Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry - Alumina Magnesium Castable for Ladle and Tundish
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or L/C
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
General Information of Alumina Magnesium Castable for Ladle and Tundish
Made as per international standards, FIREF alumina magnesium castable for ladle and tundish has been widely accpeted by the customers for its excellent corrosion resistance, long operating life and high refractoriness. Further, they can be provided in different specifications as required.
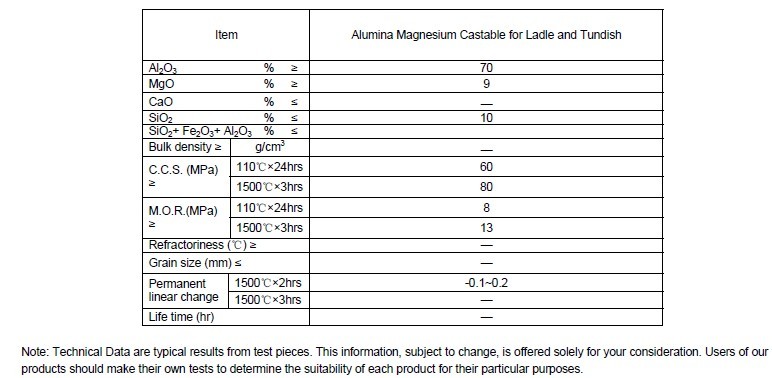
Technical data of Alumina Magnesium Castable for Ladle and Tundish
Production line and packing of Alumina Magnesium Castable for Ladle and Tundish


Feature of Alumina Magnesium Castable for Ladle and Tundish
Excellent corrosion resistance
Long operating life
High refractoriness
Application of Alumina Magnesium Castable for Ladle and Tundish
FIREF alumina magnesium castable for ladle and tundish can be used widely in Ladle and Tundish of iron and steel industry.
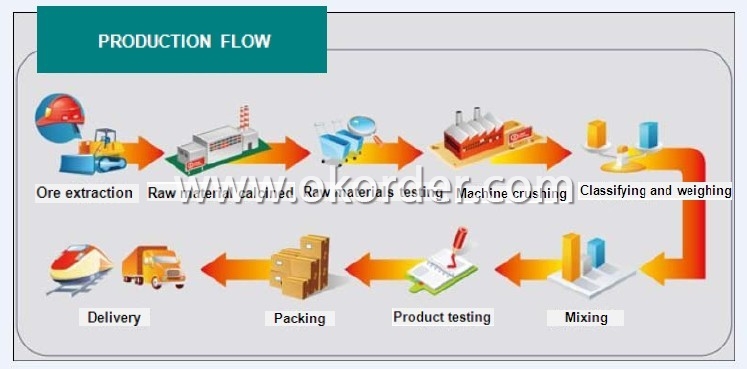
Production Flow of Alumina Magnesium Castable for Ladle and Tundish
- Q: How do monolithic refractories help in reducing energy consumption in iron and steel production?
- Monolithic refractories help in reducing energy consumption in iron and steel production by providing efficient insulation and heat retention properties. These refractories have low thermal conductivity, which minimizes heat loss and ensures that the generated heat is effectively utilized for the production processes. Their high refractoriness allows them to withstand extreme temperatures, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements that would require additional energy consumption. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer better resistance to thermal shock, which prevents thermal stress-induced cracks and extends their lifespan. Overall, the use of monolithic refractories in iron and steel production aids in optimizing energy usage and improving overall energy efficiency.
- Q: What are the typical applications of monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry?
- Monolithic refractories find several typical applications in the iron and steel industry. These include lining electric arc furnaces, ladles, tundishes, and various other equipment used in the production of iron and steel. Monolithic refractories are also commonly used for repairing and maintaining the linings of these equipment. Their high thermal conductivity, excellent resistance to thermal shock, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures make them ideal for these applications in the iron and steel industry.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the efficiency of iron and steel production?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in improving the efficiency of iron and steel production by providing superior thermal insulation and resistance to high temperatures, resulting in reduced heat loss and improved energy efficiency. Additionally, these refractories offer excellent mechanical strength and chemical resistance, enabling them to withstand the harsh conditions within the production process, leading to increased durability and extended service life. Their ability to be easily shaped and installed also facilitates faster maintenance and repair, minimizing downtime and enhancing overall operational efficiency in the iron and steel industry.
- Q: What are monolithic refractories?
- Monolithic refractories are a type of refractory material that is manufactured as a single, homogeneous unit, as opposed to being made from individual bricks or precast shapes. They are characterized by their ability to be shaped and installed in various applications without the need for joints or mortar, making them a versatile and convenient choice for lining furnaces, boilers, kilns, and other high-temperature industrial equipment. These refractories are typically composed of a mixture of refractory aggregates, binders, and additives, which are carefully selected and combined to provide the desired properties such as high temperature resistance, thermal shock resistance, and chemical durability. The aggregates used can include materials like alumina, magnesia, zirconia, and silica, while binders like clay, cement, or phosphate are added to hold the aggregates together. One of the advantages of monolithic refractories is their ability to adapt to complex shapes and designs, allowing for customized linings that can be tailored to specific equipment requirements. They are often applied by pouring, gunning, ramming, or spraying the refractory material onto the surface to be lined, allowing for quick and efficient installation. This eliminates the need for time-consuming bricklaying and jointing, reducing installation time and labor costs. Monolithic refractories are also known for their superior thermal conductivity, which enables them to withstand high temperatures and sudden temperature changes. They offer excellent insulation properties, preventing heat loss and improving energy efficiency in industrial processes. Furthermore, these refractories exhibit good resistance to chemical attack from molten metals, slags, gases, and other corrosive substances found in various industrial environments. This makes them highly suitable for applications in industries such as steel, cement, glass, petrochemical, and non-ferrous metals. In summary, monolithic refractories are a versatile and efficient solution for high-temperature applications. Their ability to be shaped and installed without joints or mortar, coupled with their excellent thermal conductivity and chemical resistance, make them a valuable choice for lining industrial equipment that operates under extreme conditions.
- Q: What are the advantages of using low-moisture castables in the iron and steel industry?
- There are several advantages of using low-moisture castables in the iron and steel industry. Firstly, low-moisture castables have a lower water content, which means they require less drying time. This is advantageous in the iron and steel industry where time is of the essence, as it reduces the overall production time and allows for faster turnaround. Secondly, low-moisture castables have superior strength and durability compared to traditional castables. They are able to withstand high temperatures and harsh environments without cracking or breaking. This is crucial in the iron and steel industry where extreme heat and abrasion are common, as it ensures the castables can endure the demanding conditions and maintain their structural integrity. Furthermore, low-moisture castables have excellent thermal shock resistance. This means they can withstand rapid changes in temperature without cracking or spalling, which is beneficial in the iron and steel industry where heating and cooling processes are frequent. Another advantage is that low-moisture castables have a higher density compared to traditional castables. This results in improved insulation properties, as they have a lower thermal conductivity. This is important in the iron and steel industry as it helps to conserve energy and reduce heat loss during various processes, ultimately leading to cost savings. Lastly, low-moisture castables offer versatility in terms of application. They can be used for various purposes in the iron and steel industry, such as lining ladles, furnaces, tundishes, and other high-temperature equipment. This versatility allows for greater flexibility in designing and constructing the infrastructure required for iron and steel production. Overall, the advantages of using low-moisture castables in the iron and steel industry include reduced drying time, increased strength and durability, enhanced thermal shock resistance, improved insulation properties, and versatility in application. These benefits ultimately contribute to more efficient and cost-effective operations in the iron and steel industry.
- Q: What are the main factors affecting the erosion resistance of monolithic refractories?
- The erosion resistance of monolithic refractories is influenced by several key factors. These factors include the chemical composition of the refractory material, the microstructure of the material, the temperature and environment in which it is used, and the mechanical properties of the material. The chemical composition of the monolithic refractory plays a crucial role in its erosion resistance. Certain chemical elements and compounds can enhance the resistance of the refractory to erosion, while others may make it more susceptible. For example, the addition of alumina (Al2O3) in the refractory composition can improve its resistance to erosion, as it forms a protective layer on the surface. On the other hand, the presence of impurities or excess amounts of certain elements can weaken the refractory and increase its susceptibility to erosion. The microstructure of the monolithic refractory is another important factor affecting erosion resistance. The refractory's microstructure refers to the arrangement and distribution of its constituent particles. A well-structured microstructure with a uniform distribution of particles can provide better erosion resistance as it ensures a more even distribution of load during exposure to erosive forces. Conversely, a poorly structured microstructure with clusters or weak bonding between particles may lead to localized erosion and failure. The temperature and environment in which the refractory is used also significantly influence erosion resistance. High temperatures can cause thermal stresses, chemical reactions, and phase changes in the refractory material, all of which can affect its erosion resistance. Additionally, the presence of corrosive gases, liquids, or slags can accelerate erosion by promoting chemical reactions or attacking the refractory material, leading to its degradation. Lastly, the mechanical properties of the monolithic refractory, such as its strength, hardness, and toughness, contribute to erosion resistance. A refractory with higher mechanical strength and hardness can withstand erosive forces better than a weaker material. Similarly, a higher toughness helps the refractory resist cracking or spalling when subjected to impact or thermal shock, reducing its vulnerability to erosion. In summary, the erosion resistance of monolithic refractories is influenced by the chemical composition, microstructure, temperature and environment, and mechanical properties of the material. Understanding and optimizing these factors can help in developing refractories with improved erosion resistance for various industrial applications.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories perform in torpedo ladle applications?
- Monolithic refractories perform exceptionally well in torpedo ladle applications due to their high thermal shock resistance, excellent erosion and corrosion resistance, and superior mechanical strength. They can withstand the extreme temperatures and aggressive molten metal environment inside the torpedo ladle, ensuring long-lasting and reliable performance. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer ease of installation and maintenance, making them a preferred choice in torpedo ladle applications.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to energy efficiency in iron and steel manufacturing?
- Monolithic refractories contribute to energy efficiency in iron and steel manufacturing through their superior insulation properties and ability to withstand high temperatures. These refractories minimize heat loss, reducing the energy required for heating and maintaining the desired temperature in the manufacturing process. Additionally, their durability and resistance to thermal shock help to extend the lifespan of furnaces and other equipment, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements, further enhancing energy efficiency.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories improve the efficiency of ladle and tundish lining systems?
- Monolithic refractories improve the efficiency of ladle and tundish lining systems by providing superior thermal insulation, excellent resistance to thermal shock, and higher mechanical strength compared to traditional brick or castable linings. This results in reduced heat loss, improved temperature control, and increased refractory life, ultimately leading to higher productivity and cost savings in steelmaking operations.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to reducing downtime in iron and steel plants?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in reducing downtime in iron and steel plants by offering several key advantages over traditional brick refractories. Firstly, monolithic refractories are highly versatile and can be easily molded and installed, allowing for quicker repairs and replacements. Unlike brick refractories that require time-consuming and labor-intensive processes, such as bricklaying and mortar application, monolithic materials can be directly applied in a castable or gunning form, significantly reducing the downtime required for repairs. Additionally, monolithic refractories provide better thermal insulation and improved resistance to thermal shocks, which are common occurrences in iron and steel plants. This enhanced thermal performance helps to maintain stable operating temperatures and prevents sudden temperature fluctuations that can lead to refractory failure and subsequent downtime. By minimizing these thermal shocks, monolithic refractories increase the overall lifespan of the refractory lining, reducing the need for frequent repairs and replacements. Furthermore, monolithic refractories offer superior chemical resistance compared to traditional brick refractories. Iron and steel plants often encounter aggressive chemical environments due to the presence of molten metal, slag, and other corrosive substances. Monolithic refractories are specifically designed to withstand these harsh conditions, preventing chemical attacks and erosion of the refractory lining. As a result, the need for unscheduled shutdowns due to refractory degradation is significantly reduced. Lastly, monolithic refractories provide better dimensional stability, minimizing the risk of cracks and spalling that can occur due to thermal cycling and mechanical stress. This increased resistance to wear and tear ensures that the refractory lining remains intact for a longer period, reducing the frequency of maintenance and enhancing the overall operational efficiency of the iron and steel plant. In summary, monolithic refractories contribute to reducing downtime in iron and steel plants by offering faster installation, improved thermal insulation, superior chemical resistance, and enhanced dimensional stability. Their versatility and performance advantages make them a reliable choice for maintaining a reliable and efficient refractory lining, ultimately reducing the frequency and duration of plant shutdowns.
1. Manufacturer Overview
| Location | Henan, China |
| Year Established | 2007 |
| Annual Output Value | Above US$ 60 Million |
| Main Markets | Mid East; Eastern Europe; North America |
| Company Certifications | ISO 9001:2008 |
2. Manufacturer Certificates
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period |
3. Manufacturer Capability
| a) Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | Tianjin |
| Export Percentage | 31% - 50% |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | 21-50 People |
| Language Spoken: | English; Chinese |
| b) Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | Above 36,000 square meters |
| No. of Production Lines | Above 5 |
| Contract Manufacturing | OEM Service Offered |
| Product Price Range | Average |
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry - Alumina Magnesium Castable for Ladle and Tundish
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or L/C
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords