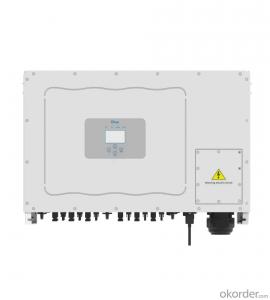
Solar 3 Phase Inverter
Solar 3 Phase Inverter Related Searches
3 Phase Solar Inverter 3 Phase Solar Power Inverter 3 Phase Inverter Solar Solar Power 3 Phase Inverter Solar Inverter 3 Phase 3 Phase Solar Battery Inverter 3 Phase Solar Hybrid Inverter 3 Phase Hybrid Solar Inverter 3-Phase Solar Inverter 3 Phase Solar Micro Inverter Three Phase Solar Inverter 3 Phase Solar Pump Inverter Hybrid Solar Inverter 3 Phase Solar Edge 3 Phase Inverter Best 3 Phase Solar Inverter Solar 3 Phase Inverter Price China 3 Phase Solar Inverter 3 Phase Solar Inverter Price 3kw Solar Inverter 3 Kilowatt Solar Inverter Abb 3 Phase Solar Inverter 3ph Solar Inverter 3kw Inverter Solar 3kv Solar Inverter Solar Inverter 3kva Solar Inverter 3 Kw 3kva Solar Inverter 3 Kva Solar Inverter 3kw Solar Hybrid Inverter 3 Mppt Solar InverterSolar 3 Phase Inverter Supplier & Manufacturer from China
Solar 3 Phase Inverters are advanced electrical devices that play a crucial role in converting the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC), which is compatible with the electrical grid and can be used to power various appliances. These inverters are specifically designed for three-phase systems, ensuring efficient energy management and optimal performance in a wide range of applications.The Solar 3 Phase Inverter finds its application in various scenarios, including residential, commercial, and industrial settings. They are particularly useful in large-scale solar power installations, where the demand for electricity is high, and a stable power supply is essential. These inverters help in reducing energy costs, promoting sustainability, and contributing to a greener environment by harnessing the power of the sun.
Okorder.com is a reputable wholesale supplier of Solar 3 Phase Inverters, boasting a vast inventory of high-quality products. They cater to the needs of customers worldwide, offering competitive prices and exceptional customer service. By partnering with Okorder.com, businesses and individuals can access a wide range of Solar 3 Phase Inverters, ensuring they have the right equipment for their specific energy requirements.
Hot Products