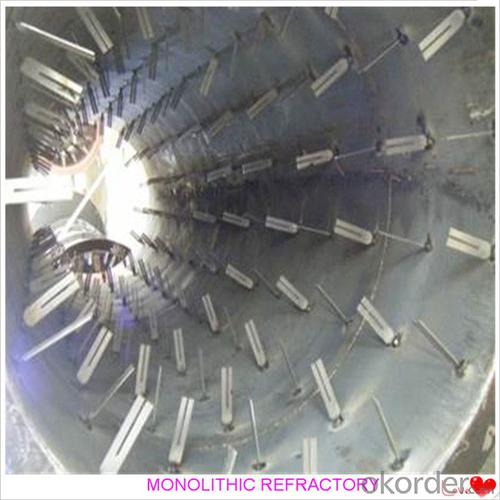
Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry:Refractory Castable for Fireplace and Industrial Furnace
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 3000000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Refractory Castable for Fireplaces and Industrial Furnaces
Product Description:
Gunning castable is manufactured according to international standards. The product is famous for its excellent abrasion resistance and low thermal conductivity. Further, these can be provided in different specifications as required by clients. Gunning castables use high purity raw materials and additives as the main material, and are made with superfine powder adding technology.
Product Features:
The material has excellent structural stability and air tightness, and has high physical and chemical properties, and also excellent working ability. If should be used with the same material products.
Product Applications:
Widely used in various kiln linings, such as boilers, blast furnace hot blast stoves, heating furnaces, ceramic kilns, heat treatment furnaces, incinerators, re-circulating fluidized bed furnaces and chemical industry and construction industry furnaces.
Product Specifications:

Product Images:
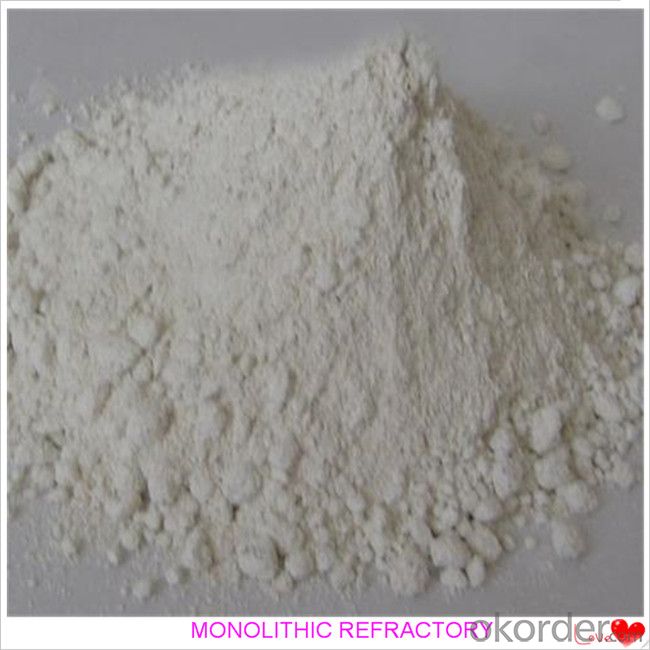
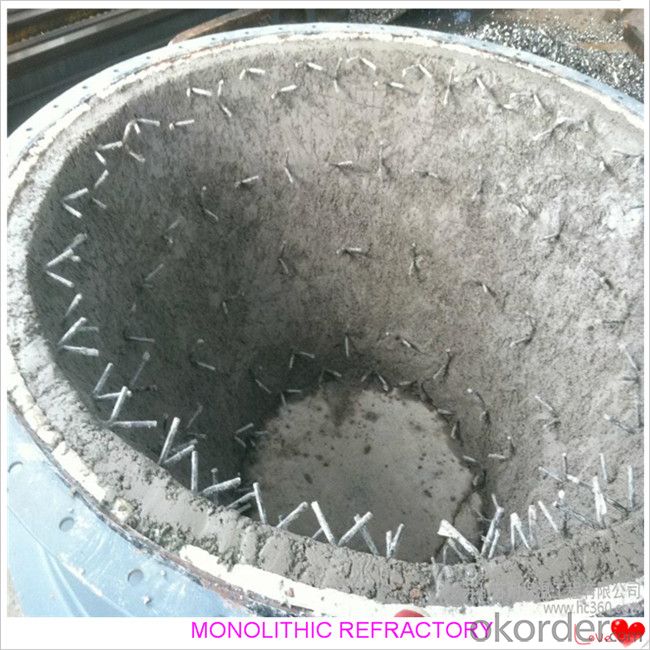




FAQ:
Q1: Why buy Materials & Equipment from OKorder.com?
A1: All products offered by OKorder.com are carefully selected from China's most reliable manufacturing enterprises. Through its ISO certifications, OKorder.com adheres to the highest standards and a commitment to supply chain safety and customer satisfaction.
Q2: How do we guarantee the quality of our products?
A2: We have established an advanced quality management system which conducts strict quality tests at every step, from raw materials to the final product. At the same time, we provide extensive follow-up service assurances as required.
Q3: What are Abrasion Resistant Coatings?
A3: ARC's abrasion resistant coatings guard against the severe wear and erosion that can chip away your plant's bottom line. These high-performance coatings protect new equipment as well as rebuild worn equipment at a fraction of traditional replacement costs.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories resist abrasion in the iron and steel industry?
- Monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry resist abrasion through their inherent properties and design features. These refractories are formulated with high levels of abrasion-resistant materials such as alumina, silicon carbide, and zirconia, which provide excellent resistance to wear and erosion caused by the movement of molten metal, slag, and other abrasive materials in the production processes. Additionally, the monolithic nature of these refractories eliminates the presence of joints and gaps, reducing weak points and enhancing their ability to withstand abrasion.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the overall efficiency of ladle transfer processes?
- Monolithic refractories contribute to the overall efficiency of ladle transfer processes by providing excellent thermal insulation and resistance to high temperatures, which helps in maintaining the heat of the molten metal during transfer. They also have high mechanical strength and erosion resistance, ensuring longer service life and reduced downtime for repairs. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer easy installation and can be shaped to fit the ladle's specific geometry, minimizing heat loss and ensuring a more efficient transfer process.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories improve the efficiency of ladle and tundish preheating stations?
- Crucial for enhancing the efficiency of ladle and tundish preheating stations, monolithic refractories are specifically designed to withstand high temperatures and thermal shocks, making them an ideal choice for preheating applications. One significant way in which monolithic refractories enhance efficiency is by offering excellent heat insulation. With low thermal conductivity, these refractories minimize heat loss from the preheating station to the surroundings. Consequently, the ladle or tundish preheating station retains more heat, resulting in faster and more efficient vessel heating. Furthermore, monolithic refractories possess outstanding heat retention properties. Once heated, these refractories can gradually store and release heat over time. This characteristic ensures a consistent and controlled heating process in the ladle or tundish preheating station. By maintaining a stable temperature, the refractories guarantee uniform vessel heating and prevent thermal shocks that could cause cracking or other damage. Moreover, monolithic refractories exhibit excellent resistance to chemical reactions and erosion caused by molten metals and slag. Ladles and tundishes frequently encounter corrosive environments, and the use of monolithic refractories protects against degradation and extends the lifespan of the preheating station. This durability reduces the need for frequent maintenance and replacement, resulting in cost savings and improved overall efficiency. To summarize, monolithic refractories enhance the efficiency of ladle and tundish preheating stations by providing exceptional heat insulation, heat retention, and resistance to chemical reactions. These properties lead to faster and more uniform heating, reduced heat loss, and increased preheating station durability. Ultimately, these advantages contribute to improved productivity and cost-effectiveness in the steelmaking process.
- Q: What are the challenges in recycling and disposing of monolithic refractories?
- Recycling and disposing of monolithic refractories pose several challenges that need to be addressed in order to minimize environmental impact and maximize resource efficiency. One of the main challenges is the handling and transportation of monolithic refractories due to their heavy and bulky nature. These materials are often used in high-temperature applications, such as furnace linings, and can be difficult to dismantle and remove from equipment. The weight and size of monolithic refractories make it challenging to transport them to recycling or disposal facilities, requiring specialized equipment and infrastructure. Another challenge is the heterogeneity of monolithic refractories, which often contain various types of refractory materials, binders, and additives. This complexity makes it difficult to separate and categorize different components for effective recycling. The lack of standardized recycling processes for monolithic refractories further complicates the recycling efforts. Furthermore, the high melting points of refractory materials used in monolithic refractories can make it energy-intensive and costly to recycle them through conventional methods like melting and remolding. Alternative recycling methods, such as thermal treatment or chemical processing, need to be explored and optimized to make the recycling process more economically and environmentally viable. Ensuring the proper disposal of monolithic refractories is also a challenge. If these materials are not recycled, they often end up in landfills, taking up valuable space and potentially leaching harmful substances into the environment. Landfilling refractories can also pose a risk of contamination if they are not properly managed or if hazardous additives are present in the materials. To address these challenges, it is crucial to invest in research and development to develop more efficient and cost-effective recycling technologies for monolithic refractories. Collaboration between manufacturers, recycling facilities, and regulatory bodies is also essential to establish guidelines and standards for the recycling and disposal of these materials. Additionally, educating industries and end-users about the importance of recycling and the availability of recycling options can help increase the demand and feasibility of recycling monolithic refractories.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the overall productivity of iron and steel production?
- The overall productivity of iron and steel production is greatly enhanced by the use of monolithic refractories. These refractories are crucial components utilized in the lining of high-temperature furnaces and other equipment employed in these industries. One of the ways in which monolithic refractories boost productivity is through their exceptional thermal insulation capabilities. By possessing high thermal conductivity, they effectively minimize heat loss from the furnaces, thereby reducing energy consumption and enhancing overall efficiency. This insulation property permits higher operating temperatures, resulting in faster and more efficient production processes. Furthermore, monolithic refractories exhibit superior resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion. Given the harsh conditions experienced during the iron and steel production process, such as rapid temperature fluctuations and exposure to molten metal and slag, these refractories are designed to withstand such extreme environments. This ensures prolonged service life and decreased downtime for maintenance and repairs, directly leading to increased productivity and reduced production costs. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer improved dimensional stability in comparison to traditional brick refractories. Their ability to conform to intricate shapes and structures allows for enhanced lining design, facilitating superior heat transfer and distribution. This uniformity in heat distribution contributes to improved process control and greater consistency in product quality. Moreover, the installation and repair of monolithic refractories are relatively simpler and quicker when compared to traditional brick refractories. This ease of installation and repair reduces downtime during maintenance, enabling more continuous production. The decreased downtime ultimately leads to increased productivity and higher output. In conclusion, monolithic refractories significantly contribute to the overall productivity of iron and steel production through their excellent thermal insulation, resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, improved dimensional stability, and ease of installation and repair. These properties result in enhanced energy efficiency, reduced downtime, improved process control, and higher product quality, ultimately leading to increased productivity and profitability for the industry.
- Q: What are the considerations for selecting monolithic refractories for ladles and tundishes?
- When it comes to choosing monolithic refractories for ladles and tundishes, there are a number of important factors to bear in mind. Firstly, it is crucial to select monolithic refractories that can withstand and maintain their strength and integrity at the extremely high temperatures experienced during metal casting processes. In addition, monolithic refractories with good thermal shock resistance are essential, as ladles and tundishes are subjected to rapid temperature changes during pouring and cooling. Such refractories can prevent cracking and spalling, ensuring the longevity and performance of these components. Erosion and corrosion resistance is another key consideration. Refractory linings can be eroded and chemically attacked by molten metal, slag, and other corrosive substances. Opting for monolithic refractories with excellent erosion and corrosion resistance can extend the service life of ladles and tundishes, reducing the need for maintenance and minimizing downtime. Mechanical strength is also important, as ladles and tundishes are frequently handled, transported, and subjected to mechanical stresses. Monolithic refractories with adequate mechanical strength can withstand these forces without cracking or breaking, thereby maintaining the structural integrity of these components. The method of applying monolithic refractories is another factor to think about. Depending on the size and shape of the ladles and tundishes, as well as the available equipment and expertise, different application methods such as gunning, casting, ramming, or spraying may be used. It is important to ensure that the selected monolithic refractories are compatible with the chosen application method. The thermal conductivity of monolithic refractories can impact heat transfer in ladles and tundishes. Opting for refractories with low thermal conductivity can help minimize heat loss and improve energy efficiency. While performance and durability are crucial, it is also important to consider the cost-effectiveness of the chosen monolithic refractories. This includes factors such as the initial cost of the refractories, installation and maintenance costs, and the expected service life. Striking a balance between performance and cost can help optimize the overall investment in ladles and tundishes. Overall, the selection of monolithic refractories for ladles and tundishes involves a combination of factors, including temperature resistance, thermal shock resistance, erosion and corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, application method compatibility, thermal conductivity, and cost-effectiveness. By carefully evaluating these factors, it is possible to choose the most suitable monolithic refractories that meet the specific requirements of ladles and tundishes in metal casting processes.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand the mechanical impacts in furnace door applications?
- Monolithic refractories withstand mechanical impacts in furnace door applications due to their high strength and resistance to thermal shock. These refractories are composed of dense and uniform materials, such as castables or plastics, which provide excellent structural integrity and the ability to withstand heavy loads and vibrations. Additionally, they have low porosity and high thermal conductivity, allowing them to dissipate heat efficiently and reduce the risk of cracking or spalling under mechanical stress.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories improve the performance and efficiency of iron and steel production?
- Improved performance and efficiency in iron and steel production are achieved through the utilization of monolithic refractories. These specialized materials are designed to withstand extreme temperatures, chemical reactions, and mechanical stresses, making them ideal for high-temperature industrial processes. A key contribution of monolithic refractories is their ability to provide a protective lining for furnaces, kilns, and other equipment used in iron and steel production. Their superior heat resistance ensures that the underlying structure is shielded from the intense heat, preventing any detrimental effects on the equipment. This results in reduced downtime, extended service life, and ultimately, enhanced overall efficiency. Furthermore, monolithic refractories play a crucial role in improving thermal efficiency during the production process. By minimizing heat losses, these materials help maintain a stable and uniform temperature distribution, thereby enhancing the energy efficiency of the system. Precise temperature control is of utmost importance in iron and steel production to achieve the desired metallurgical properties of the final product. Additionally, monolithic refractories exhibit excellent resistance to chemical corrosion, erosion, and slag attacks. They act as a barrier between the molten metal and the refractory lining, preventing unwanted reactions and material degradation. This preserves the integrity of the furnace lining, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements. Consequently, it leads to increased productivity and long-term cost savings. Moreover, the ease with which monolithic refractories can be shaped, repaired, or replaced is another advantage. Unlike traditional brick refractories, which require labor-intensive and time-consuming installation, monolithic refractories offer a more flexible and efficient application. Their flexible nature allows for easy repair of damaged areas, minimizing downtime and ensuring uninterrupted production. In summary, the utilization of monolithic refractories significantly enhances the performance and efficiency of iron and steel production. These materials provide a protective lining, improve thermal efficiency, resist chemical corrosion, and offer easy installation and repair options. By optimizing the production process, monolithic refractories contribute to higher productivity, reduced downtime, and increased cost-effectiveness in the iron and steel industry.
- Q: Can monolithic refractories be used for the lining of reheating furnaces and walking beam furnaces?
- Monolithic refractories, which are refractory materials that can be cast or gunned into place rather than being made up of individual bricks or precast shapes, can be utilized for the lining of both reheating furnaces and walking beam furnaces. This characteristic makes them highly adaptable and versatile for a variety of furnace applications. Reheating furnaces are employed to heat metal products to a specific temperature before undergoing further processing, such as rolling or forging. The lining of these furnaces is exposed to high temperatures, thermal cycling, and mechanical stress. Given their exceptional thermal shock resistance and ability to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or spalling, monolithic refractories are well-suited for these conditions. In the steel industry, walking beam furnaces are utilized for the continuous heating and transportation of steel slabs or billets. These furnaces necessitate a lining material that can endure the abrasion and mechanical stress caused by the movement of the material. Monolithic refractories with high abrasion resistance and good mechanical strength are ideal for lining walking beam furnaces. Moreover, monolithic refractories provide additional advantages such as straightforward installation, decreased downtime for repairs, and enhanced energy efficiency. They can be customized to fit specific furnace designs and can be easily repaired or replaced as needed. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are a suitable option for lining reheating furnaces and walking beam furnaces due to their ability to withstand high temperatures, thermal cycling, mechanical stress, and abrasion. Their versatility, ease of installation, and repair make them the preferred choice for these furnace applications.
- Q: What are the considerations for selecting monolithic refractories for reheating furnaces?
- There are several key considerations when selecting monolithic refractories for reheating furnaces. Firstly, the refractory material must have excellent thermal conductivity to efficiently transfer heat to the steel being reheated. Additionally, it should possess high resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress to withstand the rapid temperature changes and mechanical forces experienced in the furnace. The refractory should also have low porosity to prevent the penetration of gases and slag, ensuring a longer service life. Other factors to consider include the refractory's resistance to corrosive environments, ease of installation, and cost-effectiveness. Ultimately, choosing the right monolithic refractory is crucial to ensure optimal furnace performance and longevity.
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry:Refractory Castable for Fireplace and Industrial Furnace
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 3000000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords