ensuring optimal conditions for purging operations. Additionally, their erosion resistance properties prevent excessive wear and tear, extending the lifespan of the purging systems. Overall, monolithic refractories play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of ladle and tundish purging systems.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the safety of iron and steel plants?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in ensuring the safety of iron and steel plants. These refractories are specially designed to withstand high temperatures, chemical attacks, and mechanical stresses commonly encountered in these industrial settings. By utilizing monolithic refractories, iron and steel plants can benefit in the following ways: 1. Thermal resistance: Monolithic refractories have excellent resistance to extreme temperatures, preventing heat loss and ensuring the efficient operation of various equipment and systems. This thermal insulation contributes to the safety of the plant by reducing the risk of overheating, which could lead to equipment failure or even catastrophic accidents. 2. Chemical resistance: Iron and steel plants involve the use of various chemicals, including molten metal, slag, and corrosive gases. Monolithic refractories exhibit high resistance to these aggressive chemical environments, preventing corrosion, erosion, and material degradation. This resistance ensures the integrity of refractory linings, reducing the risk of leaks, spills, and contamination that could jeopardize the safety of workers and the environment. 3. Structural stability: Monolithic refractories provide excellent mechanical strength, offering structural stability to the linings of furnaces, ladles, and other equipment. This stability is crucial for the safe operation of iron and steel plants, as it minimizes the risk of structural failure, collapse, or damage caused by mechanical stresses or heavy loads. 4. Rapid repair and maintenance: Monolithic refractories offer the advantage of easy installation and repair compared to traditional brick refractories. Their application involves pouring, gunning, or ramming the refractory material in place, which allows for quick repairs and maintenance. This rapid response to refractory failures or damages contributes to the plant's safety by minimizing downtime and preventing potential hazards associated with equipment malfunction. 5. Flexibility and adaptability: Monolithic refractories can be tailored to meet the specific needs and requirements of iron and steel plants. They can be customized in terms of composition, density, thermal conductivity, and other properties, allowing for optimal performance under varying operating conditions. This adaptability ensures that refractory linings are well-suited for the plant's processes, reducing the likelihood of accidents or incidents caused by inadequate refractory materials. In summary, monolithic refractories enhance the safety of iron and steel plants by providing thermal resistance, chemical resistance, structural stability, rapid repair capabilities, and flexibility. By utilizing these refractories, iron and steel plants can maintain a safe working environment, minimize the risk of accidents, and ensure the reliable operation of their equipment and systems.
- Q: What are the recommended storage and handling practices for monolithic refractories?
- The recommended storage and handling practices for monolithic refractories are crucial to ensure their optimal performance and longevity. Here are some key practices to follow: 1. Storage: Monolithic refractories should be stored in a clean, dry, and well-ventilated area. The storage facility should be protected from moisture, extreme temperatures, and direct exposure to sunlight. Ideally, the refractories should be stored on pallets or racks to prevent contact with the ground and minimize the risk of damage. 2. Handling: It is essential to handle monolithic refractories with care to avoid any physical damage. Refractories should be lifted and moved using appropriate lifting equipment, such as forklifts or cranes, to prevent excessive stress or strain on the material. Avoid dropping or dragging the refractories, as this can lead to cracks or fractures. 3. Packaging: If the monolithic refractories are supplied in packaging, it is important to inspect the packaging for any signs of damage or moisture before accepting the delivery. Damaged packaging can indicate potential damage to the refractory material. If any anomalies are noticed, it is advisable to inform the supplier immediately. 4. Moisture control: Monolithic refractories are susceptible to moisture absorption, which can lead to reduced performance and structural integrity. It is crucial to protect the refractories from direct contact with water or excessive humidity during storage and handling. If refractories become wet, they should be dried thoroughly before use to eliminate any absorbed moisture. 5. Stack height: When storing monolithic refractories, it is important to consider the stack height. Excessive stacking can result in pressure on the lower layers, leading to deformation or cracking. Follow the manufacturer's recommendations for maximum stack height to ensure the refractories' structural integrity. 6. Regular inspection: Regularly inspect the refractory material for any signs of damage or degradation during storage and handling. Look for cracks, spalling, or any other visible abnormalities. If any issues are identified, consult the manufacturer or a refractory expert for guidance on whether the material is still suitable for use. By following these recommended storage and handling practices, you can minimize the risk of damage to monolithic refractories and optimize their performance, ultimately extending their service life and ensuring their effectiveness in high-temperature applications.
- Q: What are the specific requirements of monolithic refractories for continuous casting applications?
- To withstand the extreme temperatures and thermal shock conditions experienced during continuous casting, monolithic refractories have specific requirements. First and foremost, these refractories must possess high thermal conductivity, enabling them to efficiently transfer heat away from the molten metal and maintain a stable casting temperature. This is crucial in preventing the formation of defects such as cracks, hot spots, and uneven solidification in the cast product. Secondly, monolithic refractories for continuous casting applications need to exhibit high refractoriness. This means they can endure the high temperatures of the molten metal without melting or deforming, ensuring the refractories can provide a protective lining and maintain their structural integrity throughout the casting process. In addition, these refractories must demonstrate excellent resistance to thermal shock. The continuous casting process involves rapid cooling and heating cycles, resulting in significant temperature differentials and inducing thermal stresses. Monolithic refractories with low thermal expansion and high thermal shock resistance can endure these conditions without cracking or spalling. Moreover, good erosion and corrosion resistance are vital requirements for monolithic refractories in continuous casting applications. The molten metal and slag can be highly corrosive and abrasive, causing wear and chemical attack on the refractory lining. Therefore, refractories with high resistance to erosion and corrosion are essential to ensure the longevity and stability of the lining. Lastly, monolithic refractories for continuous casting applications should possess good workability and ease of installation. This allows for efficient and precise lining installation, minimizing downtime during maintenance or repairs. Overall, the specific requirements for monolithic refractories in continuous casting encompass high thermal conductivity, refractoriness, thermal shock resistance, erosion and corrosion resistance, as well as good workability. Fulfilling these requirements guarantees that the refractories effectively safeguard the casting equipment and maintain the quality of the cast products.
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories High Performance Ladle Slide Gate for Iron and Steel Industry
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords