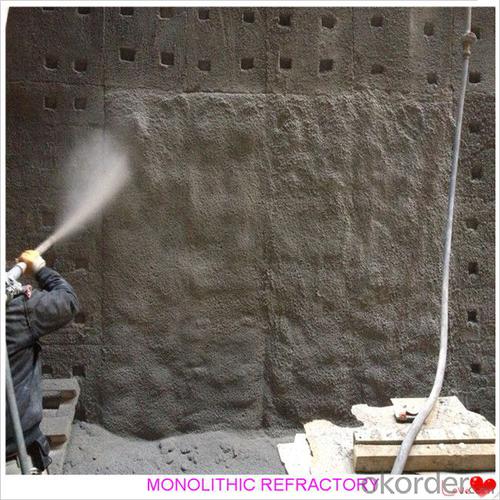
Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry:Cheap Castable Solutions for Fireplace and Industrial Furnace
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 3000000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Cheap Castable For Fireplace and Industrial Furnace in Iron and Steel
Product Description:
Cheap castable is manufactured according to international standards. The product is famous for its excellent abrasion resistance and low thermal conductivity. Further, these can be provided in different specifications as required by the clients. The Cheap castables are used high purity raw materials and additives as the main material, and made of under superfine powder adding technology.
Product Advantages:
The material has excellent structural stability and air tightness, and has high physical and chemical properties, also has a fine working ability.They should be used with the same material products.
Product Applications:
For feature of Cheap castable, they have excellent abrasion resistance, thermal shock resistance, high-temperature resistance, anti-corrode and have high intensity.
Designed for refractory lining of blast furnace iron and slag runners, skimmers and soon
They can be used in troughs of small and mid size BFs and in all positions of the troughs where fast tapping is required.
Product Specifications:

FAQ:
1. How you can control your quality?
For each production processing, we have complete QC system for the chemical composition
and Physical properties. After production, all the goods will be tested, and the quality certificate
will be shipped along with goods.
2. What's your delivery time?
It usually needs about 20days- 45 days after receiving the deposit.
3. Do you provide free samples?
Yes, we can provide a free sample for testing, If we have sample in stock,
The quantity based on the material type, The buyer should bear all the shipping costs.
4. What's your payment terms?
We can accept 30% deposit, 70% balance before shipment for ordrs over $ 2000.
5. Can we visit your Company?
Yes, certainly. You are very welcome to China and we will be honored to have a customer and friend.
Product Picture:




- Q: What are the challenges faced in the application of monolithic refractories?
- The application of monolithic refractories presents several challenges. Firstly, a major hurdle is the correct installation of these refractories. Unlike traditional brick refractories that can be easily stacked, specialized skills and techniques are required for the proper application of monolithic refractories. The consistency and workability of the refractory material must be carefully controlled, and specialized equipment such as gunning machines or vibrating tools are often necessary for the installation process. Another challenge lies in selecting the appropriate monolithic refractory material for a specific application. There are various types of monolithic refractories available, each with its own unique properties and suitability for different environments. Choosing the wrong type of refractory material can lead to premature failure and expensive repairs. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the operating conditions, including temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress, in order to select the most suitable monolithic refractory material. Additionally, monolithic refractories are prone to thermal shock and erosion due to their composition and method of application. They are typically made from fine powders that are mixed with water or other binding agents to form a paste. This paste is then applied and dried to create a solid refractory lining. However, during the heating and cooling cycles, monolithic refractories can experience thermal expansion and contraction, resulting in cracks and spalling. Furthermore, chemical reactions occurring in certain industrial processes can cause chemical attack and erosion of the refractory lining, reducing its lifespan. Furthermore, the maintenance and repair of monolithic refractories can also pose a challenge. Unlike brick refractories that can be easily replaced, repairing monolithic refractories often requires skilled personnel and specialized techniques. The damaged area must be removed, and a new layer of refractory material must be applied, ensuring proper bonding and compatibility with the existing lining. This process can be time-consuming and costly, especially in high-temperature applications where extended downtime can result in significant production losses. In conclusion, the application of monolithic refractories presents challenges in terms of proper installation techniques, material selection, susceptibility to thermal shock and erosion, and complex maintenance and repair procedures. Overcoming these challenges requires expertise, careful planning, and a comprehensive understanding of the specific operating conditions and requirements for each application.
- Q: How are monolithic refractories recycled or disposed of at the end of their lifespan?
- Monolithic refractories, widely utilized in high-temperature industrial applications, offer various means of recycling or disposal once their lifespan concludes. The preferred approach depends on the specific monolithic refractory type and its composition. Reclamation stands as a common method for recycling monolithic refractories. This process entails collecting used refractory materials and subjecting them to processing to eliminate any impurities or contaminants. The resultant reclaimed refractory material can then be crushed, ground, or milled into a fine powder suitable for utilization as a raw material in manufacturing new refractories. Thermal treatment represents an alternative means of recycling monolithic refractories. This method involves exposing the used refractory material to high temperatures within a controlled environment, such as a kiln or furnace. The heat effectively breaks down the refractory material, eliminating any binders or impurities. The resulting material can then be reused as a raw material or integrated into other applications, such as construction aggregates. When recycling is not feasible, specialized facilities designed for handling and treating hazardous waste offer a disposal avenue for monolithic refractories. These facilities ensure the proper containment and treatment of the refractory material, minimizing any potential environmental impact. This disposal method is typically reserved for refractories containing hazardous substances or those that cannot be recycled due to their composition. It is important to emphasize that the appropriate disposal or recycling method for monolithic refractories must adhere to local regulations and guidelines. These regulations aim to ensure the safe handling, treatment, and disposal of these materials, taking into account their potential environmental and health effects. Therefore, industries and businesses must collaborate closely with waste management professionals and adhere to the appropriate procedures to responsibly manage monolithic refractories at the end of their lifespan.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories impact the overall productivity of iron and steel operations?
- The overall productivity of iron and steel operations is greatly enhanced by monolithic refractories. These refractories are specifically designed to withstand extreme temperatures, chemical reactions, and mechanical stress that occur during production. One important way that monolithic refractories impact productivity is by reducing downtime and increasing operational efficiency. These refractories have high thermal conductivity and are resistant to thermal shock, allowing them to maintain stable temperatures within the furnace. This prevents sudden temperature fluctuations that can lead to equipment failure and production delays. As a result, the production process can continue uninterrupted, leading to increased productivity. Furthermore, monolithic refractories offer superior corrosion resistance, preventing the erosion and degradation of furnace linings. This resistance to chemical attacks from molten metals and slag helps prolong the lifespan of the refractory lining, reducing the need for repairs and replacements. This leads to less downtime and higher productivity for iron and steel operations. Additionally, monolithic refractories enable faster installation and repair processes compared to traditional brick refractories. They have a fluid-like consistency that makes application and shaping easy, resulting in shorter installation and curing times. This quick turnaround time minimizes production interruptions during repairs or maintenance, further increasing overall productivity. Moreover, the use of monolithic refractories can optimize energy consumption in iron and steel operations. Their excellent insulation properties help retain heat within the furnace, reducing heat loss and energy waste. This improves energy efficiency and leads to cost savings, ultimately contributing to increased productivity and profitability. In conclusion, monolithic refractories have a significant impact on the productivity of iron and steel operations. Their ability to withstand extreme conditions, reduce downtime, resist corrosion, facilitate quick repairs, and optimize energy consumption all contribute to improved efficiency and productivity in the industry.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the reduction of heat loss in iron and steel furnaces?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in reducing heat loss in iron and steel furnaces. These refractories are designed to provide a continuous lining throughout the furnace, eliminating joints and seams that can result in thermal leaks. One way monolithic refractories contribute to heat loss reduction is through their excellent thermal insulation properties. They have low thermal conductivity, meaning they are effective at restricting the transfer of heat from the furnace to its surroundings. This insulation helps to maintain the high temperatures required for efficient iron and steel production within the furnace, while minimizing heat loss to the surrounding environment. Another way monolithic refractories contribute to heat loss reduction is by providing a protective barrier that prevents the escape of hot gases and molten metal. This barrier helps to maintain the integrity of the furnace lining, preventing any gaps or cracks that could allow heat to escape. By ensuring a tight and continuous lining, monolithic refractories reduce heat loss by keeping the heat contained within the furnace. Furthermore, monolithic refractories have high resistance to thermal shock and erosion, which are common challenges in iron and steel furnaces. These refractories can withstand rapid temperature changes, preventing any sudden cracks or failures that could lead to heat loss. Additionally, they are resistant to the corrosive effects of molten metal and hot gases, ensuring the longevity of the lining and maintaining its insulating properties over time. In summary, monolithic refractories contribute to the reduction of heat loss in iron and steel furnaces through their excellent thermal insulation properties, ability to provide a continuous lining, resistance to thermal shock and erosion, and protection against corrosive substances. By minimizing heat loss, these refractories optimize the energy efficiency and productivity of the furnace, ultimately leading to cost savings and improved overall performance in the iron and steel industry.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories resist chemical corrosion in iron and steel applications?
- Monolithic refractories are highly resistant to chemical corrosion in iron and steel applications due to their unique characteristics and composition. These refractories are engineered with a combination of different materials such as aggregates, binders, and additives, which provide them with exceptional resistance to chemical attack. One key factor that contributes to their resistance is the use of high-quality raw materials. Monolithic refractories are typically made from high-alumina or alumina-silica aggregates, which have excellent resistance to chemical reactions. These aggregates are carefully selected to ensure they can withstand the harsh conditions encountered in iron and steel applications, including exposure to molten metal, slag, and various chemical compounds. Moreover, the binders used in monolithic refractories play a crucial role in their resistance to chemical corrosion. Common binders include clay, calcium aluminate cement, or colloidal silica. These binders help to hold the refractory materials together and provide additional protection against chemical attack. They form a dense and impermeable structure, which prevents corrosive substances from penetrating the refractory lining. Furthermore, monolithic refractories often incorporate additives that enhance their chemical resistance. These additives can include antioxidants, anti-spalling agents, and various other compounds that further protect the refractory lining from chemical attack. These additives help to neutralize corrosive elements, inhibit the formation of harmful compounds, and reduce the overall corrosion rate. Additionally, the unique installation method of monolithic refractories also contributes to their resistance to chemical corrosion. Unlike traditional brick refractories, monolithic refractories are installed as a single, continuous lining. This eliminates the need for joints or gaps that could potentially serve as weak points for chemical penetration. The monolithic nature of these refractories ensures a tight and seamless lining, reducing the vulnerability to chemical attack. Overall, the combination of high-quality raw materials, effective binders, and beneficial additives, along with the monolithic installation technique, grants monolithic refractories exceptional resistance to chemical corrosion in iron and steel applications. This resistance allows them to withstand the harsh conditions encountered in these industries, ensuring the longevity and efficiency of the refractory lining.
- Q: What are the key properties of monolithic refractories?
- The key properties of monolithic refractories include high strength, thermal shock resistance, erosion and abrasion resistance, good thermal conductivity, and excellent chemical resistance. These properties make monolithic refractories suitable for applications where high temperatures, harsh environments, and mechanical stresses are present, such as in furnaces, kilns, and reactors.
- Q: What are the common failure mechanisms of monolithic refractories?
- Monolithic refractories commonly fail due to thermal spalling, chemical attack, erosion, and mechanical stress. Thermal spalling arises from abrupt temperature changes, causing the refractory material to crack and break. This can result from thermal shock or cyclic heating and cooling. Chemical attack occurs when aggressive chemicals or gases interact with the refractory material, degrading its lining. This can lead to the formation of new compounds or the dissolution of the refractory material, weakening its structure and reducing its resistance to further chemical attack. Erosion is another prevalent failure mechanism, particularly in scenarios where the refractory lining is exposed to high-speed gas or liquid flows. The abrasive action of the medium can gradually erode the refractory material, causing thinning and eventual failure of the lining. Mechanical stress, such as thermal expansion or contraction mismatch, can also lead to failure in monolithic refractories. Rapid temperature changes can result in differential expansion or contraction, leading to the development of cracks and fractures in the lining. To mitigate these failure mechanisms, several techniques can be utilized. These include careful material selection based on operating conditions, meticulous design to minimize thermal gradients, application of protective coatings, and regular inspection and maintenance to promptly detect and address signs of failure or degradation.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the safety of iron and steel operations?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in enhancing the safety of iron and steel operations. These refractories are made of a single, continuous material, which offers several benefits that contribute to the overall safety of the operations. Firstly, monolithic refractories provide excellent thermal insulation. They are designed to withstand high temperatures, preventing heat transfer to the surrounding environment. This insulation property helps in maintaining a safe working temperature for the operators, reducing the risk of burns or other heat-related injuries. Furthermore, monolithic refractories have high resistance to chemical attack. In iron and steel operations, various chemicals and molten metals are used, which can be corrosive and hazardous. The use of monolithic refractories as lining materials creates a protective barrier that resists the corrosive effects of these substances, preventing leaks and potential accidents. Another safety benefit is the ability of monolithic refractories to withstand mechanical stress. Steelmaking processes involve heavy machinery and equipment, which can exert significant pressure on the refractory linings. Monolithic refractories have excellent mechanical strength, which enables them to withstand these stresses and maintain their integrity. This prevents the risk of sudden failure or collapse, reducing the possibility of accidents and injuries due to falling debris. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer easy installation and repair. They can be applied as a castable or gunning material, allowing for quick and efficient lining of furnaces, ladles, and other equipment. This ease of installation reduces downtime during maintenance or repairs, minimizing the risk of accidents caused by delayed or prolonged shutdowns. In summary, monolithic refractories contribute to the safety of iron and steel operations through their excellent thermal insulation, resistance to chemical attack, ability to withstand mechanical stress, and ease of installation and repair. By providing a protective barrier, these refractories help in preventing injuries, maintaining a safe working environment, and minimizing the potential hazards associated with high temperatures, corrosive substances, and mechanical failures.
- Q: What are some common maintenance practices for monolithic refractories in iron and steel furnaces?
- There are several common maintenance practices for monolithic refractories in iron and steel furnaces: 1. It is essential to conduct regular inspections. Trained professionals should inspect the refractories to identify any potential issues, such as wear, erosion, or damage. 2. Promptly repairing and patching damaged or eroded areas is crucial to maintain the integrity of the refractories. Refractory mortars or castable refractories can be used for this purpose. 3. Regularly cleaning the refractory lining is important to remove any build-up of impurities that can affect performance. Mechanical cleaning with brushes or scrapers, as well as chemical cleaning with acids, can be employed. 4. Controlled thermal cycling is often performed to condition and strengthen the refractories. Gradually increasing and decreasing the furnace temperature improves their resistance to thermal shock. 5. Applying protective coatings or sealants to the refractory lining enhances its resistance to chemical attack, erosion, and thermal cycling. These act as barriers against molten metals or slags. 6. Monitoring and controlling operating conditions inside the furnace, such as temperature, pressure, and atmosphere, is crucial. This helps prevent sudden changes that may negatively affect the refractories. 7. Regular training and education for furnace operators and maintenance personnel are crucial. This ensures they understand the importance of proper refractory maintenance, reducing the risk of premature failure. Implementing these maintenance practices significantly prolongs the lifespan of monolithic refractories in iron and steel furnaces. It maximizes their performance, leading to improved efficiency and cost-effectiveness in the production process.
- Q: What are the key properties of patching mixes used for monolithic refractory repairs?
- The key properties of patching mixes used for monolithic refractory repairs include high thermal conductivity, excellent adhesion, good workability, high strength, resistance to thermal shock, and suitable setting and drying times. These properties ensure effective repairs and long-lasting performance in high-temperature applications.
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry:Cheap Castable Solutions for Fireplace and Industrial Furnace
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 3000000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords