Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry:AL2O3-SIO2-C Castable for Blast Furnace Tapping Channel
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or L/C
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
General Information of Al2O3-SiO2-C Castable for Blast Furnace Tapping Channel
FIREF Al2O3- SiO2-C castable for blast furnace tapping channel is known for its excellent corrosion and scouring resistance of iron steel which is made strictly as per international standards. Beside, FIREF Al2O3- SiO2-C castable for blast furnace tapping channel has gained a good fame for its long operating life and easy execution and mending.
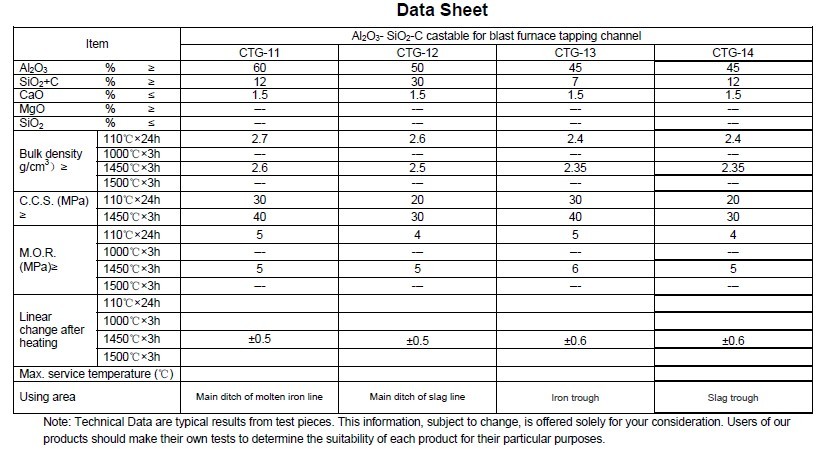
Technical data of Al2O3-SiO2-C Castable for Blast Furnace Tapping Channel
Production line and packing of Al2O3-SiO2-C Castable for Blast Furnace Tapping Channel


Feature of Al2O3-SiO2-C Castable for Blast Furnace Tapping Channel
Long operating life
Excellent corrosion and scouring resistance of iron steel
Easy execution and mending
Application of Al2O3-SiO2-C Castable for Blast Furnace Tapping Channel
FIREF Al2O3-SiO2-C castable for blast furnace tapping channel can be used widely for in situ casting or pre-casting for tri-angle area of UHP EAF roof.
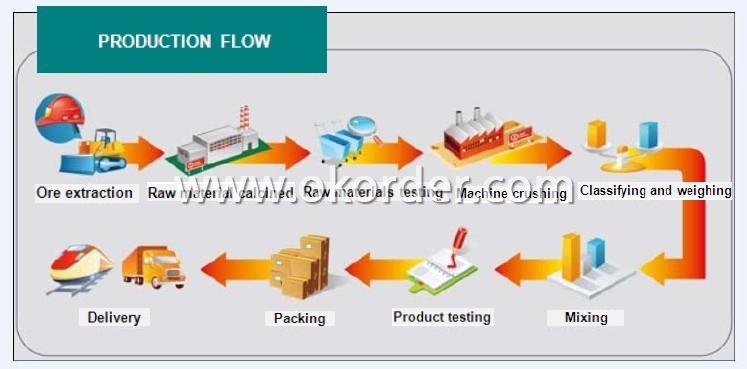
Production Flow of Al2O3-SiO2-C Castable for Blast Furnace Tapping Channel
- Q: What are the common failure modes of monolithic refractories in iron and steel applications?
- Monolithic refractories, known for their exceptional thermal shock resistance, high temperature stability, and mechanical strength, find extensive use in iron and steel applications. However, like any other material, they are susceptible to failure. Numerous failure modes are associated with monolithic refractories in iron and steel applications. 1. Spalling, the detachment of refractory material from the surface, stands as one of the most prevalent failure modes. This detachment occurs due to thermal cycling, mechanical stress, or chemical reactions. Mismatched thermal expansion coefficients between the refractory and the surrounding structure can lead to cracking and subsequent detachment. 2. Erosion, another common failure mode, arises when the refractory material encounters the erosive action of molten metal, slag, or gases. Physical impact from flowing metal or chemical attack by corrosive slag components can contribute to erosion. This results in the loss of refractory material, reduced lining thickness, and compromised performance. 3. Corrosion, a significant failure mode, particularly affects iron and steel applications in contact with aggressive atmospheres or molten metal. The interaction between the refractory material and corrosive agents, such as oxides, sulfides, or alkalis present in the environment, leads to corrosion. Corrosion products weaken the refractory lining and shorten its lifespan. 4. Thermal shock, caused by extreme temperature fluctuations, poses a risk to monolithic refractories in iron and steel applications. Rapid heating or cooling can trigger thermal shock, resulting in cracking and failure of the refractory material. Thermal shock can occur due to uneven heating or cooling, sudden temperature changes, or thermal gradients within the refractory lining. 5. Abrasion is a potential failure mode in specific iron and steel applications, where monolithic refractories are exposed to abrasive wear. This wear occurs when the refractory lining comes into contact with solid particles like metallic oxides, slags, or raw materials. The repeated impact and rubbing action of these particles cause erosion and abrasion of the refractory material, leading to failure. To mitigate these failure modes, it is crucial to select appropriate refractories, employ proper installation techniques, and practice regular maintenance. Regular inspections, repair of damaged areas, and the application of protective coatings can greatly enhance the lifespan and performance of monolithic refractories in iron and steel applications.
- Q: What are the recent developments in monolithic refractories for the iron and steel industry?
- In recent years, there have been several significant developments in monolithic refractories for the iron and steel industry. Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in the production of iron and steel, as they provide high-temperature resistance and insulation to the lining of furnaces and other equipment used in the industry. One of the key advancements in monolithic refractories is the development of advanced alumina-based castables. These castables offer superior thermal shock resistance, high strength, and excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for use in the iron and steel industry. They can withstand extreme temperatures and mechanical stresses, ensuring longer service life and reduced downtime for maintenance. Another notable development is the introduction of low-cement and ultra-low cement castables. These castables have a reduced cement content compared to traditional castables, resulting in improved refractory properties. They offer higher hot strength, reduced porosity, and enhanced resistance to slag and metal corrosion. This allows for increased productivity and efficiency in iron and steel manufacturing processes. Furthermore, there have been advancements in the use of insulating refractories in the iron and steel industry. Insulating castables and bricks are now being used to line ladles, tundishes, and other equipment, providing better insulation and energy efficiency. These materials help to reduce heat loss and improve thermal efficiency, resulting in cost savings and reduced environmental impact. Additionally, the development of monolithic refractories with improved installation techniques has been a significant development. Traditional brick lining methods require skilled labor and a longer installation time. However, with the introduction of gunning and shotcreting techniques, the installation process has become faster and more efficient. These techniques involve spraying refractory materials onto the lining surface, ensuring better adherence and reducing the risk of lining failure. Overall, the recent developments in monolithic refractories for the iron and steel industry have focused on improving thermal shock resistance, corrosion resistance, insulation properties, and installation techniques. These advancements have resulted in increased efficiency, reduced downtime, and improved productivity in the iron and steel manufacturing processes.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the overall efficiency of steel ladle operations?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in enhancing the overall efficiency of steel ladle operations. These refractories are engineered materials that are installed as a single, unbroken structure within the ladle. They offer numerous benefits that directly contribute to the efficiency of the steel ladle operations. Firstly, monolithic refractories are known for their excellent thermal insulation properties. They have low thermal conductivity, which means they can effectively retain and contain heat within the ladle. This insulation property helps in maintaining the desired temperature of the molten steel, preventing heat loss during transportation and reducing the need for frequent reheating. By minimizing heat loss, monolithic refractories enable more efficient use of energy resources, resulting in cost savings and improved productivity. Additionally, monolithic refractories exhibit high refractoriness, which refers to their ability to withstand high temperatures without losing their structural integrity. This characteristic is vital in steel ladle operations, as the ladles are exposed to extreme temperatures during the steelmaking process. The high refractoriness of monolithic refractories ensures that they can withstand the intense heat and prevent any damage or failure of the ladle lining. This durability translates into reduced downtime and maintenance requirements, leading to increased operational efficiency. Moreover, monolithic refractories offer excellent resistance to chemical attack. The ladles used in steelmaking are in contact with various corrosive substances, such as molten metals, slag, and fluxes. The chemical resistance of monolithic refractories prevents them from reacting with these substances, ensuring the integrity and longevity of the ladle lining. This resistance to chemical attack reduces the frequency of repairs and replacements, minimizing downtime and improving the overall efficiency of ladle operations. Furthermore, the installation of monolithic refractories is relatively quick and straightforward compared to traditional brick linings. This ease of installation saves time and labor costs, allowing for faster turnaround between ladle operations. It enables steel manufacturers to optimize their production schedules and enhance overall operational efficiency. In conclusion, monolithic refractories contribute significantly to the overall efficiency of steel ladle operations. Their excellent thermal insulation properties, high refractoriness, resistance to chemical attack, and ease of installation all play vital roles in improving energy efficiency, reducing downtime, and enhancing productivity. By choosing monolithic refractories, steel manufacturers can achieve optimized ladle performance and ultimately improve their overall steelmaking process.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories protect the lining of ladles and tundishes?
- Monolithic refractories protect the lining of ladles and tundishes by forming a strong and durable barrier against high temperatures, chemical reactions, and mechanical stresses. These refractories are designed to be resistant to thermal shock and erosion, ensuring that the lining remains intact and unaffected by the molten metal or slag. They also provide insulation, minimizing heat loss and reducing energy consumption. Overall, monolithic refractories act as a reliable shield, extending the lifespan of the ladles and tundishes and preventing any detrimental effects on the lining.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories resist thermal shock in the iron and steel industry?
- Monolithic refractories are specifically designed to resist thermal shock in the iron and steel industry. This is primarily achieved through their unique composition and structure. Firstly, monolithic refractories are made from high-quality raw materials, such as alumina, magnesia, and silica, which have excellent thermal properties. These materials are carefully selected to provide a high melting point, low thermal conductivity, and good thermal expansion characteristics. Secondly, the manufacturing process of monolithic refractories involves precise control of the grain size distribution and the addition of bonding agents. This results in a dense and homogeneous structure, which enhances their resistance to thermal shock. The bonding agents also play a crucial role in enhancing the refractory's strength and integrity. Additionally, monolithic refractories are often formulated with additives that provide increased resistance to thermal shock. These additives can include zirconia, silicon carbide, or graphite, which improve the refractory's ability to withstand rapid temperature changes. Moreover, monolithic refractories are designed to have low porosity, reducing the penetration of molten metal or slag into the material. This helps to prevent the formation of cracks and spalling, which can occur due to thermal shock. Furthermore, monolithic refractories are often applied as a lining or coating on the surface of the furnace or other equipment. This allows them to form a protective barrier, reducing direct exposure to extreme temperatures and thermal cycling. Overall, the combination of high-quality raw materials, careful manufacturing processes, additives, low porosity, and proper application techniques make monolithic refractories highly resistant to thermal shock in the iron and steel industry. They can withstand rapid temperature changes, prevent cracks, and maintain their structural integrity, ensuring reliable and efficient operation of furnaces and other equipment in this demanding industry.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories enhance the performance of ladle and tundish covers?
- The performance of ladle and tundish covers is significantly improved by the utilization of monolithic refractories. There are several ways in which this enhancement is achieved. Primarily, monolithic refractories possess remarkable thermal insulation properties. The steelmaking process subjects ladles and tundishes to extreme temperatures. Through the use of monolithic refractories, the covers effectively trap and retain heat, preventing excessive heat loss. This insulation ability not only helps maintain the desired temperature of the molten steel but also reduces the energy consumption required for heating. Secondly, monolithic refractories demonstrate exceptional resistance to thermal shock. When ladles and tundishes are filled with molten steel, there is a rapid and drastic temperature change in the refractory lining. This sudden shift can cause cracking and spalling of the lining, jeopardizing its integrity. However, monolithic refractories possess high thermal shock resistance, enabling them to endure these abrupt temperature fluctuations without significant damage. This ensures the longevity and durability of the ladle and tundish covers. Additionally, monolithic refractories exhibit excellent corrosion resistance. The presence of molten steel and other corrosive substances in ladles and tundishes can erode the refractory lining over time. Nonetheless, monolithic refractories are specifically engineered to withstand these corrosive environments, shielding the covers from chemical attack and erosion. This corrosion resistance enhances the lifespan of the ladle and tundish covers, reducing the need for frequent replacements and associated downtime. Furthermore, monolithic refractories provide good mechanical strength and stability. Ladles and tundishes undergo various mechanical stresses, including the weight of the molten steel, thermal expansions, and vibrations. The use of monolithic refractories furnishes the necessary strength and stability to endure these mechanical forces, averting structural failures and maintaining the integrity of the covers. To summarize, monolithic refractories heighten the performance of ladle and tundish covers by providing exceptional thermal insulation, resistance to thermal shock and corrosion, and sufficient mechanical strength. These properties guarantee efficient steelmaking processes, diminish maintenance costs, and extend the lifespan of ladles and tundishes.
- Q: What are monolithic refractories and how are they used in the iron and steel industry?
- Monolithic refractories are a type of refractory material that are characterized by their unified and continuous structure. Unlike traditional refractory bricks, which are made by firing individual pieces in a kiln, monolithic refractories are composed of a single, seamless mass. This allows for greater flexibility in terms of shape and size, making them ideal for various applications in the iron and steel industry. In the iron and steel industry, monolithic refractories are widely used due to their superior thermal and mechanical properties. They are employed in a range of applications, including lining furnaces, kilns, ladles, and tundishes. These refractories are designed to withstand extreme temperatures, chemical erosion, and mechanical stress, ensuring the efficient and continuous operation of the steelmaking process. One common use of monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry is the lining of blast furnaces. Blast furnaces are large, cylindrical structures used for the production of pig iron from iron ore. The lining of these furnaces is subjected to intense heat and chemical reactions, as well as the abrasive nature of iron ore and hot gases. Monolithic refractories, such as castables and gunning mixes, are utilized to create a durable lining that can withstand these harsh conditions. Another application is the lining of ladles, which are used to transport molten metal from the blast furnace to the steelmaking process. Monolithic refractories are used to line the ladles, protecting them from the corrosive effects of hot metal and slag. In this case, the ability to form monolithic shapes allows for precise fitting and easy installation. Monolithic refractories also find use in tundishes, which are vessels used to distribute molten metal evenly into molds during continuous casting. The refractories used in tundishes must have excellent thermal shock resistance and erosion resistance to withstand the high temperatures and abrasive nature of the molten metal. Monolithic refractories, such as ramming and patching mixes, are utilized to repair and maintain the tundish lining. Overall, monolithic refractories are essential in the iron and steel industry for their ability to withstand extreme conditions and provide long-lasting linings in various applications. By utilizing these advanced refractory materials, the industry can achieve improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and enhanced productivity in the steelmaking process.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand thermal cycling in the iron and steel industry?
- Monolithic refractories withstand thermal cycling in the iron and steel industry through their unique properties and composition. These refractories are made from a single piece or mass, which eliminates joints and weak points that could be susceptible to thermal stress. Additionally, their high thermal conductivity and low thermal expansion help them absorb and distribute heat evenly, reducing the risk of cracking or damage during rapid temperature changes. The use of advanced bonding agents further enhances their durability and resistance to thermal cycling, allowing them to withstand the extreme conditions of the iron and steel industry.
- Q: What are the advantages of using low-moisture castables in the iron and steel industry?
- Low-moisture castables offer numerous benefits to the iron and steel industry. Firstly, their lower water content results in shorter drying times, which is crucial in this fast-paced industry. This reduction in overall production time allows for quicker turnaround and increased efficiency. Secondly, low-moisture castables exhibit superior strength and durability when compared to traditional castables. They can withstand extreme temperatures and harsh environments without cracking or breaking. This resilience is essential in an industry marked by high heat and abrasion, ensuring that the castables maintain their structural integrity and endure demanding conditions. Additionally, low-moisture castables boast excellent thermal shock resistance. This means they can handle rapid temperature changes without experiencing cracks or spalling. In an industry that frequently relies on heating and cooling processes, this attribute is highly advantageous. Moreover, low-moisture castables possess a higher density than traditional castables, resulting in improved insulation properties and lower thermal conductivity. This insulation efficiency conserves energy and minimizes heat loss during various processes, ultimately leading to significant cost savings. Lastly, low-moisture castables offer versatility in their application. They can be utilized for various purposes in the iron and steel industry, serving as linings for ladles, furnaces, tundishes, and other high-temperature equipment. This versatility allows for greater flexibility in designing and constructing the necessary infrastructure for iron and steel production. In conclusion, the utilization of low-moisture castables in the iron and steel industry provides a range of advantages, including reduced drying time, increased strength and durability, enhanced thermal shock resistance, improved insulation properties, and versatile application possibilities. These benefits contribute to more efficient and cost-effective operations in this industry.
- Q: What are the factors to consider when selecting monolithic refractories for specific applications?
- When choosing monolithic refractories for specific applications, one must take into account several factors. These factors encompass the operating temperature, chemical environment, mechanical stress, and desired performance characteristics of the refractory material. The operating temperature plays a pivotal role and varies depending on the monolithic refractory. It is crucial to select a refractory material that can withstand the specific temperature range without experiencing thermal spalling or degradation. The chemical environment also plays a vital role. Different applications may expose the refractory to various chemicals, acids, alkalis, or gases. It is essential to choose a monolithic refractory that is chemically resistant to the specific environment to ensure durability and performance over time. Mechanical stress is another critical consideration. Certain applications may subject the refractory to high mechanical stress, such as abrasion, impact, or thermal shock. It is important to choose a refractory material that can withstand these stresses without cracking or failing. The desired performance characteristics of the refractory material should also be taken into account. This includes factors such as thermal conductivity, thermal expansion, density, and strength. The specific requirements of the application will dictate the necessary performance characteristics, and the refractory material should be chosen accordingly. Other factors to consider include the method of installation, availability, cost, and maintenance requirements. Some monolithic refractories may require specialized installation techniques, while others may be readily available and cost-effective. Additionally, the maintenance requirements of the refractory material should be considered to ensure ease of upkeep and longevity. In conclusion, selecting the appropriate monolithic refractories for specific applications necessitates careful consideration of factors such as operating temperature, chemical environment, mechanical stress, desired performance characteristics, installation method, availability, cost, and maintenance requirements. By taking these factors into account, one can choose a refractory material that will provide optimal performance and durability in the given application.
1. Manufacturer Overview
| Location | Henan, China |
| Year Established | 2007 |
| Annual Output Value | Above US$ 60 Million |
| Main Markets | Mid East; Eastern Europe; North America |
| Company Certifications | ISO 9001:2008 |
2. Manufacturer Certificates
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period |
3. Manufacturer Capability
| a) Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | Tianjin |
| Export Percentage | 31% - 50% |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | 21-50 People |
| Language Spoken: | English; Chinese |
| b) Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | Above 36,000 square meters |
| No. of Production Lines | Above 5 |
| Contract Manufacturing | OEM Service Offered |
| Product Price Range | Average |
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry:AL2O3-SIO2-C Castable for Blast Furnace Tapping Channel
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or L/C
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords