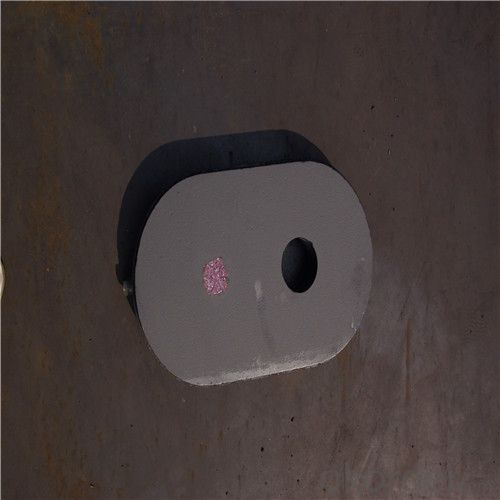
Monolithic Refractories for High Performance & Temperature Ladle Sliding Gate in Steel Industry
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for High Performance Refractory Ladle Slide Gate
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Shape: | Plate | Material: | Alumina Block |
| SiO2 Content (%): | N/A | Al2O3 Content (%): | 80-90% | MgO Content (%): | N/A |
| CaO Content (%): | N/A | Refractoriness (Degree): | 1770°< Refractoriness< 2000° | CrO Content (%): | N/A |
| SiC Content (%): | N/A | Model Number: | CS80 | Brand Name: | |
| Product name: | High performance refractory ladle slide gate | Model No.: | cs80 | Brand name: | CMAX |
| Quality: | Al-C or Al-Zr-C | Service life: | 4-6 heats | Apparent porosity: | 7% Max |
| Bulk density:: | 3.1 MIN | C.C.S: | 120MPA | MOQ: | 100 pcs for trial |
| Delivery time: | 60 working days upon receipt of deposit |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Inner carton packing, outer wooden case suitable for long term sea shipping |
| Delivery Detail: | three months working days upon receipt of deposit |
Specifications
Surface flatness less than 0.05mm
High mechanical strength
Erosion resistance
Oxidation resistance
Thermal shock stability
Slide gate plate widely including Alumina carbon and Alumina Zirconia Carbon slide gate plate, MgO and MgO-spinel slide gate plate,nonoxides bonding slide gate plateand unburned slide gate plate.
General Chemical Analysis for refractory ladle slide gate :
Alumina -Zirconia-Carbon material
| Al-Zr-C Material | |||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) |
| 85 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
Composite type: Al-Zr-C for working line, outer Al-C material
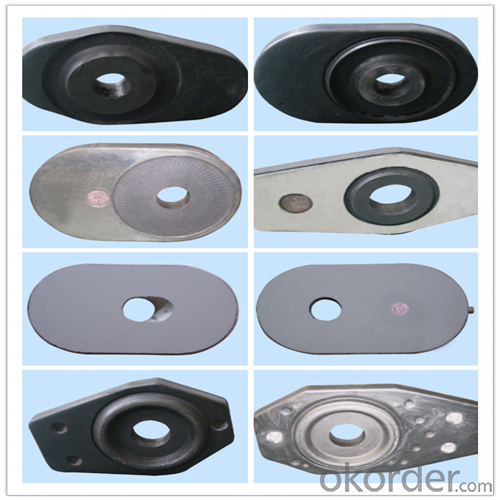

| Al-Zr-C & Al-C Material | ||||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S | |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) | |
| Inner side (Working face) | 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| Outside | 90 | 3 | 0 | 9 | 3 | |


About us


Sample is on your request.
Welcome to visit our factory~
- Q: How are monolithic refractories used in the repair and maintenance of ladle and tundish covers?
- Monolithic refractories are commonly used in the repair and maintenance of ladle and tundish covers due to their excellent thermal resistance and durability. Ladles and tundishes are crucial components in the steelmaking process, and their covers play a vital role in the containment of molten metal and the prevention of heat loss. When ladle and tundish covers are subjected to high temperatures and thermal cycling, they can experience wear and tear, leading to cracks, spalling, or even complete failure. This is where monolithic refractories come into play. Monolithic refractories are unshaped refractory materials that can be easily molded and applied to the damaged areas of ladle and tundish covers. They can be cast, gunned, or sprayed onto the surface, allowing for quick and efficient repairs. These refractories are typically composed of a matrix material, such as alumina, silica, or magnesia, along with various additives and bonding agents. The specific composition depends on the application requirements and the severity of the operating conditions. The repair process begins by identifying the damaged areas of the ladle or tundish cover. Any loose or damaged refractory material is removed, and the surface is prepared for the application of the monolithic refractory. This may involve cleaning, roughening, or even preheating the surface, depending on the specific requirements. The monolithic refractory is then mixed with water or a suitable binder to form a workable consistency. It is then applied to the damaged areas using the appropriate method, such as casting or spraying. After application, the refractory material is allowed to dry and cure, typically through a controlled heating process. Once cured, the monolithic refractory forms a strong and durable lining that can withstand the high temperatures, thermal cycling, and chemical reactions that occur during ladle and tundish operation. It provides excellent thermal insulation, preventing heat loss and reducing energy consumption. Furthermore, monolithic refractories offer superior resistance to slag, metal penetration, and erosion, ensuring extended service life for ladle and tundish covers. They also have good thermal shock resistance, allowing them to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or spalling. In summary, monolithic refractories are essential in the repair and maintenance of ladle and tundish covers due to their thermal resistance, durability, and ease of application. Their ability to withstand high temperatures, thermal cycling, and chemical reactions ensures the integrity and efficiency of ladle and tundish operations in the steelmaking industry.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the overall productivity of iron and steel production?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in enhancing the overall productivity of iron and steel production. These refractories are widely used in various applications such as furnaces, ladles, and tundishes, offering excellent thermal stability and resistance to chemical attacks. By providing a durable lining, monolithic refractories ensure longer campaigns and reduced downtime for repairs and maintenance. This leads to increased production efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and improved product quality, ultimately contributing to the overall productivity of iron and steel production.
- Q: Can monolithic refractories be used in electric arc furnaces and induction furnaces?
- Yes, monolithic refractories can be used in both electric arc furnaces and induction furnaces. Monolithic refractories are versatile and can be shaped and installed easily, making them suitable for various types of furnaces, including electric arc furnaces and induction furnaces. These refractories are composed of a single material, such as castables, gunning mixes, ramming mixes, and plastic refractories, which can withstand high temperatures and thermal shock. They are commonly used to line the walls, roofs, and bottoms of furnaces to provide insulation and protection against the extreme heat generated during the melting and refining processes. Monolithic refractories offer excellent resistance to chemical attack, erosion, and mechanical stress, making them ideal for use in electric arc furnaces and induction furnaces, where intense heat and harsh operating conditions are encountered.
- Q: How can the lifespan of monolithic refractories be extended?
- The lifespan of monolithic refractories can be extended through proper installation techniques, regular maintenance, and careful handling.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories perform in reheating furnace roof applications?
- Monolithic refractories are highly effective in reheating furnace roof applications. These refractories are known for their excellent thermal shock resistance, which is crucial in the extreme temperature conditions inside a reheating furnace. They can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or spalling, ensuring the longevity and durability of the furnace roof. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer superior insulation properties, which help in maintaining the desired temperature inside the furnace. These refractories have low thermal conductivity, preventing heat loss and reducing energy consumption. This not only improves the energy efficiency of the furnace but also contributes to cost savings for the operators. Furthermore, monolithic refractories provide excellent resistance to chemical attacks from gases and molten metals present in the furnace environment. They are designed to withstand corrosive atmospheres and prevent the penetration of harmful substances, thus prolonging the life of the roof refractory. Moreover, monolithic refractories offer easy installation and repair options. Their ability to be cast or gunned in place allows for a seamless and precise application to the roof structure. This feature also enables quick and efficient repairs or maintenance, minimizing downtime and production losses. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are a reliable and efficient choice for reheating furnace roof applications. Their exceptional thermal shock resistance, insulation properties, chemical resistance, and ease of installation make them an ideal solution for maintaining the structural integrity and performance of the furnace roof.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand the mechanical impacts in furnace door applications?
- Monolithic refractories have been specially designed to endure the mechanical impacts experienced in furnace door applications as a result of their unique properties and composition. These refractories are manufactured from a solitary piece of material, which eliminates the necessity for joints or seams that are susceptible to cracking or failure under mechanical stress. An essential characteristic of monolithic refractories is their elevated density, which grants them exceptional strength and resistance against mechanical impacts. Their compact structure makes them less prone to cracking or fracturing when exposed to sudden or repeated impacts, such as the opening or closing of a furnace door. Along with their density, monolithic refractories also possess substantial tensile strength and toughness. These qualities enable them to absorb and disperse the energy from mechanical impacts, reducing the likelihood of damage or failure. This is particularly crucial in furnace door applications, where the refractories are constantly subjected to the stress of door movement. Moreover, monolithic refractories frequently incorporate additives or bonding agents that enhance their mechanical properties. These additives may consist of fibers or aggregates that fortify the structure and improve impact resistance. They can also enhance the refractory's ability to endure thermal cycling, which is common in furnace door applications. Overall, monolithic refractories are meticulously engineered to withstand the mechanical impacts encountered in furnace door applications. Their dense composition with high strength, combined with the utilization of additives and bonding agents, guarantees their durability and longevity in these demanding environments.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand chemical attack from molten metals and slag?
- Due to their unique composition and structure, monolithic refractories exhibit high resistance to chemical attack from molten metals and slag. Unlike refractories with joints or seams, monolithic refractories are made from a single, solid piece, minimizing the chance of chemical penetration. The ability to withstand chemical attack is attributed to several factors. Firstly, monolithic refractories have a high melting point, which surpasses the temperature of the molten substances they encounter. This prevents them from melting or deforming upon contact with hot metals or slag. Additionally, the chemical resistance of monolithic refractories is enhanced by their formulation with materials that possess excellent resistance to chemicals. These materials, such as alumina, magnesia, and zirconia, form stable compounds and have a strong affinity for oxygen. Consequently, when exposed to molten substances, the refractories develop a protective oxide layer on their surface, effectively shielding them from chemical attack. Furthermore, the dense and compact structure of monolithic refractories plays a crucial role in their ability to resist chemical attack. The absence of joints and seams reduces the chances of molten metals and slag infiltrating the refractories and initiating chemical reactions. This dense structure also reduces the porosity of the material, making it less permeable to aggressive substances. Moreover, manufacturers often incorporate specialized additives, such as fibers, binders, and corrosion inhibitors, into monolithic refractories to further enhance their chemical resistance. These additives contribute to the refractories' ability to withstand chemical attack. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are designed to endure chemical attack from molten metals and slag through their high melting point, chemically resistant composition, dense structure, and specialized additives. These properties enable them to maintain their integrity and performance even in the most challenging environments, making them an ideal choice for applications involving high temperatures and corrosive substances.
- Q: Can monolithic refractories be used for the lining of reheating furnaces and walking beam furnaces?
- Monolithic refractories, which are refractory materials that can be cast or gunned into place rather than being made up of individual bricks or precast shapes, can be utilized for the lining of both reheating furnaces and walking beam furnaces. This characteristic makes them highly adaptable and versatile for a variety of furnace applications. Reheating furnaces are employed to heat metal products to a specific temperature before undergoing further processing, such as rolling or forging. The lining of these furnaces is exposed to high temperatures, thermal cycling, and mechanical stress. Given their exceptional thermal shock resistance and ability to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or spalling, monolithic refractories are well-suited for these conditions. In the steel industry, walking beam furnaces are utilized for the continuous heating and transportation of steel slabs or billets. These furnaces necessitate a lining material that can endure the abrasion and mechanical stress caused by the movement of the material. Monolithic refractories with high abrasion resistance and good mechanical strength are ideal for lining walking beam furnaces. Moreover, monolithic refractories provide additional advantages such as straightforward installation, decreased downtime for repairs, and enhanced energy efficiency. They can be customized to fit specific furnace designs and can be easily repaired or replaced as needed. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are a suitable option for lining reheating furnaces and walking beam furnaces due to their ability to withstand high temperatures, thermal cycling, mechanical stress, and abrasion. Their versatility, ease of installation, and repair make them the preferred choice for these furnace applications.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the safety of iron and steel plants?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in ensuring the safety of iron and steel plants. These refractories are specially designed to withstand high temperatures, chemical attacks, and mechanical stresses commonly encountered in these industrial settings. By utilizing monolithic refractories, iron and steel plants can benefit in the following ways: 1. Thermal resistance: Monolithic refractories have excellent resistance to extreme temperatures, preventing heat loss and ensuring the efficient operation of various equipment and systems. This thermal insulation contributes to the safety of the plant by reducing the risk of overheating, which could lead to equipment failure or even catastrophic accidents. 2. Chemical resistance: Iron and steel plants involve the use of various chemicals, including molten metal, slag, and corrosive gases. Monolithic refractories exhibit high resistance to these aggressive chemical environments, preventing corrosion, erosion, and material degradation. This resistance ensures the integrity of refractory linings, reducing the risk of leaks, spills, and contamination that could jeopardize the safety of workers and the environment. 3. Structural stability: Monolithic refractories provide excellent mechanical strength, offering structural stability to the linings of furnaces, ladles, and other equipment. This stability is crucial for the safe operation of iron and steel plants, as it minimizes the risk of structural failure, collapse, or damage caused by mechanical stresses or heavy loads. 4. Rapid repair and maintenance: Monolithic refractories offer the advantage of easy installation and repair compared to traditional brick refractories. Their application involves pouring, gunning, or ramming the refractory material in place, which allows for quick repairs and maintenance. This rapid response to refractory failures or damages contributes to the plant's safety by minimizing downtime and preventing potential hazards associated with equipment malfunction. 5. Flexibility and adaptability: Monolithic refractories can be tailored to meet the specific needs and requirements of iron and steel plants. They can be customized in terms of composition, density, thermal conductivity, and other properties, allowing for optimal performance under varying operating conditions. This adaptability ensures that refractory linings are well-suited for the plant's processes, reducing the likelihood of accidents or incidents caused by inadequate refractory materials. In summary, monolithic refractories enhance the safety of iron and steel plants by providing thermal resistance, chemical resistance, structural stability, rapid repair capabilities, and flexibility. By utilizing these refractories, iron and steel plants can maintain a safe working environment, minimize the risk of accidents, and ensure the reliable operation of their equipment and systems.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories improve the efficiency of ladle and tundish drying furnaces?
- Monolithic refractories improve the efficiency of ladle and tundish drying furnaces by providing excellent thermal insulation, high resistance to thermal shock, and superior strength. These properties ensure minimal heat loss during the drying process, allowing for faster and more efficient heating. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer better resistance to erosion and corrosion, prolonging the lifespan of the furnaces and reducing maintenance requirements. Overall, the use of monolithic refractories enhances the performance and productivity of ladle and tundish drying furnaces.
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories for High Performance & Temperature Ladle Sliding Gate in Steel Industry
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords