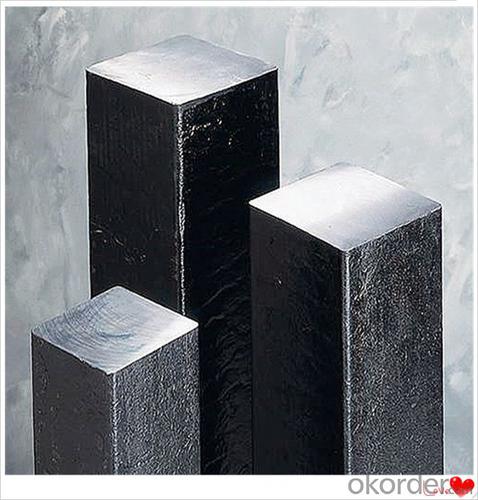
Clamps Billet Aluminum Q235,Q255,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 20 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Clamps Billet Aluminum Q235,Q255,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi
Specification
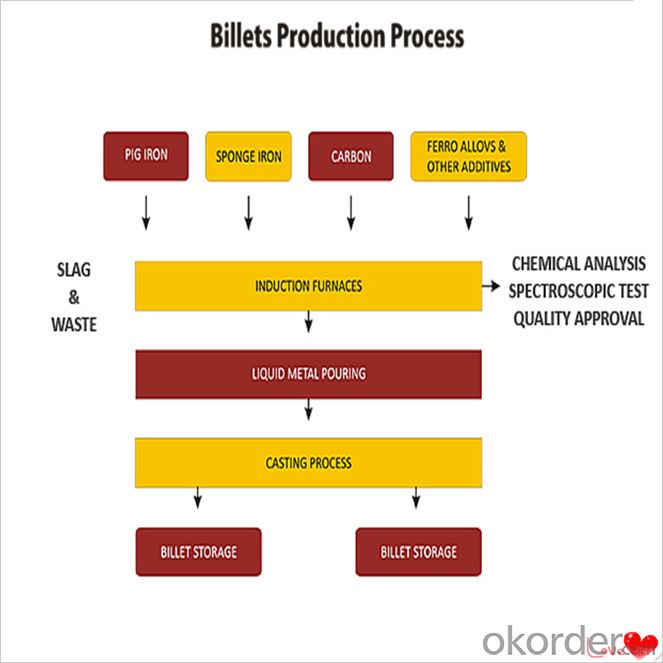
Steel billet(ingot) by cogging or breakdown of semi-finished products, is the raw material of all kinds of steel mill. Billet section of square, round, flat, rectangular and abnormity of several kinds of, mainly related to the shape of rolled products.
CNBM Q235,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi Billets Steel
Hot Rolled Steel Billets/ Mild Steel Bar/ Billet Steel
Specification (see below)
Standard: GB/JIS/ASTM
Size: 50*50mm-180*180mm
Length: 3-12mtrs or Customised
Steel material: Q235,Q255,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi
Technique: Hot rolled
FOB Unit Ton Price $250-350 and Usually I will quote you CFR price.
MOQ: Usually 1000-10000MT/size
Shipment:By Container,Bulk Vessel
Packaging Details: bundles with steel strips or as customers's requirements
Delivery time: Usually within 30 days after the deposit/LC
Inspection:Third party inspection before loading.
Technical data
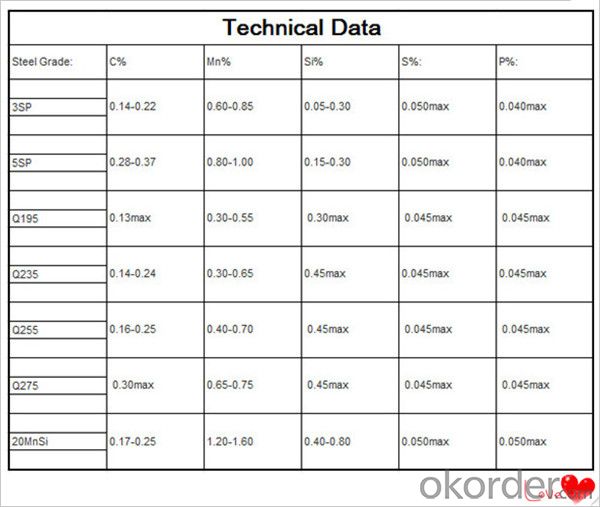
Feature Steel Billet
Rectangular billet continuous casting billet and mainly general carbon steel, low carbon low silicon cold-rolled material, high quality carbon structural steel, high strength low alloy steel, special steel, etc.
The billet is mainly divided into two kinds from the shape:
Slab: cross section width and height of the ratio of the larger, mainly used for rolling plate.
Billet: equal cross section width and height, or a huge difference, mainly used for rolling steel, wire rod. ,
Steel billets have distinct characteristics as compared with already furnished steel bars and products. Billets have a specific grain structure, which enables the metal to be processed more intricately. Steel billets are also known for their malleability and ductility, especially when exposed to varying temperatures during shaping and molding.
Packaging & Shipping
1. Packaging:
1) Small size: in bundles
2)Big size: in bulk
3)in plastic packing or as per customer requirement
2. Delivery time:
1) Normal size: within 7days send from warehouse directly
2) Special size: with 25-30days customer made for you
3. Trade terms:FOB/CFR/CIF
4. Shippment:
1) length:≤5.8m loaded in 20FT Container with 25-27tons
2) length:≤11.8m loaded in 40FT Container with 25-27tons
3) lengnth:≥12m shipped by bulk vessel, FILO terms
Steel Billet Images






Processing
Usage-Billet Steel
Used for the plant, the bridge,shipment building high-rise building construction,lifting and transportation machinery, equipment manufracturing base building the support foundation pile manufacturing.
Billets, or ingots (as they sometimes referred to), are not of practical use until they have been formed into more functional shapes and sizes. While they have already been put in the furnace, they still require a series of shaping and molding procedures such as hot and cold working, milling and cutting before they are sold in hardware stores, or used for different applications. The unformed billets, however, can be used in striking currency such as coins and as reserves, similar to gold bars.
FAQ-Billet Steel
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1) How about your company?
A world class manufacturer & supplier of castings forging in carbon steel and alloy steel,is one of the large-scale professional investment casting production bases in China,consisting of both casting foundry forging and machining factory. Annually more than 8000 tons Precision casting and forging parts are exported to markets in Europe,America and Japan. OEM casting and forging service available according to customer’s requirements.
2) How to guarantee the quality of the products?
We have established the international advanced quality management system,every link from raw material to final product we have strict quality test;We resolutely put an end to unqualified products flowing into the market. At the same time, we will provide necessary follow-up service assurance.
3) How long can we receive the product after purchase?
In the purchase of product within three working days, We will arrange the factory delivery as soon as possible. The pecific time of receiving is related to the state and position of customers.Commonly 7 to 10 working days can be served.
4)Do you have your own QC department?
Yes, we have, our QC department will inspect the goods during the process of mass production and after completion of production.
hot sale!!! Cast Steel Grades/ mild steel bar/ billet steel
(1): High quality steel with reasonable price.
(2): Wide excellent experiences with after-sale service.
(3): Every process will be checked by responsible QC which insures every product's quality.
(4): Professional packing teams which keep every packing safely.
(5): Trial order can be done in one week.
(6): Samples can be provided as your requirements.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of oil and gas components?
- Steel billets play a crucial role in the manufacturing process of oil and gas components. These billets serve as essential materials and are created through a process known as casting. In this process, molten steel is poured into a mold and allowed to solidify into a rectangular shape, resulting in semi-finished products. Once formed, steel billets are utilized in various ways to produce components for the oil and gas industry. One common application involves their use in the production of pipes, which are vital for transporting oil and gas from reservoirs to processing facilities or end-users. Depending on project requirements, steel billets can be further processed to create seamless or welded pipes. Aside from pipes, steel billets are also employed in the manufacturing of other important oil and gas components such as valves, fittings, flanges, and pressure vessels. These components are crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of oil and gas facilities, as they facilitate proper flow control, connection, and containment of fluids under high pressures and temperatures. The utilization of steel billets in the manufacturing process of oil and gas components offers several advantages. Firstly, steel is widely recognized for its strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion, making it highly suitable for the harsh and demanding operating conditions of the industry. Additionally, steel billets allow for flexibility in terms of size, shape, and composition, enabling manufacturers to produce components tailored to meet specific project requirements. In conclusion, steel billets play a critical role in the production of oil and gas components. They provide the necessary strength, durability, and versatility required for the safe and efficient operation of the industry.
- Q: What are the potential applications of steel billets in the agricultural sector?
- Steel billets have a wide range of potential applications in the agricultural sector. One of the primary uses of steel billets in agriculture is for the manufacturing of farm equipment and machinery. Steel billets can be used to produce durable and sturdy components such as plows, cultivators, and seeders, which are essential for tilling the soil, planting seeds, and maintaining agricultural land. Steel billets can also be utilized in the construction of storage structures on farms. Steel is known for its strength and durability, making it an ideal material for constructing grain silos, barns, and sheds. These structures provide farmers with a reliable and long-lasting solution for storing crops, livestock, and equipment. In addition, steel billets can be used to fabricate fences and gates for animal enclosures. Steel fences offer superior strength and security, ensuring the safety of farm animals and preventing them from wandering off. These fences are also resistant to corrosion and are capable of withstanding harsh weather conditions. Furthermore, steel billets can be employed in the construction of irrigation systems and water management infrastructure on farms. Steel pipes and fittings are commonly used to transport water from a source to the fields, ensuring proper irrigation and efficient water distribution. Lastly, steel billets can be utilized in the production of machinery used for processing agricultural products. For example, steel components can be used to manufacture grain mills, threshers, and sorting machines, which aid in the processing and packaging of crops. Overall, the potential applications of steel billets in the agricultural sector are vast and varied. From farm equipment and storage structures to fencing and irrigation systems, steel billets play a crucial role in enhancing efficiency, durability, and productivity in agriculture.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the production of pipe fittings?
- The production of pipe fittings heavily relies on steel billets, which are a vital raw material. Pipe fittings, which are essential components for connecting and controlling fluid flow in piping systems, are manufactured from steel billets. To make steel billets suitable for manufacturing pipe fittings, they are initially heated to a specific temperature. This heating process makes the billets malleable and easier to work with. Subsequently, the billets undergo a series of processes, such as hot rolling, forging, or extrusion, depending on the desired shape and size of the pipe fitting. During hot rolling, the steel billet is passed through rollers that apply pressure and shape it into a cylindrical form. This particular shape is ideal for producing pipe fittings like elbows, tees, reducers, and couplings. Forging involves subjecting the steel billet to extreme heat and pressure, enabling it to be shaped into complex and custom designs. This method is commonly used to manufacture high-pressure pipe fittings that require exceptional strength and durability. Extrusion is another method employed in the production of pipe fittings. In this process, the steel billet is forced through a die with the desired cross-sectional shape, resulting in pipe fittings with consistent outer and inner diameters. Once the desired shape is achieved, the pipe fittings undergo further processing, such as cutting, threading, or welding, to create the final product. These additional steps ensure that the fittings are prepared for installation and can be securely connected to the piping system. In essence, steel billets are crucial in the production of pipe fittings as the primary raw material. Through processes like hot rolling, forging, or extrusion, they are transformed into a wide range of pipe fittings used in various industries and applications.
- Q: What are the potential applications of steel billets in the automotive industry?
- Due to their exceptional strength and durability, steel billets offer a wide range of potential applications in the automotive industry. One notable use is in the manufacturing of automotive components such as engine blocks, crankshafts, and transmission parts. These components necessitate a material that can endure high temperatures, heavy loads, and repetitive stress, which steel billets can provide. Another significant application is in the production of chassis and body panels. Steel billets are frequently employed to construct the structural framework of a vehicle, ensuring safety and stability by delivering the necessary strength and rigidity. Additionally, steel billets can be shaped and sized in various ways, permitting the customization of chassis components to meet the specific requirements of different vehicle models. Steel billets are also utilized in the production of suspension systems and steering mechanisms. These parts require a material capable of absorbing vibrations, damping shocks, and providing precise control. Steel billets possess these properties, making them an ideal choice for these essential automotive components. Furthermore, steel billets find applications in the production of exhaust systems due to their ability to withstand high temperatures and corrosive environments. The resistance of steel to rust and corrosion guarantees the longevity of the exhaust system, contributing to the overall performance and efficiency of the vehicle. In conclusion, the potential applications of steel billets in the automotive industry are extensive. From engine components to chassis parts, suspension systems to exhaust systems, steel billets offer the required strength, durability, and versatility to meet the demanding needs of the automotive sector.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of structural components?
- The manufacturing of structural components heavily relies on steel billets, which are an essential raw material. These billets, usually square or round in shape, are produced through continuous casting, a process that solidifies molten steel into a semi-finished product. After the formation of steel billets, they undergo further processing using different techniques like hot rolling, forging, or extrusion. Hot rolling includes heating the billets and passing them through a sequence of rollers to shape them into desired profiles, such as beams, channels, or angles. This method is crucial for achieving the necessary dimensions, strength, and surface finish. Forging is another technique employed with steel billets, involving heating the billets and shaping them using compressive forces. It is primarily used for manufacturing components that require enhanced strength and durability, like crankshafts, connecting rods, or turbine blades. Extrusion, on the other hand, is a specialized process that utilizes heated billets to create complex shapes by forcing them through a die. This technique is commonly utilized in the production of tubular components, such as pipes, tubes, or hollow sections. These components are extensively used in the construction of structures like bridges, buildings, or infrastructure. Steel billets play a critical role in the manufacturing of structural components by providing the necessary raw material that can be shaped using various fabrication techniques. Their adaptability and versatility make them an indispensable component in the construction industry, ensuring that buildings and structures possess the required strength and durability to withstand different loads and environmental conditions.
- Q: How are steel billets inspected before they are used in production?
- Before being used in production, steel billets undergo a thorough inspection to ensure their quality and adherence to required specifications. The inspection process involves several key steps. Firstly, a visual inspection is conducted to examine the billets' surface for any defects such as cracks, seams, or deformities. Any irregularities can indicate potential weaknesses or problems that may affect performance during production. Secondly, dimensional inspection is performed to verify the billets' size, length, width, and other critical dimensions. This is crucial to ensure that the billets meet the precise requirements of the production process and can be seamlessly integrated into manufacturing operations. Thirdly, ultrasonic testing is often used to detect any internal defects or discontinuities within the billets. Ultrasonic waves are passed through the billet, and reflections or echoes are analyzed to identify any flaws such as voids, inclusions, or cracks that may compromise the billets' structural integrity. Moreover, magnetic particle inspection may be carried out to identify surface or near-surface defects that are not visible to the naked eye. This technique involves applying magnetic particles to the billet's surface and detecting any magnetic leakage caused by defects through the use of magnetic fields. Additionally, chemical analysis is frequently performed to ensure that the steel billets have the desired chemical composition. This involves taking samples from the billets and subjecting them to various tests to determine the percentages of different elements present. This analysis guarantees that the billets possess the necessary chemical properties for the intended application. In conclusion, steel billets undergo a comprehensive inspection process that includes visual examination, dimensional verification, ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle inspection, and chemical analysis. This multi-faceted approach ensures that the billets meet the required quality standards and are suitable for use in production, minimizing the risk of any performance issues or failures during manufacturing processes.
- Q: What are the safety precautions when handling steel billets?
- To minimize the likelihood of accidents and injuries when dealing with steel billets, it is crucial to adhere to various safety measures. Firstly, it is of utmost importance to wear suitable personal protective equipment (PPE) such as safety goggles, steel-toed boots, gloves, and a hard hat. Before commencing the handling of steel billets, it is necessary to ensure that the work area is free from any obstructions or debris that could potentially cause trips or falls. Additionally, it is essential to stack and store the billets correctly to prevent unexpected falls or shifts. When it comes to lifting or moving steel billets, one should exercise caution regarding their weight and size. Utilizing appropriate lifting equipment like cranes, forklifts, or hoists is necessary to avoid strains or musculoskeletal injuries. It is crucial to always adhere to the weight limits and load capacities specified for the equipment being employed. To prevent slippage or falling, it is important to maintain a secure grip on the billets. One should avoid sharp edges or protruding parts that could result in cuts or puncture wounds. If required, the use of protective covers or padding can prevent contact with sharp or jagged edges. Proper communication plays a vital role in the handling of steel billets. It is imperative to establish clear communication among the workers involved in the process to prevent accidents or mishaps. Hand signals or radios can be employed to facilitate effective communication, especially in noisy environments. Regular inspection of the steel billets should be conducted before handling them to identify any defects or damage. Cracks, rust, or any other issues can compromise the structural integrity of the billets and increase the risk of accidents. If any defects are detected, they should be reported to a supervisor, and the appropriate procedures for handling or disposing of the billets should be followed. Lastly, it is crucial to always be aware of one's surroundings and the movements of other workers when handling steel billets. Standing or working in the swing radius of lifting equipment or near moving machinery should be avoided to prevent being struck or crushed. By adhering to these safety precautions, the risk of accidents and injuries during the handling of steel billets can be significantly reduced, thereby creating a safer work environment.
- Q: Can steel billets be used in the production of pipes?
- Indeed, the utilization of steel billets is possible in the fabrication of pipes. Steel billets serve as the primary material for the creation of diverse steel goods, comprising pipes. The procedure entails subjecting the steel billets to elevated temperatures and subsequently molding them into pipes utilizing distinct techniques like hot rolling, cold rolling, or extrusion. Steel billets furnish the essential strength, durability, and consistency necessary for the manufacturing of pipes. Furthermore, they can undergo further processing and treatment to fulfill specific prerequisites such as resistance to corrosion or improved mechanical properties. Thus, steel billets assume a crucial function in pipe production and find extensive application in the steel industry for this very purpose.
- Q: How does billet caster pull out billet cracking?
- The strict two cooling water distribution system, the degree of purification of the molten steel, and the precise arc are related!
- Q: How are steel billets inspected for quality?
- Steel billets are typically inspected for quality using various non-destructive testing methods such as visual inspection, ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle inspection, and dye penetrant testing. These tests help identify any surface defects, cracks, or internal flaws in the billets, ensuring that they meet the required quality standards before further processing.
Send your message to us
Clamps Billet Aluminum Q235,Q255,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 20 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords

































