Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry:Alumina Spinel Castable for Ladle and Tundish
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or L/C
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
General Information of Alumina Spinel Castable for Ladle and Tundish
FIREF alumina spinel castable for ladle and tundish made as per international standards, is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, long operating life and high refractoriness. Further, it can be provided in different specifications as required.
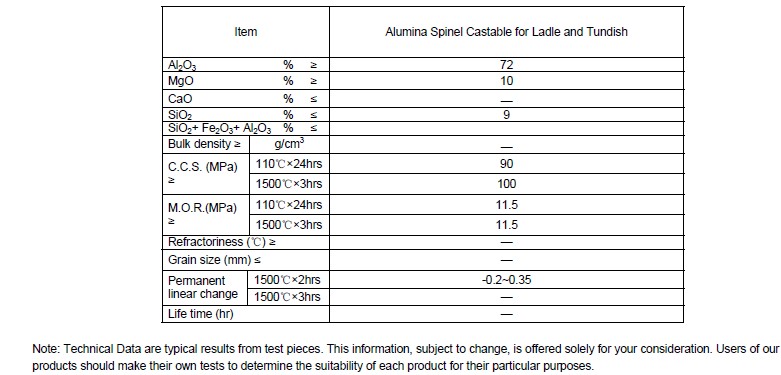
Technical data of Alumina Spinel Castable for Ladle and Tundish
Production line and packing of Alumina Spinel Castable for Ladle and Tundish


Feature of Alumina Spinel Castable for Ladle and Tundish
Long operating life
Excellent corrosion resistance
High refractoriness
Application of Alumina Spinel Castable for Ladle and Tundish
FIREF alumina spinel castable for ladle and tundish can be used widely in ladle and tundish.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories protect lining in ladles and tundishes?
- Monolithic refractories protect lining in ladles and tundishes by forming a strong and durable barrier against the harsh conditions of high temperatures, thermal shock, and chemical corrosion. They are designed to withstand the extreme heat and mechanical stresses that occur during metal pouring and handling, ensuring the integrity and longevity of the lining. Additionally, monolithic refractories provide excellent insulation properties, reducing heat loss and conserving energy in the ladles and tundishes.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the overall productivity of iron and steel plants?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in enhancing the overall productivity of iron and steel plants. These refractories are characterized by their ability to be shaped and installed without the need for joints or mortar, making them highly versatile and efficient. One major contribution of monolithic refractories to the productivity of iron and steel plants is their ability to withstand high temperatures. These refractories are designed to have excellent thermal shock resistance, meaning they can withstand rapid changes in temperature without cracking or breaking. This allows them to be used in various high-temperature applications such as blast furnaces, converters, and ladles. By using monolithic refractories in these critical areas, iron and steel plants can operate at higher temperatures, leading to increased production rates. The refractories provide effective insulation, reducing heat losses and improving energy efficiency. This results in cost savings and higher output for the plant. Furthermore, monolithic refractories are known for their excellent resistance to chemical attacks from molten metals and slags. They can withstand the corrosive effects of molten iron, steel, and other alloys, protecting the underlying structures and extending their lifespan. This reduces downtime for maintenance and repairs, allowing for continuous operation and higher productivity. Moreover, monolithic refractories offer easy installation and maintenance, which further contributes to productivity. Unlike traditional refractories that require time-consuming bricklaying and jointing, monolithic refractories can be sprayed, troweled, or pumped into place, saving both time and labor costs. Additionally, their ability to be easily repaired or replaced without major disruptions to the production processes ensures minimal downtime, maximizing overall plant productivity. In summary, monolithic refractories enhance the productivity of iron and steel plants by withstanding high temperatures, providing insulation and energy efficiency, resisting chemical attacks, and offering easy installation and maintenance. Their ability to perform under extreme conditions and their cost-effective nature make them an essential component in the iron and steel industry, contributing to increased output and profitability.
- Q: How are monolithic refractories installed and repaired in iron and steel plants?
- Monolithic refractories in iron and steel plants are typically installed through a process called gunning, where a specialized gunning machine is used to spray the refractory material onto the desired surface. The refractory material is mixed with water or a bonding agent to form a dense and durable lining. In terms of repairs, damaged or worn-out monolithic refractories are typically removed by mechanical means, such as jackhammers or pneumatic tools. The damaged area is then cleaned and prepared before new refractory material is applied using the gunning method. In some cases, patching materials may be used to repair smaller areas of damage. Overall, the installation and repair of monolithic refractories in iron and steel plants require skilled technicians and specialized equipment to ensure the optimum performance and longevity of the refractory lining.
- Q: What are the specific requirements of monolithic refractories for steel ladle purging applications?
- Monolithic refractories used for steel ladle purging applications need to possess specific characteristics. These include high resistance to thermal shock and spalling, excellent erosion and corrosion resistance, low porosity, and high strength at high temperatures. Additionally, they should have good thermal conductivity and be capable of withstanding aggressive steel compositions and temperatures. Overall, the specific requirements for monolithic refractories in steel ladle purging applications are aimed at ensuring durability, longevity, and optimal performance in the harsh conditions of the steelmaking process.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the safety of iron and steel operations?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in ensuring the safety of iron and steel operations. They provide excellent thermal insulation and resistance to high temperatures, preventing heat transfer to the environment and minimizing the risk of accidents or fires. Additionally, these refractories possess high mechanical strength and chemical resistance, protecting the structural integrity of furnaces and other equipment under extreme conditions. By effectively containing heat and maintaining the stability of the production process, monolithic refractories enhance the overall safety and reliability of iron and steel operations.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the overall reliability of iron and steel processes?
- Monolithic refractories play a significant role in enhancing the overall reliability of iron and steel processes. These refractories are specifically designed to withstand extreme temperatures and harsh conditions found in iron and steel manufacturing environments. One key contribution of monolithic refractories is their ability to provide superior insulation. They have low thermal conductivity, which significantly reduces heat loss from the furnace or kiln. This insulation property allows for efficient energy usage and helps maintain stable operating conditions, leading to consistent and reliable production. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer excellent resistance to chemical attacks from molten metals, slag, and other corrosive substances. They can withstand the high alkalinity and high temperature of molten iron and steel, preventing any damage to the refractory lining. This resistance ensures the longevity of the refractory material, minimizing the need for frequent maintenance and replacement, thus contributing to the overall reliability of the iron and steel processes. Moreover, monolithic refractories exhibit good mechanical strength and stability, even at elevated temperatures. This strength allows them to withstand the mechanical stresses and strains exerted during the iron and steel manufacturing processes, such as thermal cycling, mechanical impact, and abrasion. By maintaining their structural integrity, monolithic refractories prevent the formation of cracks or spalling, which could lead to downtime or even catastrophic failure. This reliability ensures uninterrupted operations and reduces the risk of costly shutdowns. Furthermore, monolithic refractories offer flexibility in terms of installation and repair. They can be easily shaped and applied to various furnace shapes and sizes, allowing for efficient lining construction. Additionally, monolithic refractories can be repaired or patched quickly, minimizing downtime and maintaining the operational reliability of the iron and steel processes. In conclusion, monolithic refractories contribute to the overall reliability of iron and steel processes by providing superior insulation, resistance to chemical attacks, mechanical strength, and flexibility in installation and repair. By ensuring consistent performance, durability, and reduced maintenance requirements, monolithic refractories play a crucial role in optimizing the efficiency and reliability of iron and steel manufacturing operations.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories perform in electric arc furnace roof applications?
- Monolithic refractories are highly effective in electric arc furnace (EAF) roof applications due to their unique properties and characteristics. These refractories, which are composed of a single, solid material, offer several advantages in this specific application. Firstly, monolithic refractories provide excellent thermal insulation, which is crucial in EAF roof applications. The intense heat generated in the furnace can cause structural damage to traditional brick refractories, but monolithic refractories have a higher resistance to thermal shock, reducing the risk of cracking and spalling. This allows them to maintain their integrity and insulation properties even in extreme temperature conditions. Moreover, monolithic refractories have high strength and abrasion resistance, ensuring their durability and longevity in EAF roof applications. The roof of an electric arc furnace is exposed to harsh conditions, including the impact of scrap materials and the erosive effect of molten metal and slag. Monolithic refractories are designed to withstand these challenges, offering superior resistance to mechanical wear and erosion. Another advantage of monolithic refractories is their ease of installation. Unlike traditional brick refractories, which require time-consuming and complex installation processes, monolithic refractories can be applied quickly and efficiently. They can be cast, gunned, or sprayed onto the roof surface, conforming to any shape or contour, thus reducing downtime during installation or repair. Furthermore, monolithic refractories provide increased energy efficiency in EAF roof applications. Their superior insulation properties minimize heat loss, resulting in reduced energy consumption and cost savings. This is particularly important for electric arc furnaces, as they rely on high temperatures to melt and process metals, and any heat loss can significantly impact the efficiency and productivity of the furnace. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are highly suitable for electric arc furnace roof applications due to their exceptional thermal insulation, strength, abrasion resistance, ease of installation, and energy efficiency. These refractories offer significant advantages over traditional brick refractories, ensuring optimal performance and prolonged service life in the demanding environment of an electric arc furnace.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories help in enhancing the durability of iron and steel equipment?
- Monolithic refractories help enhance the durability of iron and steel equipment by providing a protective lining that withstands high temperatures, chemical corrosion, and mechanical stress. This lining acts as a barrier, preventing the contact between the equipment and harsh operating conditions, thus minimizing wear and extending the lifespan of the equipment.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the overall efficiency of ladle cleaning operations?
- Enhancing the overall efficiency of ladle cleaning operations is a crucial role played by monolithic refractories. Composed of a single, homogeneous structure, these refractory materials offer several key advantages that contribute to improved efficiency. To begin with, monolithic refractories possess exceptional thermal insulation properties. This means they can withstand high temperatures without cracking or deteriorating, thereby allowing for more efficient and effective ladle cleaning operations. By consistently maintaining a specific temperature, these refractories minimize heat loss and ensure uninterrupted and timely completion of the cleaning process. Furthermore, monolithic refractories exhibit high resistance to chemical attacks. In steelmaking processes, ladles often come into contact with aggressive molten metals and slag that can erode and corrode the refractory lining. However, monolithic refractories are designed specifically to endure these harsh conditions, providing a longer service life and reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements. This not only saves time but also reduces the overall cost of ladle maintenance. In addition, monolithic refractories possess excellent flowability and workability. They can be easily shaped and installed in the ladle lining, enabling quick and precise application. This ease of installation results in shorter downtime during ladle cleaning operations, as the refractory lining can be swiftly repaired or replaced. Moreover, the flowability of monolithic refractories ensures better coverage and adherence to the ladle's surface, leaving no gaps or weak points. This enhances the overall effectiveness of the cleaning process and prevents potential contamination or reactivity issues. In conclusion, monolithic refractories significantly contribute to the overall efficiency of ladle cleaning operations by providing exceptional thermal insulation, high resistance to chemical attacks, and easy workability. These properties lead to reduced downtime, increased durability, and cost savings, making monolithic refractories a vital component in optimizing ladle cleaning processes.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories improve energy efficiency in the iron and steel industry?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in improving energy efficiency in the iron and steel industry through various mechanisms. Firstly, these refractories have excellent insulation properties, which help in reducing heat loss during the production process. By minimizing heat loss, monolithic refractories ensure that more heat is retained within the furnace, resulting in higher energy efficiency. Moreover, monolithic refractories have low thermal conductivity, allowing for better heat transfer within the furnace. This means that the heat generated during the production process can be efficiently distributed throughout the furnace, enabling optimal temperature control and reducing energy wastage. In addition, monolithic refractories have high resistance to thermal shock and corrosion, which are common challenges in the iron and steel industry. By withstanding extreme temperatures and chemical reactions, these refractories prevent premature wear and tear, thus reducing the need for frequent repairs and replacements. This not only saves energy but also minimizes downtime, leading to increased productivity and energy efficiency. Furthermore, the use of monolithic refractories allows for better furnace design and optimization. Their flexibility enables the creation of custom shapes and linings that suit specific furnace requirements, resulting in improved heat transfer and combustion efficiency. This customized approach promotes energy savings by maximizing the utilization of fuel and reducing emissions. Lastly, monolithic refractories have a longer lifespan compared to traditional brick refractories. This prolonged durability reduces the frequency of refractory replacements, resulting in lower energy consumption associated with the manufacturing and installation of new refractories. Overall, monolithic refractories contribute significantly to energy efficiency in the iron and steel industry by reducing heat loss, improving heat transfer, withstanding thermal shock and corrosion, enabling better furnace design, and increasing refractory lifespan. Their use not only saves energy but also enhances productivity and sustainability within the industry.
1. Manufacturer Overview
| Location | Henan, China |
| Year Established | 2007 |
| Annual Output Value | Above US$ 60 Million |
| Main Markets | Mid East; Eastern Europe; North America |
| Company Certifications | ISO 9001:2008 |
2. Manufacturer Certificates
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period |
3. Manufacturer Capability
| a) Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | Tianjin |
| Export Percentage | 31% - 50% |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | 21-50 People |
| Language Spoken: | English; Chinese |
| b) Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | Above 36,000 square meters |
| No. of Production Lines | Above 5 |
| Contract Manufacturing | OEM Service Offered |
| Product Price Range | Average |
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry:Alumina Spinel Castable for Ladle and Tundish
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or L/C
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords