Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry - Acid Ramming Mass for Induction Furnace Lining
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 m.t
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 m.t/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Acid Ramming Mass for Induction Furnace Lining
Product Description:
To ensure the quality of our raw materials, we only purchase our raw materials from our long-term trusted suppliers. With every purchase, our quality control staff performs the first inspection at our supplier’s site. Once the raw materials arrive at our facility, our quality control team performs a second inspection on the batch. Each time raw materials enter our facility, they are inspected again prior to being accepted.
Process Quality Control:
From raw material to final product, our process control inspectors ensure that our procedures are consistently and correctly applied each step of the way. In addition to rigorous process control, our quality control team inspects the output of each process to ensure material quality and consistency. In each of our workshops, our employees understand that the output of their workshop is the input for the next manufacturing department. Therefore they have been trained to always carefully inspect the previous workshop’s work and be responsible for their own output
Product Advantages:
• Strong penetration resistance to molten steel
• Corrosion resistance, easy sintering,
• High packing density
• Professional technical staff track the progress of each project, provide construction instruction and after-sales services
• Provide personalized products, including design and production of the completed series of refractories
• Testing, inspection services
• Product consultation
Product Specifications:
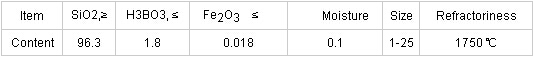
Product Images:
FAQ:
Q1: Why buy Materials & Equipment from OKorder.com?
A1: All products offered by OKorder.com are carefully selected from China's most reliable manufacturing enterprises. Through its ISO certifications, OKorder.com adheres to the highest standards and a commitment to supply chain safety and customer satisfaction.
Q2: How do we guarantee the quality of our products?
A2: We have established an advanced quality management system which conducts strict quality tests at every step, from raw materials to the final product. At the same time, we provide extensive follow-up service assurances as required.
Q3: What are Abrasion Resistant Coatings?
A3: ARC's abrasion resistant coatings guard against the severe wear and erosion that can chip away your plant's bottom line. These high-performance coatings protect new equipment as well as rebuild worn equipment at a fraction of traditional replacement costs.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the overall productivity of iron and steel production?
- The overall productivity of iron and steel production is greatly enhanced by the use of monolithic refractories. These refractories are crucial components utilized in the lining of high-temperature furnaces and other equipment employed in these industries. One of the ways in which monolithic refractories boost productivity is through their exceptional thermal insulation capabilities. By possessing high thermal conductivity, they effectively minimize heat loss from the furnaces, thereby reducing energy consumption and enhancing overall efficiency. This insulation property permits higher operating temperatures, resulting in faster and more efficient production processes. Furthermore, monolithic refractories exhibit superior resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion. Given the harsh conditions experienced during the iron and steel production process, such as rapid temperature fluctuations and exposure to molten metal and slag, these refractories are designed to withstand such extreme environments. This ensures prolonged service life and decreased downtime for maintenance and repairs, directly leading to increased productivity and reduced production costs. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer improved dimensional stability in comparison to traditional brick refractories. Their ability to conform to intricate shapes and structures allows for enhanced lining design, facilitating superior heat transfer and distribution. This uniformity in heat distribution contributes to improved process control and greater consistency in product quality. Moreover, the installation and repair of monolithic refractories are relatively simpler and quicker when compared to traditional brick refractories. This ease of installation and repair reduces downtime during maintenance, enabling more continuous production. The decreased downtime ultimately leads to increased productivity and higher output. In conclusion, monolithic refractories significantly contribute to the overall productivity of iron and steel production through their excellent thermal insulation, resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, improved dimensional stability, and ease of installation and repair. These properties result in enhanced energy efficiency, reduced downtime, improved process control, and higher product quality, ultimately leading to increased productivity and profitability for the industry.
- Q: What are the different techniques for installing monolithic refractories?
- Some of the different techniques for installing monolithic refractories include gunning, casting, ramming, and troweling. Gunning involves spraying a mixture of refractory material and water onto the surface using a high-pressure gun. Casting involves pouring the refractory material into a mold and allowing it to harden. Ramming involves manually packing the refractory material into place using a ramming tool. Troweling involves applying the refractory material with a trowel, similar to applying mortar.
- Q: How long is the lifespan of monolithic refractories in iron and steel applications?
- Several factors can influence the lifespan of monolithic refractories in iron and steel applications. These factors encompass the type of refractory material utilized, the specific application, the operational conditions, and the implemented maintenance practices. Monolithic refractories employed in iron and steel applications are generally engineered to endure high temperatures, thermal shock, chemical attack, and mechanical stress. When compared to other refractory materials, they are expected to possess a relatively extended lifespan. Under normal operating conditions and with appropriate maintenance, monolithic refractories can typically endure anywhere from several months to several years in iron and steel applications. Nevertheless, it is important to acknowledge that certain areas of the application may be subjected to more severe conditions, necessitating more frequent repairs or replacements. Regular inspections and monitoring of the refractories' condition are vital in order to detect any signs of deterioration or damage. Any necessary repairs or replacements should be promptly executed to prevent further damage and reduce downtime. It is also noteworthy to mention that advancements in refractory technology and materials have resulted in the development of more resilient and durable monolithic refractories. These advancements have extended the lifespan of refractories in iron and steel applications, ultimately enhancing the overall efficiency and productivity of the operations.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories respond to changes in thermal conditions?
- Monolithic refractories have the ability to withstand and adapt to changes in thermal conditions. They have a high thermal shock resistance, meaning they can handle rapid changes in temperature without cracking or breaking. Additionally, they exhibit good thermal conductivity, allowing them to efficiently conduct and distribute heat. Overall, monolithic refractories demonstrate a stable and reliable response to changes in thermal conditions.
- Q: Can monolithic refractories be used for the lining of continuous casting tundishes and molds?
- Indeed, tundishes and molds used in continuous casting can utilize monolithic refractories for their lining. These refractories consist of a single, uniform structure, in contrast to traditional refractories that are composed of multiple bricks or tiles. The utilization of monolithic refractories offers various advantages in the lining of tundishes and molds during continuous casting procedures. Firstly, their monolithic nature allows for convenient installation and repair, as they can be cast or gunned into place, eliminating the need for intricate brickwork. Consequently, this reduces downtime and enhances productivity. Furthermore, monolithic refractories demonstrate exceptional resistance to thermal shock, which is critical for tundishes and molds that undergo rapid and extreme temperature fluctuations throughout the casting process. Their high thermal conductivity additionally ensures efficient heat transfer, facilitating uniform cooling and solidification of the cast metal. Additionally, monolithic refractories exhibit commendable resistance to chemical attack, ensuring prolonged performance even in the presence of molten metal and slag. Their low porosity further prevents metal penetration and the formation of cracks or spalling. In summary, monolithic refractories are a practical and efficient choice for lining continuous casting tundishes and molds, offering superior performance, ease of installation, and durability in the demanding conditions of the casting process.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories improve the efficiency of ladle and tundish preheaters?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in improving the efficiency of ladle and tundish preheaters through several key mechanisms. Firstly, monolithic refractories provide excellent thermal insulation properties. They have low thermal conductivity, which means they are effective in preventing heat loss from the preheaters. By minimizing heat loss, monolithic refractories ensure that the majority of the heat generated by the preheater is utilized for preheating the ladle or tundish. This results in reduced energy consumption and improved efficiency of the preheating process. Secondly, monolithic refractories offer high thermal shock resistance. Ladle and tundish preheaters are subjected to rapid and extreme temperature changes during operation. The ability of monolithic refractories to withstand these thermal shocks ensures their long-lasting performance, minimizing the need for frequent repairs or replacements. This not only enhances the efficiency of the preheaters but also reduces downtime and maintenance costs. Furthermore, monolithic refractories exhibit excellent mechanical strength and abrasion resistance. The ladle and tundish preheaters experience constant wear and tear due to the movement of ladles or tundishes, and the abrasive nature of the materials being processed. The use of monolithic refractories prevents erosion and damage to the preheaters, ensuring their longevity and optimal functioning. This, in turn, improves the overall efficiency of ladle and tundish preheaters by reducing downtime and maintenance requirements. Lastly, monolithic refractories offer design flexibility. They can be customized and shaped according to the specific requirements of the ladle or tundish preheaters. This allows for better fitting and insulation, maximizing heat transfer efficiency. The ability to tailor the refractory lining to the preheater's design also ensures uniform heating, minimizing temperature variations and improving overall operational efficiency. In summary, the use of monolithic refractories in ladle and tundish preheaters improves efficiency by providing superior thermal insulation, thermal shock resistance, mechanical strength, abrasion resistance, and design flexibility. These properties result in reduced heat loss, minimized downtime, enhanced durability, and optimized heat transfer, ultimately leading to improved efficiency of the preheating process.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the reduction of emissions in iron and steel plants?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in reducing emissions in iron and steel plants through their superior thermal insulation properties. These refractories line the furnaces and other high-temperature equipment, preventing heat loss and enhancing energy efficiency. By minimizing heat wastage, monolithic refractories enable iron and steel plants to operate at higher temperatures, leading to increased combustion efficiency and reduced fuel consumption. This, in turn, results in lower greenhouse gas emissions, making monolithic refractories an essential component in the overall efforts to mitigate environmental impact in the iron and steel industry.
- Q: What are the recommended curing times for monolithic refractories?
- The recommended curing times for monolithic refractories vary depending on the specific type and manufacturer's instructions. However, in general, it is recommended to allow monolithic refractories to cure for at least 24 to 48 hours before subjecting them to any heat or thermal stress. It is important to follow the specific curing guidelines provided by the manufacturer to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the refractory material.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to energy efficiency in iron and steel manufacturing?
- Monolithic refractories contribute to energy efficiency in iron and steel manufacturing through their superior insulation properties and ability to withstand high temperatures. These refractories minimize heat loss, reducing the energy required for heating and maintaining the desired temperature in the manufacturing process. Additionally, their durability and resistance to thermal shock help to extend the lifespan of furnaces and other equipment, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements, further enhancing energy efficiency.
- Q: What are the common challenges faced by monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry?
- The iron and steel industry heavily relies on monolithic refractories, which have a vital role in various applications like lining furnaces, ladles, and tundishes. However, these materials encounter common challenges in this industry. Thermal shock is a major challenge. Monolithic refractories undergo extreme temperature changes, especially during start-up and shut-down phases. This rapid heating and cooling can cause thermal stress, leading to cracking and spalling. To combat this, refractory manufacturers create high-quality monolithic materials with enhanced thermal shock resistance. Corrosion is another significant challenge. The iron and steel industry exposes refractory linings to aggressive materials like molten metal, slag, and gases, which chemically attack them. This corrosion results in material degradation, erosion, and reduced service life. To address this, specialized monolithic refractories with excellent corrosion resistance are used, often containing additives that can withstand the corrosive environment. Abrasion is also a common challenge faced by monolithic refractories in this industry. The movement of raw materials, molten metal, and slag causes mechanical wear on the refractory lining, leading to material loss and compromised performance. Refractory manufacturers develop abrasion-resistant monolithic materials that can withstand intense wear and tear, ensuring extended service life. Moreover, good thermal conductivity is often required in the iron and steel industry. This is crucial for efficient heat transfer and maintaining optimal operating conditions. Achieving the right balance between thermal conductivity and mechanical strength can be challenging, as refractories with high thermal conductivity often have lower mechanical strength. Therefore, selecting the appropriate monolithic refractory with desired thermal conductivity properties is crucial for optimal performance. Lastly, installation and maintenance present challenges for monolithic refractories. The application of these refractories requires skilled personnel and careful installation techniques due to their liquid or semi-liquid nature. Additionally, regular maintenance and repairs are necessary to ensure the refractory lining's longevity and performance. Regular inspections, repairs, and proper curing techniques are vital to mitigate these challenges and optimize refractory performance. In conclusion, monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry face challenges such as thermal shock, corrosion, abrasion, thermal conductivity, and installation/maintenance. Addressing these challenges through the development of specialized refractory materials and employing proper installation and maintenance techniques are crucial for ensuring efficient and reliable performance in this demanding industry.
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry - Acid Ramming Mass for Induction Furnace Lining
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 m.t
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 m.t/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords