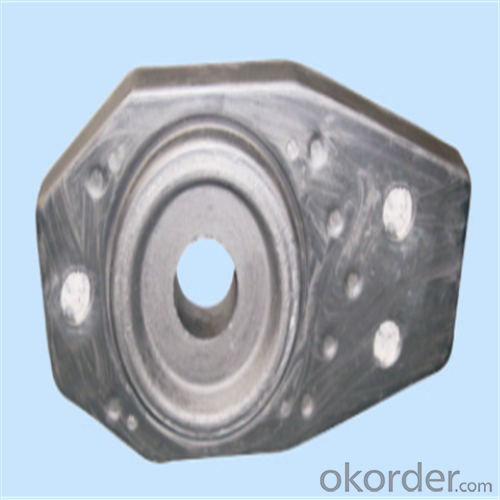
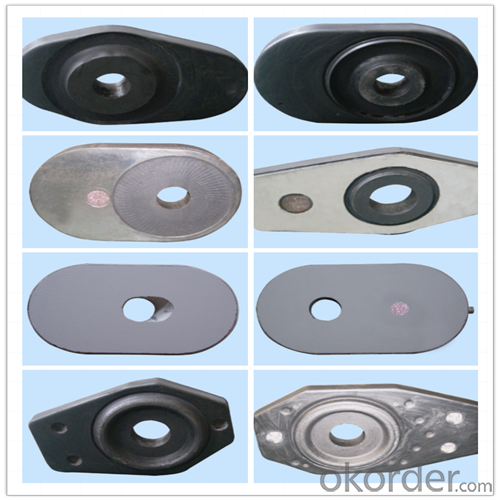
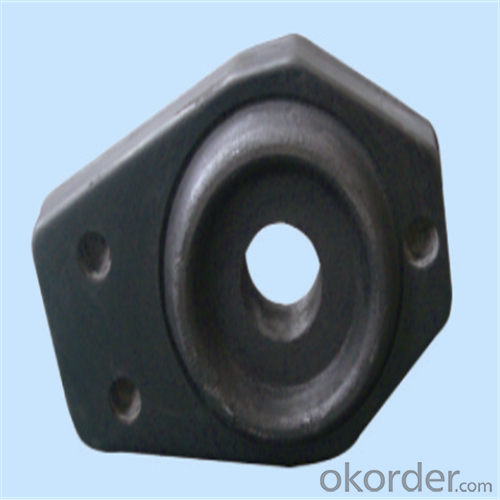
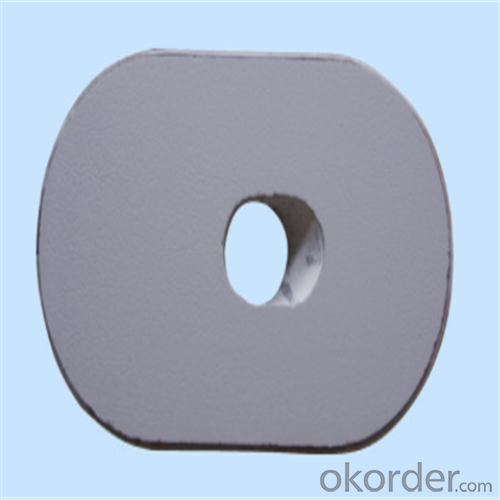
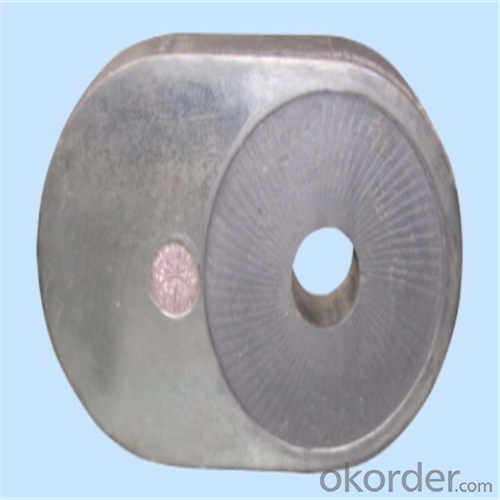
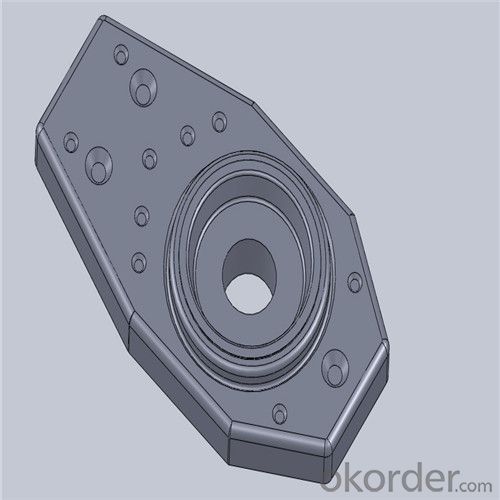
Monolithic Refractories High Performance Ladle Slide Gate
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for High Performance Refractory Ladle Slide Gate
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Shape: | Plate | Material: | Alumina Block |
| SiO2 Content (%): | N/A | Al2O3 Content (%): | 80-90% | MgO Content (%): | N/A |
| CaO Content (%): | N/A | Refractoriness (Degree): | 1770°< Refractoriness< 2000° | CrO Content (%): | N/A |
| SiC Content (%): | N/A | Model Number: | CS80 | Brand Name: | |
| Product name: | High performance refractory ladle slide gate | Model No.: | cs80 | Brand name: | CMAX |
| Quality: | Al-C or Al-Zr-C | Service life: | 4-6 heats | Apparent porosity: | 7% Max |
| Bulk density:: | 3.1 MIN | C.C.S: | 120MPA | MOQ: | 100 pcs for trial |
| Delivery time: | 60 working days upon receipt of deposit |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Inner carton packing, outer wooden case suitable for long term sea shipping |
| Delivery Detail: | three months working days upon receipt of deposit |
Specifications
Surface flatness less than 0.05mm
High mechanical strength
Erosion resistance
Oxidation resistance
Thermal shock stability
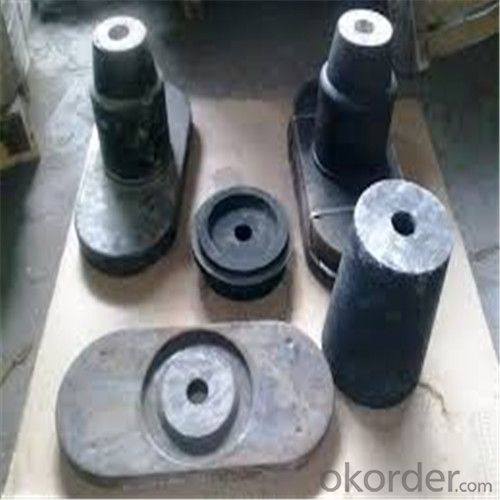
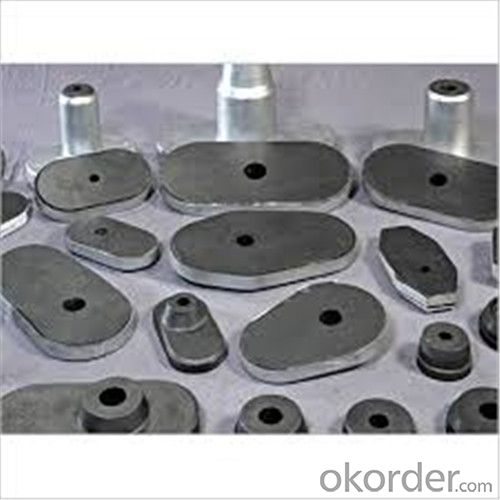
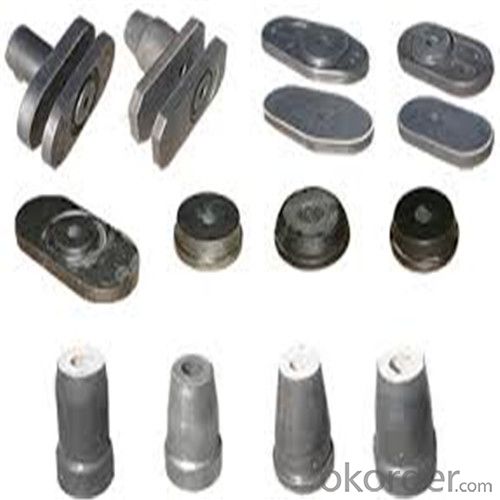
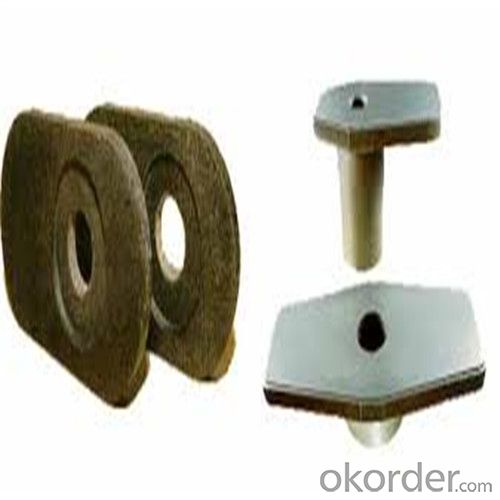





General Chemical Analysis for refractory ladle slide gate :
slide gate plate widely including Alumina carbon and Alumina Zirconia Carbon slide gate plate, MgO and MgO-spinel slide gate plate,nonoxides bonding slide gate plateand unburned slide gate plate.
Alumina -Zirconia-Carbon material
| Al-Zr-C Material | |||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) |
| 85 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
Composite type: Al-Zr-C for working line, outer Al-C material
| Al-Zr-C & Al-C Material | ||||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S | |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) | |
| Inner side (Working face) | 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| Outside | 90 | 3 | 0 | 9 | 3 | |
Sample is on your request.
Welcome to visit our factory~
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand the chemical attacks in copper smelting applications?
- Due to their unique properties and composition, monolithic refractories are capable of enduring chemical attacks in copper smelting applications. These refractories are specifically engineered to resist the harsh and corrosive environment found in copper smelting processes. To begin with, monolithic refractories are crafted from high-quality materials such as alumina, silica, and magnesia. These materials possess high melting points and chemical stability. Carefully selected, they are able to withstand the corrosive effects of copper smelting, including the presence of sulfur compounds and acidic gases. The refractory's composition also includes various additives and bonding agents that enhance its resistance to chemical attacks. In addition, monolithic refractories exhibit exceptional thermal shock resistance. This means they can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or spalling. In copper smelting applications, where extreme temperatures are involved, this refractory quality is crucial in preventing the formation of cracks and ensuring long-term performance. Furthermore, monolithic refractories possess a dense and compact structure. This structure serves as an effective barrier against the infiltration of molten copper and other corrosive substances. By preventing the penetration of chemical attacks, the refractory lining's durability and longevity are ensured. Moreover, monolithic refractories offer superior erosion resistance. This is particularly important in copper smelting applications, where high-velocity gases and flows of molten metal can cause erosion of the refractory lining. The refractory's erosion resistance prevents the degradation of the lining and maintains its structural integrity. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are specially designed to withstand the chemical attacks encountered in copper smelting applications. Through the use of high-quality materials, the incorporation of additives, and the possession of excellent thermal shock resistance, density, and erosion resistance, these refractories provide a reliable and durable lining that can endure the harsh conditions of copper smelting processes.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories improve the lining of converters and refining vessels?
- Improving the lining of converters and refining vessels is a crucial role played by monolithic refractories in several ways. To begin with, these refractories offer exceptional thermal insulation properties, which effectively maintain the desired temperature within the converters and refining vessels. This is particularly important as the metallurgical processes require high temperatures to be effective. Furthermore, the high chemical resistance of monolithic refractories is vital in the harsh conditions of converters and refining vessels. These vessels often come into contact with corrosive materials and aggressive slags, but the monolithic refractories prevent any deterioration or erosion of the lining caused by these substances. In addition, the mechanical strength and stability provided by monolithic refractories ensure that the lining remains intact even under high operational stresses. This is especially significant in converters and refining vessels where frequent mechanical movements and thermal expansions occur. Moreover, monolithic refractories offer easy installation and repair compared to traditional bricks, which require complex and time-consuming assembling. Monolithic refractories can be applied as a single mass, minimizing downtime during installation or repair. This results in time and cost savings for maintaining the lining of converters and refining vessels. Overall, the utilization of monolithic refractories significantly enhances the performance and longevity of converters and refining vessels. Their excellent thermal insulation, chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and ease of installation and repair guarantee efficient and reliable operation in metallurgical processes.
- Q: Can monolithic refractories be used for the lining of continuous casting tundishes and molds?
- Indeed, tundishes and molds used in continuous casting can utilize monolithic refractories for their lining. These refractories consist of a single, uniform structure, in contrast to traditional refractories that are composed of multiple bricks or tiles. The utilization of monolithic refractories offers various advantages in the lining of tundishes and molds during continuous casting procedures. Firstly, their monolithic nature allows for convenient installation and repair, as they can be cast or gunned into place, eliminating the need for intricate brickwork. Consequently, this reduces downtime and enhances productivity. Furthermore, monolithic refractories demonstrate exceptional resistance to thermal shock, which is critical for tundishes and molds that undergo rapid and extreme temperature fluctuations throughout the casting process. Their high thermal conductivity additionally ensures efficient heat transfer, facilitating uniform cooling and solidification of the cast metal. Additionally, monolithic refractories exhibit commendable resistance to chemical attack, ensuring prolonged performance even in the presence of molten metal and slag. Their low porosity further prevents metal penetration and the formation of cracks or spalling. In summary, monolithic refractories are a practical and efficient choice for lining continuous casting tundishes and molds, offering superior performance, ease of installation, and durability in the demanding conditions of the casting process.
- Q: What are the considerations for repairing and patching monolithic refractories?
- When it comes to the repair and patching of monolithic refractories, there are several key factors that must be taken into consideration. First and foremost, it is crucial to thoroughly evaluate the extent and severity of the damage or deterioration. This assessment will help determine the most appropriate repair method and materials required. Minor cracks or small damages may only necessitate a simple patch or seal, whereas larger or more serious damage may require a complete replacement or a more extensive repair process. Secondly, the type of monolithic refractory material being utilized is a critical factor to consider. Different types of monolithic refractories possess varying properties and characteristics, such as thermal conductivity, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength. Therefore, it is vital to select a repair material that is compatible with the existing refractory material, ensuring proper bonding and optimal performance. Another factor to take into account is the operating conditions and environment in which the monolithic refractory is exposed. Variables such as temperature, pressure, chemical exposure, and abrasion can significantly impact the durability and longevity of the refractory material. Understanding these conditions will assist in selecting the appropriate repair materials and techniques that can withstand and perform well under these specific circumstances. Furthermore, it is imperative that the repair process is carried out by experienced personnel who possess knowledge about refractory materials and their installation. Improper repairs can lead to further damage or diminished performance, so it is essential to have skilled professionals who can execute the repair work correctly. Lastly, regular inspection and maintenance of the monolithic refractories are crucial in order to detect any potential damage or deterioration early on. Timely repairs and patching can prevent further deterioration and prolong the service life of the refractory material. In summary, the considerations for repairing and patching monolithic refractories involve evaluating the extent of damage, selecting compatible repair materials, understanding the operating conditions, employing skilled personnel, and conducting regular inspections and maintenance. By taking these factors into account, one can ensure effective repairs and the continued performance of monolithic refractories.
- Q: What are the specific requirements of monolithic refractories for ladle purging applications?
- The specific requirements of monolithic refractories for ladle purging applications include high thermal shock resistance, excellent erosion resistance, good slag resistance, and low porosity. Thermal shock resistance is crucial in ladle purging applications as the refractory material needs to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or spalling. This is particularly important during ladle purging, where the ladle is exposed to high temperatures during molten metal pouring and then quickly cooled down during purging. Erosion resistance is another important requirement for monolithic refractories in ladle purging applications. The refractory material should be able to withstand the erosive action of molten metal streams and metalloids during purging. It should have a high resistance to chemical attack, preventing the material from deteriorating or eroding away. Slag resistance is also necessary for monolithic refractories used in ladle purging. The refractory material should have good resistance to the corrosive effects of slag, which can be present in ladles during purging. Slag can cause chemical reactions that can degrade the refractory material, leading to premature failure. Low porosity is an essential requirement for monolithic refractories in ladle purging applications. Low porosity ensures that the refractory material is impermeable to molten metal, preventing it from infiltrating the material and causing damage. This also helps to maintain the integrity and performance of the refractory lining during ladle purging. Overall, monolithic refractories for ladle purging applications need to exhibit high thermal shock resistance, excellent erosion resistance, good slag resistance, and low porosity to ensure the durability and longevity of the refractory lining in ladles during purging operations.
- Q: What are some common maintenance practices for monolithic refractories in iron and steel furnaces?
- Some common maintenance practices for monolithic refractories in iron and steel furnaces include: 1. Regular inspections: Conducting routine inspections is essential to identify any potential issues with the monolithic refractories. Inspections should be carried out by trained professionals who can assess the condition of the refractories and detect any signs of wear, erosion, or damage. 2. Repair and patching: Promptly repairing any damaged or eroded areas is crucial to prevent further deterioration and maintain the integrity of the refractories. Patching materials, such as refractory mortars or castable refractories, can be used to fill in gaps or repair small cracks. 3. Cleaning: Regularly cleaning the refractory lining helps to remove any build-up of slag, scale, or other impurities that can negatively impact the performance of the refractories. Cleaning can be done mechanically, using brushes or scrapers, or through chemical methods such as acid cleaning. 4. Thermal cycling: Controlled thermal cycling is often performed to condition and strengthen the monolithic refractories. This involves gradually increasing and decreasing the temperature of the furnace to improve the refractory's resistance to thermal shock. 5. Coating and sealing: Applying protective coatings or sealants to the refractory lining can help enhance its resistance to chemical attack, erosion, and thermal cycling. These coatings act as a barrier, preventing the penetration of molten metals or slags into the refractory material. 6. Monitoring and control: Continuous monitoring of operating conditions such as temperature, pressure, and atmosphere inside the furnace is important to prevent any sudden changes that may negatively affect the refractories. Maintaining proper control over these parameters helps to extend the life of the monolithic refractories. 7. Training and education: Providing regular training and education to furnace operators and maintenance personnel is crucial for them to understand the importance of proper refractory maintenance practices. This ensures that the refractories are handled and operated correctly, reducing the risk of premature failure. Overall, implementing these maintenance practices can significantly prolong the lifespan of monolithic refractories in iron and steel furnaces and maximize their performance, ultimately leading to improved efficiency and cost-effectiveness in the production process.
- Q: What are the recommended curing times for monolithic refractories?
- The recommended curing times for monolithic refractories vary depending on the specific type and manufacturer's instructions. However, in general, it is recommended to allow monolithic refractories to cure for at least 24 to 48 hours before subjecting them to any heat or thermal stress. It is important to follow the specific curing guidelines provided by the manufacturer to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the refractory material.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories resist corrosion and erosion in the iron and steel industry?
- Monolithic refractories resist corrosion and erosion in the iron and steel industry through their unique composition and properties. They are made of a single material structure, which eliminates joints and seams, reducing the likelihood of corrosion. Additionally, these refractories are designed to have high density and low porosity, making them resistant to penetration by corrosive elements. The refractories also have excellent thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength, which helps them withstand the harsh conditions of the iron and steel industry. Overall, the combination of their composition, density, and strength enables monolithic refractories to effectively resist corrosion and erosion in this industry.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories improve the durability of furnace linings?
- The durability of furnace linings is significantly enhanced by the unique characteristics and properties of monolithic refractories. Unlike traditional brick refractories, which are made up of individual bricks or tiles, monolithic refractories consist of a single, homogeneous structure. A key advantage of monolithic refractories is their ability to eliminate joints and seams, which are weak points in traditional brick refractories. These joints can lead to cracks and failures due to thermal expansion and contraction. In contrast, monolithic refractories are poured or gunned into place, creating a seamless lining that minimizes the potential for cracks. This seamless structure increases the durability of the lining and reduces its susceptibility to thermal stress. In addition, monolithic refractories exhibit excellent thermal shock resistance, which is crucial for furnace linings that experience rapid and extreme temperature changes. The monolithic structure allows for better heat transfer and distribution, preventing localized hotspots that can cause thermal shock and lining failure. This enhanced thermal shock resistance enables the furnace lining to withstand repeated heating and cooling cycles without significant damage, thus improving its overall durability. Furthermore, monolithic refractories offer superior resistance to erosion and corrosion. Furnace linings are often exposed to harsh chemicals, molten metals, and abrasive materials, which can cause erosion and corrosion over time. Monolithic refractories are specifically designed to resist these corrosive agents, protecting the lining from chemical attacks and physical wear. This resistance ensures a longer lifespan for the furnace lining and reduces the need for frequent repairs or replacements. Moreover, monolithic refractories possess better insulation properties compared to traditional brick refractories. They have lower thermal conductivity, meaning that heat transfer through the lining is minimized. This insulation property helps to maintain a more stable and uniform temperature within the furnace, reducing thermal stress on the lining and contributing to its longevity. To summarize, monolithic refractories enhance the durability of furnace linings by eliminating joints and seams, improving thermal shock resistance, providing erosion and corrosion resistance, and offering superior insulation properties. These materials are specifically engineered to withstand the extreme conditions inside furnaces, ensuring a longer lifespan for the lining and reducing maintenance costs in the long term.
- Q: What are the key factors to consider when designing the lining system with monolithic refractories?
- When designing a lining system with monolithic refractories, there are several key factors that need to be considered in order to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the lining. These factors include: 1. Material selection: Choosing the right monolithic refractory material is crucial. Factors such as the operating temperature, chemical environment, and mechanical stress need to be taken into account. Different monolithic refractories have varying properties and performance characteristics, so selecting the most suitable material for the specific application is essential. 2. Thermal expansion: Monolithic refractories, like any other material, expand and contract with changes in temperature. It is important to consider the thermal expansion properties of the refractory material and how it will interact with the surrounding structure. Proper expansion joints or design features should be incorporated to accommodate thermal expansion and prevent cracking or spalling. 3. Installation technique: The method of installation plays a critical role in the performance of the lining system. It is important to follow the manufacturer's guidelines for mixing, placing, and curing the monolithic refractory material. Improper installation can lead to reduced lining integrity, decreased thermal conductivity, and compromised structural stability. 4. Bonding and anchoring: Ensuring a strong bond between the monolithic refractory and the substrate is essential for effective lining performance. Proper surface preparation, selection of suitable bonding agents, and appropriate anchoring techniques should be considered to enhance the adhesion and stability of the lining system. 5. Structural design: The structural design of the lining system should be carefully planned to withstand the mechanical stresses and operational conditions. Factors such as load-bearing capacity, thermal shock resistance, and thermal cycling should be taken into consideration during the design phase. Reinforcement materials, such as steel fibers or mesh, may be required to enhance the structural integrity and prevent cracking or spalling. 6. Maintenance and repair: Anticipating the need for maintenance and repair is crucial for the longevity of the lining system. Consideration should be given to access points, inspection ports, and repair techniques. Regular inspections and proactive maintenance can help identify and address any issues before they escalate and lead to major failures. By considering these key factors when designing the lining system with monolithic refractories, one can ensure a well-designed and effective lining that can withstand the harsh conditions and provide long-term performance.
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories High Performance Ladle Slide Gate
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords