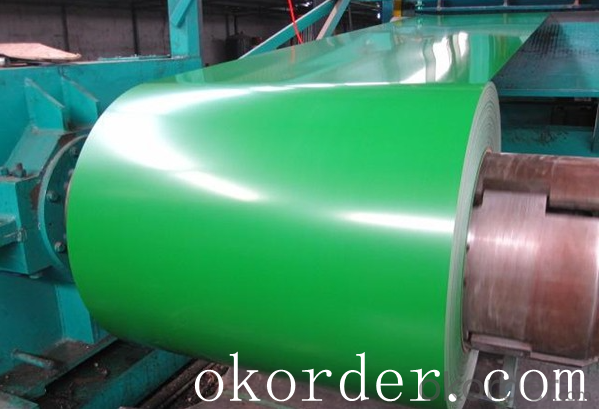
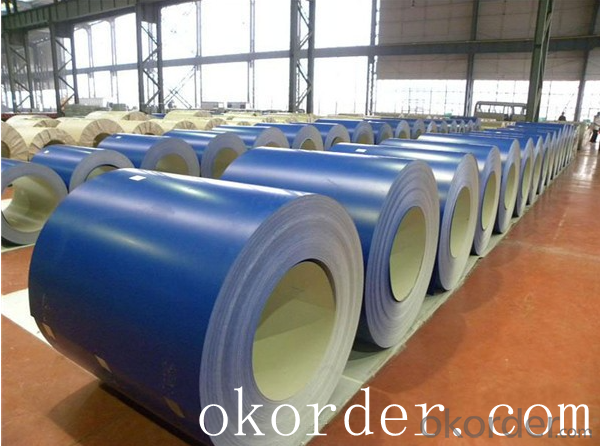
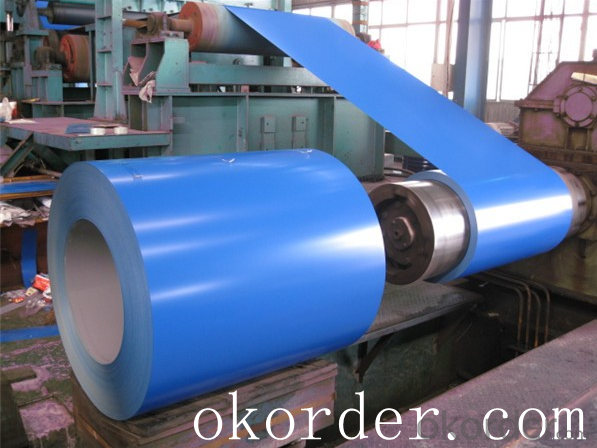
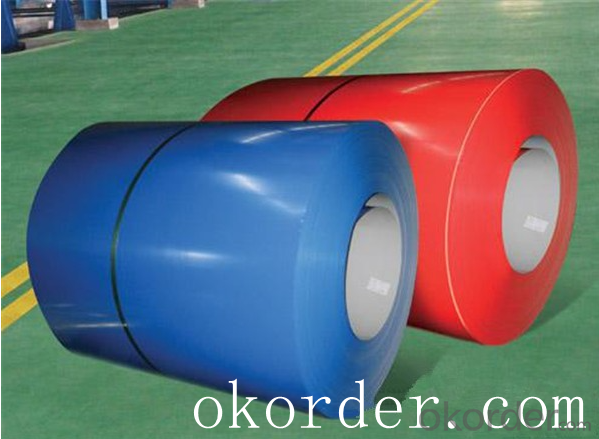
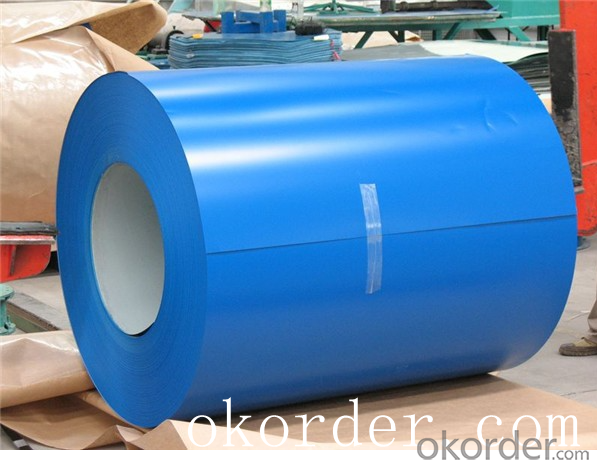
Prime quality prepainted galvanized steel 615mm
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Construction building material galvanized color prepainted cold
rolled steel coil
Prepainted steel sheet is coated with organic layer, which provides higher anti-corrosion property and
a longer lifespan than that of galvanized steel sheets.
The base metals for prepainted steel sheet consist of cold-rolled, HDG electro-galvanized and hot-dip
Alu-zinc coated. The finish coats of prepainted steel sheets can be classified into groups as follows:
polyester, silicon modified polyesters, polyvinylidene fluoride, high-durability polyester, etc
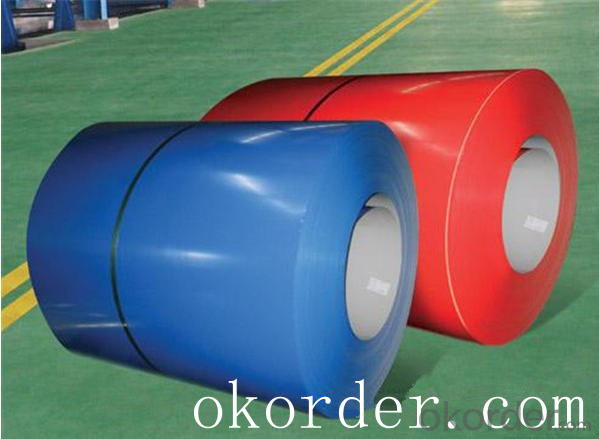

Standard and Grade :
Pre-paint galvanized steel coil | ||||
ASTM A755M-03 | EN10169:2006 | JISG 3312-2012 | ||
Commercial quality | CS | DX51D+Z | CGCC | |
Structure steel | SS GRADE 230 | S220GD+Z | CGC340 | |
SS GRADE 255 | S250GD+Z | CGC400 | ||
SS GRADE 275 | S280GD+Z | CGC440 | ||
SS GRADE 340 | S320GD+Z | CGC490 | ||
SS GRADE550 | S350GD+Z | CGC570 | ||
S550GD+Z | ||||
Application:
Outdoor | Roof, roof structure, surface sheet of balcony, frame of window, door of garage, rolled shutter door, booth, Persian blinds, cabana, etc |
Indoor | Door, isolater, frame of door, light steel structure of house, home electronic appliances, ect. |
- Q: How are steel billets packaged for shipment?
- Steel billets are typically packaged for shipment by placing them on wooden pallets or in steel cages. They are then secured using steel strapping or shrink wrap to prevent movement or damage during transportation. Labels are also attached to the packaging to identify the type, quantity, and destination of the billets.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of telecommunications equipment?
- Steel billets are used in the manufacturing of telecommunications equipment as they serve as raw material for various components such as brackets, frames, and enclosures. These billets are shaped and machined into precise forms to provide structural support and protection for sensitive electronic components within telecommunications devices. Additionally, steel billets may also be used in the production of antenna towers and infrastructure, ensuring stability and durability in the telecommunications industry.
- Q: How do steel billets differ from steel ingots?
- Steel billets and steel ingots, both intermediate forms of steel in the steel manufacturing process, have distinct differences. To begin with, the shape and size of steel billets and steel ingots vary. Steel billets are typically square or rectangular, with a cross-sectional area of roughly 36 square inches. They are long and slim, measuring approximately 6 to 12 inches in width and 1 to 12 feet in length. Conversely, steel ingots are generally larger and possess irregular shapes. Depending on the production method employed, they can be cylindrical, rectangular, or a combination of shapes. Steel ingots tend to be much larger than billets, weighing anywhere from several tons to over 100 tons. Secondly, the production process for steel billets and steel ingots also differs. Steel billets are commonly formed through continuous casting, which involves pouring molten steel into a mold and subsequently cooling and solidifying it to shape the billet. This process ensures a more precise and uniform shape, size, and composition. In contrast, steel ingots are typically produced via ingot casting, where molten steel is poured into a sizable mold and left to solidify. This method is often utilized for larger ingots, allowing for a more adaptable and flexible production process. Lastly, the purpose and usage of steel billets and steel ingots also vary. Steel billets are frequently employed as raw materials for further processing and shaping into various steel products, such as bars, rods, wire, and tubes. They serve as the initial stage in the production of finished steel goods. Conversely, steel ingots are commonly utilized for more specialized applications, such as the production of large steel components, forgings, or specialty alloys. Their larger size and irregular shape make them suitable for demanding applications of this nature. In conclusion, steel billets and steel ingots differ in terms of their shape, size, production process, and usage. While steel billets are slender, square or rectangular, and used as raw material for further processing, steel ingots are larger, possess irregular shapes, and are often employed for specialized applications.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the production of mining conveyors?
- The production of mining conveyors heavily relies on steel billets, which are essential for creating sturdy and durable components. Mining conveyors are responsible for transporting bulk materials like coal, ore, and gravel across long distances. To withstand the harsh conditions of a mining environment, these conveyors require robustness and durability. Conveyor rollers, crucial for the conveyor system's functionality, are manufactured using steel billets as the raw material. These rollers provide support and guidance to the conveyor belt. Initially, the steel billets undergo a heating process, which enhances their malleability, making shaping easier. Once heated, they are rolled into desired shapes to form the conveyor rollers. By incorporating steel billets into the production of mining conveyors, the resulting rollers possess excellent strength and resistance to wear and tear. The steel's properties, including toughness and hardness, make it highly suitable for enduring heavy loads and abrasive materials. Moreover, steel billets offer customization options to cater to specific requirements. Each mining operation may have unique needs in terms of conveyor dimensions, load capacities, and environmental conditions. With the use of steel billets, manufacturers can produce conveyor rollers of various sizes and specifications, ensuring a tailored fit for each mining operation. In conclusion, steel billets play a vital role in the production of mining conveyors as they serve as the primary material for manufacturing conveyor rollers. These rollers are indispensable for supporting and guiding the conveyor belt, enabling efficient and reliable transportation of bulk materials in the mining industry. By utilizing steel billets, the resulting conveyor rollers are strong, durable, and capable of withstanding the harsh conditions prevalent in the mining sector.
- Q: What are the main factors affecting the dimensional tolerances of steel billets?
- Various factors can influence the dimensional tolerances of steel billets. The manufacturing process itself is one of the main factors. The method employed to produce the billets, whether it be casting or hot rolling, can impact the final dimensions. Casting processes, for instance, can introduce variations in the cooling rate, thereby affecting the overall shape and size of the billets. Another crucial factor is the initial quality of the raw material. The composition and homogeneity of the steel utilized in billet production can contribute to dimensional variations. Impurities or uneven distribution of alloying elements can result in inconsistencies in the size and shape of the billets. The temperature maintained during the manufacturing process is also significant. High temperatures have the potential to cause thermal expansion, leading to dimensional changes in the billets. Proper control of cooling rates and the cooling process is vital to maintaining the desired tolerances. The design and condition of the manufacturing equipment can also impact dimensional tolerances. Adequate maintenance and calibration of machinery are essential to ensure consistent and accurate production. Lastly, external factors like handling and transportation can affect the dimensional tolerances of steel billets. Improper handling or rough transportation conditions can result in physical deformations or damage to the billets, leading to variations in their dimensions. In summary, achieving the desired dimensional accuracy in steel billets necessitates attention to factors such as the manufacturing process, raw material quality, temperature control, equipment condition, and handling and transportation practices.
- Q: What is the role of steel billets in the production of railway wagons?
- Steel billets play a critical role in the production of railway wagons as they serve as the raw material for manufacturing various components, such as the wagon body, chassis, and structural elements. These billets are heated and shaped into desired forms through processes like rolling and forging, which enable the creation of strong and durable wagon parts. By providing the necessary strength and structural integrity, steel billets contribute to the overall safety, reliability, and longevity of railway wagons, ensuring they can withstand the demanding conditions and heavy loads encountered during their service on the railways.
- Q: How are steel billets inspected for defects?
- Steel billets are inspected for defects through a series of thorough and systematic processes to ensure the quality and integrity of the final product. The inspection methods used may vary depending on the specific requirements and standards of the industry, but generally, the following techniques are commonly employed: 1. Visual Inspection: Skilled inspectors visually examine the surface of the billets for any visible defects such as cracks, surface irregularities, seams, or any other abnormalities. This is the initial step to identify any obvious defects that may affect the quality of the billets. 2. Magnetic Particle Testing (MPT): MPT is a non-destructive testing method that utilizes magnetic fields and iron particles to detect surface and near-surface defects in steel billets. The billets are magnetized, and iron particles are applied to the surface. If there are any defects, the magnetic field will cause the particles to cluster around them, making them visible to the inspector. 3. Ultrasonic Testing (UT): UT uses high-frequency sound waves to inspect the internal structure of steel billets. A probe is used to transmit ultrasonic waves into the billet, and the reflected waves are analyzed to determine the presence of any internal defects like voids, inclusions, or cracks. 4. Eddy Current Testing (ECT): This technique uses electromagnetic induction to identify surface and subsurface defects. A probe is used to create eddy currents within the billet, and any disruptions caused by defects will alter the electrical conductivity, which can be detected and analyzed. 5. Radiographic Testing (RT): RT involves the use of X-rays or gamma rays to inspect the internal structure of steel billets. The billets are exposed to radiation, and the resulting image is examined for any internal defects such as cracks, voids, or inclusions. 6. Ultrasonic Phased Array Testing (PAUT): PAUT utilizes multiple ultrasonic beams to inspect the entire volume of the billet. This technique allows for better defect detection and sizing by controlling the beam angle, frequency, and focus. These inspection methods are typically performed at various stages of the manufacturing process, including before and after the billets are heated, rolled, or further processed. By implementing these rigorous inspection techniques, manufacturers can identify and address any defects early on, ensuring the quality and reliability of the steel billets.
- Q: Who knows the diamond is?Who knows the diamond is carbon? Is it C60?
- It is also called the diamond diamond, crystal, it is not the molecules themselves, so the formula does not apply to.C said it is only by this kind of carbon elements. While C60 is footballene is another matter, the 60 is because it is a molecular crystal, each molecule consists of 60 carbon.
- Q: What are the challenges faced in the distribution and supply chain of steel billets?
- Some challenges faced in the distribution and supply chain of steel billets include transportation and logistics issues, such as the need for specialized equipment and efficient handling processes due to the heavyweight and bulky nature of steel billets. Additionally, ensuring timely delivery and managing inventory levels can be challenging due to various factors like unpredictable demand fluctuations and production delays. Quality control and inspection of steel billets during transit and storage is also crucial to prevent damage or deterioration. Lastly, coordinating with multiple stakeholders, including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and customers, requires effective communication and collaboration to maintain a smooth and reliable supply chain.
- Q: What are the different heat treatment processes applied to steel billets?
- There are several different heat treatment processes applied to steel billets, including annealing, normalizing, quenching, tempering, and case hardening. Annealing involves heating the steel to a specific temperature and then slowly cooling it to relieve internal stresses and improve its machinability. Normalizing is similar to annealing, but the steel is cooled in still air instead of a controlled environment. Quenching involves rapidly cooling the steel to harden it, typically by immersing it in a liquid or oil. Tempering is a process that follows quenching, where the steel is reheated to a specific temperature and then cooled again to enhance its toughness and reduce brittleness. Case hardening is a process where the surface of the steel is hardened while the core remains relatively softer, usually through the addition of carbon or nitrogen.
Send your message to us
Prime quality prepainted galvanized steel 615mm
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords