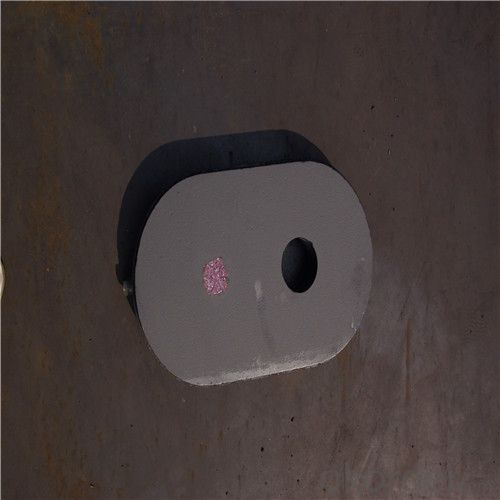
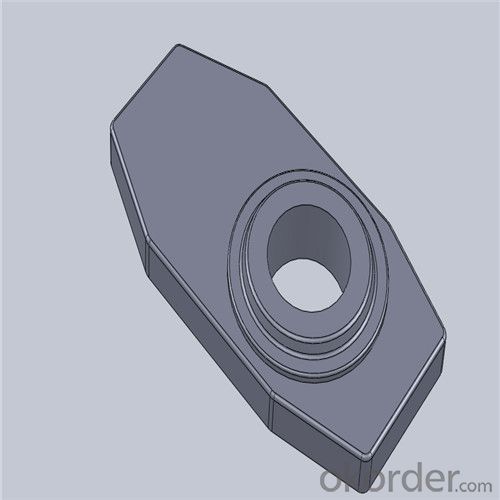
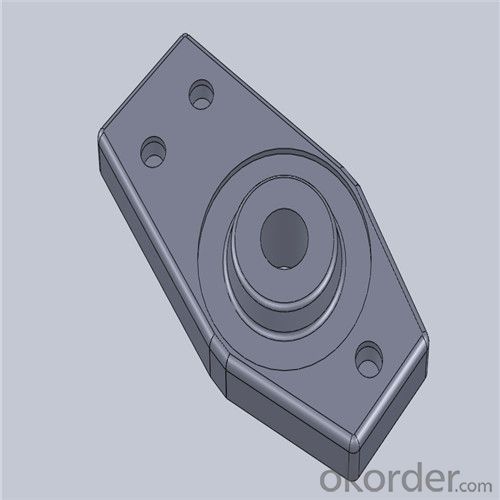
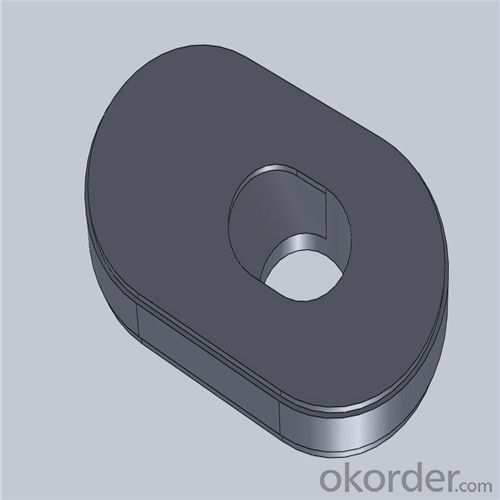
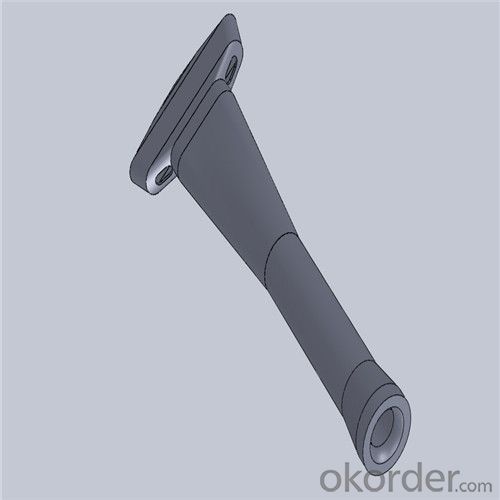
Monolithic Refractories High Performance & Temperature Ladle Sliding Gate for Iron and Steel Industry
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for High Performance Refractory Ladle Slide Gate
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Shape: | Plate | Material: | Alumina Block |
| SiO2 Content (%): | N/A | Al2O3 Content (%): | 80-90% | MgO Content (%): | N/A |
| CaO Content (%): | N/A | Refractoriness (Degree): | 1770°< Refractoriness< 2000° | CrO Content (%): | N/A |
| SiC Content (%): | N/A | Model Number: | CS80 | Brand Name: | |
| Product name: | High performance refractory ladle slide gate | Model No.: | cs80 | Brand name: | CMAX |
| Quality: | Al-C or Al-Zr-C | Service life: | 4-6 heats | Apparent porosity: | 7% Max |
| Bulk density:: | 3.1 MIN | C.C.S: | 120MPA | MOQ: | 100 pcs for trial |
| Delivery time: | 60 working days upon receipt of deposit |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Inner carton packing, outer wooden case suitable for long term sea shipping |
| Delivery Detail: | three months working days upon receipt of deposit |
Specifications
Surface flatness less than 0.05mm
High mechanical strength
Erosion resistance
Oxidation resistance
Thermal shock stability
Using the raw materials of tabular alumina, zirconia-corundum, carbon and other high-grade additives, after sintering to obtain characteristics of oxidation resistance, scour strength, erosion resistance, thermal shock resistance, shape stable and long service life, made our products the preferred materials for the large and medium-sized steel ladle, refining ladle, series of alloy steel ladle, and tundish. Our high performance sintering sliding gates include alumina carbon , Al2O3-ZrO2-C, etc, can meet the needs of different steel grade.
General Chemical Analysis for refractory ladle slide gate :
slide gate plate widely including Alumina carbon and Alumina Zirconia Carbon slide gate plate, MgO and MgO-spinel slide gate plate,nonoxides bonding slide gate plateand unburned slide gate plate.
Alumina -Zirconia-Carbon material
| Al-Zr-C Material | |||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) |
| 85 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
Composite type: Al-Zr-C for working line, outer Al-C material
| Al-Zr-C & Al-C Material | ||||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S | |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) | |
| Inner side (Working face) | 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| Outside | 90 | 3 | 0 | 9 | 3 | |



Other Products


About us


Welcome to visit our factory~
- Q: How are monolithic refractories applied in the hot face and cold face of furnace linings?
- Because of their superior thermal and mechanical properties, monolithic refractories are commonly utilized in furnace linings. These materials are employed in both the hot face and cold face of furnace linings, but their application methods differ for each. When it comes to the hot face of furnace linings, monolithic refractories are applied to endure extreme temperatures and harsh conditions. This area directly faces the heat source and is exposed to the highest temperatures. In this region, the refractory material is specifically engineered to possess excellent thermal conductivity and high resistance to thermal shock. To apply monolithic refractories in the hot face, the commonly used technique is gunning. Gunning involves the spraying or troweling of the refractory material onto the lining's surface. This technique enables quick and efficient application, ensuring a uniform and dense layer of refractory material. Gunning is especially suitable for areas with intricate shapes and contours. On the other hand, the primary concern for the cold face of furnace linings is insulation and protection. The cold face refers to the area that does not directly come into contact with the heat source and experiences lower temperatures. In this area, the refractory material is designed to possess low thermal conductivity and high insulation properties. The application of monolithic refractories in the cold face is typically accomplished using the technique called ramming. Ramming involves compacting the refractory material into place using a pneumatic or hydraulic ramming tool. This technique ensures the creation of a dense and solid layer of refractory material, providing excellent insulation and protection against heat loss. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are vital components of furnace linings as they provide the necessary thermal insulation and mechanical strength required in high-temperature environments. The application techniques of gunning and ramming allow for efficient and effective installation in both the hot face and cold face of furnace linings.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the overall efficiency of iron and steel production?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in enhancing the overall efficiency of iron and steel production. These refractories, which are made from a single material, provide exceptional thermal insulation, resistance to high temperatures, and excellent mechanical strength. By lining the furnaces, ladles, and other equipment used in the production process, monolithic refractories help in maintaining and regulating the required high temperatures for melting, refining, and shaping iron and steel. This insulation reduces heat loss, minimizes energy consumption, and ensures a more efficient and cost-effective production process. Additionally, the mechanical strength of monolithic refractories allows for better protection against wear and tear, resulting in increased equipment lifespan and reduced downtime for repairs and maintenance. Overall, the use of monolithic refractories significantly contributes to the efficiency, productivity, and sustainability of the iron and steel production industry.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories improve the efficiency of reheating furnaces in steel plants?
- Monolithic refractories improve the efficiency of reheating furnaces in steel plants by providing a superior lining material that offers high thermal conductivity, excellent heat resistance, and resistance to thermal shock. These refractories help to minimize heat loss and improve heat transfer, resulting in reduced energy consumption and increased furnace productivity. Additionally, the use of monolithic refractories eliminates the need for time-consuming bricklaying, allowing for quicker furnace start-up times and reduced maintenance downtime.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the reduction of heat loss in iron and steel furnaces?
- Reducing heat loss in iron and steel furnaces is a crucial role played by monolithic refractories. These refractories are specifically designed to create a seamless lining throughout the furnace, eliminating any joints or seams that could result in thermal leaks. Monolithic refractories effectively contribute to heat loss reduction in two ways. Firstly, they possess excellent thermal insulation properties that restrict the transfer of heat from the furnace to its surroundings. With their low thermal conductivity, they effectively maintain the high temperatures required for efficient iron and steel production within the furnace, while minimizing heat loss to the surrounding environment. Secondly, monolithic refractories act as a protective barrier, preventing the escape of hot gases and molten metal. This barrier ensures the integrity of the furnace lining, preventing any gaps or cracks that could allow heat to escape. By creating a tight and continuous lining, monolithic refractories significantly reduce heat loss by keeping the heat contained within the furnace. Furthermore, monolithic refractories exhibit a high resistance to thermal shock and erosion, which are common challenges faced in iron and steel furnaces. These refractories can withstand rapid temperature changes, preventing sudden cracks or failures that could result in heat loss. Additionally, they are resistant to the corrosive effects of molten metal and hot gases, guaranteeing the longevity of the lining and preserving its insulating properties over time. To summarize, monolithic refractories contribute to the reduction of heat loss in iron and steel furnaces through their exceptional thermal insulation properties, ability to provide a continuous lining, resistance to thermal shock and erosion, and protection against corrosive substances. By minimizing heat loss, these refractories optimize energy efficiency and productivity in the furnace, leading to cost savings and improved overall performance in the iron and steel industry.
- Q: What are the advantages of using castables in the iron and steel industry?
- There are several advantages of using castables in the iron and steel industry. 1. Excellent Thermal Insulation: Castables have a high thermal insulation property, which helps in maintaining the temperature of the molten metal. This prevents heat loss and ensures efficient energy usage, leading to cost savings. 2. High Refractory Strength: Castables are known for their high refractory strength, which allows them to withstand extreme temperatures and harsh operating conditions. This ensures the longevity and durability of the refractory lining, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements. 3. Versatility: Castables can be easily molded into various shapes and sizes, making them highly versatile for different applications in the iron and steel industry. This allows for customization and flexibility in designing the refractory lining to suit specific requirements. 4. Easy Installation: Castables can be installed quickly and easily, reducing downtime during installation or maintenance. Their ability to be applied as a monolithic lining eliminates the need for individual bricks or tiles, saving time and effort. 5. Resistance to Chemical Attack: Castables are resistant to chemical attacks from molten metal, slag, and other corrosive substances commonly encountered in the iron and steel industry. This ensures the integrity of the refractory lining and prevents contamination of the metal being processed. 6. Reduced Material Costs: Castables typically require fewer raw materials compared to traditional refractory bricks or tiles. This leads to cost savings in terms of material procurement, transportation, and storage, making castables a cost-effective solution. 7. Enhanced Production Efficiency: The use of castables in the iron and steel industry improves production efficiency by providing a smooth and uniform lining. This facilitates better heat transfer, improved metal flow, and reduced downtime, ultimately increasing overall productivity. In conclusion, the advantages of using castables in the iron and steel industry include excellent thermal insulation, high refractory strength, versatility, easy installation, resistance to chemical attack, reduced material costs, and enhanced production efficiency. These advantages make castables a preferred choice for lining furnaces, ladles, tundishes, and other equipment in the iron and steel manufacturing process.
- Q: What are the environmental considerations associated with monolithic refractories?
- Monolithic refractories, utilized in various high-temperature applications, pose several environmental concerns that must be taken into account. Firstly, the production of monolithic refractories necessitates the utilization of raw materials such as clay, silica, and alumina, which are frequently extracted from the earth, resulting in habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution. Furthermore, the manufacturing process of monolithic refractories commonly involves considerable energy consumption and the emission of greenhouse gases. The firing of refractory materials necessitates high temperatures, often achieved through the combustion of fossil fuels, contributing to carbon dioxide emissions and climate change. These emissions have broad environmental consequences, including air pollution, acid rain, and ozone layer depletion. Additionally, the disposal of monolithic refractories at the end of their useful life can present environmental challenges. Although monolithic refractories are highly durable and long-lasting, there may come a time when replacement or repair is necessary. The disposal of refractory waste can be problematic as it often contains hazardous substances such as chromium, lead, and asbestos. Inadequate disposal methods can lead to contamination of soil and water, posing risks to both human health and the environment. To address these environmental concerns, efforts are underway to develop more sustainable refractory materials and manufacturing processes. For instance, alternative raw materials like recycled refractory materials or industrial by-products can be employed to decrease the environmental impact of mining. Moreover, the adoption of more energy-efficient manufacturing techniques, such as utilizing renewable energy sources or implementing advanced firing technologies, can help minimize greenhouse gas emissions. In conclusion, the environmental considerations associated with monolithic refractories encompass habitat destruction, energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and waste disposal. Prioritizing sustainability and implementing measures to mitigate these environmental impacts, such as using alternative raw materials, enhancing manufacturing processes, and endorsing responsible waste management practices, are imperative for the refractory industry.
- Q: What are the considerations for selecting monolithic refractories for ladles and tundishes?
- When it comes to choosing monolithic refractories for ladles and tundishes, there are a number of important factors to bear in mind. Firstly, it is crucial to select monolithic refractories that can withstand and maintain their strength and integrity at the extremely high temperatures experienced during metal casting processes. In addition, monolithic refractories with good thermal shock resistance are essential, as ladles and tundishes are subjected to rapid temperature changes during pouring and cooling. Such refractories can prevent cracking and spalling, ensuring the longevity and performance of these components. Erosion and corrosion resistance is another key consideration. Refractory linings can be eroded and chemically attacked by molten metal, slag, and other corrosive substances. Opting for monolithic refractories with excellent erosion and corrosion resistance can extend the service life of ladles and tundishes, reducing the need for maintenance and minimizing downtime. Mechanical strength is also important, as ladles and tundishes are frequently handled, transported, and subjected to mechanical stresses. Monolithic refractories with adequate mechanical strength can withstand these forces without cracking or breaking, thereby maintaining the structural integrity of these components. The method of applying monolithic refractories is another factor to think about. Depending on the size and shape of the ladles and tundishes, as well as the available equipment and expertise, different application methods such as gunning, casting, ramming, or spraying may be used. It is important to ensure that the selected monolithic refractories are compatible with the chosen application method. The thermal conductivity of monolithic refractories can impact heat transfer in ladles and tundishes. Opting for refractories with low thermal conductivity can help minimize heat loss and improve energy efficiency. While performance and durability are crucial, it is also important to consider the cost-effectiveness of the chosen monolithic refractories. This includes factors such as the initial cost of the refractories, installation and maintenance costs, and the expected service life. Striking a balance between performance and cost can help optimize the overall investment in ladles and tundishes. Overall, the selection of monolithic refractories for ladles and tundishes involves a combination of factors, including temperature resistance, thermal shock resistance, erosion and corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, application method compatibility, thermal conductivity, and cost-effectiveness. By carefully evaluating these factors, it is possible to choose the most suitable monolithic refractories that meet the specific requirements of ladles and tundishes in metal casting processes.
- Q: What are the factors affecting the thermal expansion of monolithic refractories?
- There are several factors that influence the thermal expansion of monolithic refractories. 1. Chemical Composition: The chemical composition of the refractory material plays a significant role in its thermal expansion. Different chemical elements and compounds have different coefficients of thermal expansion. For example, materials containing high levels of silica tend to have lower coefficients of thermal expansion compared to materials with higher concentrations of alumina. 2. Particle Size: The particle size distribution of the refractory material can affect its thermal expansion. Smaller particle sizes tend to result in higher thermal expansion due to increased surface area and greater contact between particles. 3. Temperature: The temperature at which the monolithic refractory is exposed can greatly impact its thermal expansion. As the temperature increases, the kinetic energy of the particles increases, causing them to move more vigorously and expand. Different refractory materials have different temperature ranges at which they exhibit significant expansion. 4. Thermal History: The thermal history of the refractory material, including its heating and cooling cycles, can influence its thermal expansion behavior. Repeated heating and cooling cycles can induce microstructural changes in the material, affecting its thermal expansion properties. 5. Porosity: The porosity of the monolithic refractory can affect its thermal expansion. Higher porosity generally leads to higher thermal expansion due to the presence of voids and gaps within the material. 6. Binder Content: Monolithic refractories often contain binders that hold the particles together. The type and amount of binder used can impact the thermal expansion of the refractory. Different binders have different coefficients of thermal expansion, which can influence the overall expansion behavior of the material. 7. Thermal Shock: Rapid temperature changes, such as during quenching or exposure to alternating heating and cooling, can cause thermal shock in the refractory material. This can lead to cracks, spalling, and changes in the thermal expansion behavior. Understanding these factors is crucial in selecting the appropriate monolithic refractory material for specific applications, as the thermal expansion characteristics can directly impact the performance and longevity of the refractory in high-temperature environments.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to energy efficiency in iron and steel manufacturing?
- The use of monolithic refractories is crucial for improving energy efficiency in iron and steel manufacturing processes. Made from a single material, typically a combination of high-quality aggregates, binders, and additives, these refractories are easily installed and repaired. One way in which monolithic refractories enhance energy efficiency is by minimizing heat loss. Their excellent insulation properties help maintain high temperatures in the furnace or kiln. This reduces the energy needed to maintain the desired temperature, resulting in lower energy consumption and cost savings. Additionally, monolithic refractories are designed with high thermal conductivity, allowing for efficient heat transfer from hot gases or flames to the iron and steel being processed. This leads to faster heating rates and shorter processing times, resulting in energy savings and increased production capacity. Another advantage of monolithic refractories is their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and harsh conditions. They are resistant to thermal shock, corrosion, and erosion, which extends their lifespan and reduces the need for frequent repairs or replacements. This minimizes downtime, enabling continuous operation and improved energy efficiency. Moreover, monolithic refractories offer design flexibility, allowing for the optimization of furnace and kiln geometries. By customizing the shape and dimensions of the refractory linings, heat distribution can be improved, ensuring more uniform heating and reducing energy wastage. This flexibility also enables the implementation of advanced combustion technologies, further enhancing energy efficiency. In conclusion, monolithic refractories contribute to energy efficiency in iron and steel manufacturing through the reduction of heat loss, enhancement of heat transfer, ability to withstand extreme conditions, optimization of furnace geometries, and facilitation of advanced combustion technologies. By utilizing these refractories, the industry can achieve significant energy savings, cost reductions, and environmental benefits.
- Q: What are the advantages of using monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry?
- There are several advantages of using monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry. Firstly, monolithic refractories offer excellent thermal insulation properties. This means that they are able to withstand and retain high temperatures, which is crucial in the iron and steel manufacturing process. The ability to withstand extreme heat ensures that the refractories maintain their structural integrity, reducing the risk of failure and maintaining operational efficiency. Secondly, monolithic refractories have superior corrosion resistance. In the iron and steel industry, where materials are exposed to harsh chemicals and corrosive agents, the use of monolithic refractories helps to protect the equipment and structures from degradation. This not only extends the lifespan of the refractories but also reduces maintenance costs and downtime. Another advantage of monolithic refractories is their versatility. Unlike traditional refractory bricks, which are rigid and require skilled labor for installation, monolithic refractories can be cast or sprayed into various shapes and sizes. This flexibility allows for easier installation and customization, resulting in better lining design and improved performance. Additionally, monolithic refractories can be easily repaired or patched in case of damage, minimizing production disruptions. Furthermore, monolithic refractories have excellent mechanical strength and abrasion resistance. In the iron and steel industry, where materials are constantly being moved and processed, the refractories must be able to withstand mechanical stresses and abrasion. Monolithic refractories provide the necessary strength and resistance, ensuring that they can withstand the rigors of the industry without compromising performance. Lastly, the use of monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry can lead to cost savings. Due to their versatility and ease of installation, monolithic refractories require less labor and time for installation, resulting in reduced installation costs. Additionally, their longer lifespan and resistance to corrosion and thermal shock minimize the need for frequent replacements, reducing maintenance and downtime costs. In conclusion, the advantages of using monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry include excellent thermal insulation, corrosion resistance, versatility, mechanical strength, and cost savings. These benefits make monolithic refractories an ideal choice for lining furnaces, ladles, and other equipment used in the production of iron and steel.
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories High Performance & Temperature Ladle Sliding Gate for Iron and Steel Industry
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords