Square Steel Billets Q235,Q255,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 20 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Square Steel Billets Q235,Q255,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi
Specification
Steel billet(ingot) by cogging or breakdown of semi-finished products, is the raw material of all kinds of steel mill. Billet section of square, round, flat, rectangular and abnormity of several kinds of, mainly related to the shape of rolled products.
CNBM Q235,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi Billets Steel
Hot Rolled Steel Billets/ Mild Steel Bar/ Billet Steel
Specification (see below)
Standard: GB/JIS/ASTM
Size: 50*50mm-180*180mm
Length: 3-12mtrs or Customised
Steel material: Q235,Q255,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi
Technique: Hot rolled
FOB Unit Ton Price $250-350 and Usually I will quote you CFR price.
MOQ: Usually 1000-10000MT/size
Shipment:By Container,Bulk Vessel
Packaging Details: bundles with steel strips or as customers's requirements
Delivery time: Usually within 30 days after the deposit/LC
Inspection:Third party inspection before loading.
Technical data
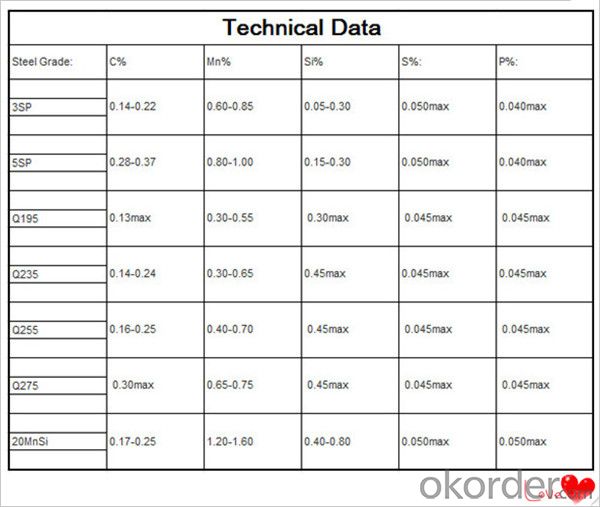
Feature Steel Billet
Rectangular billet continuous casting billet and mainly general carbon steel, low carbon low silicon cold-rolled material, high quality carbon structural steel, high strength low alloy steel, special steel, etc.
The billet is mainly divided into two kinds from the shape:
Slab: cross section width and height of the ratio of the larger, mainly used for rolling plate.
Billet: equal cross section width and height, or a huge difference, mainly used for rolling steel, wire rod. ,
Steel billets have distinct characteristics as compared with already furnished steel bars and products. Billets have a specific grain structure, which enables the metal to be processed more intricately. Steel billets are also known for their malleability and ductility, especially when exposed to varying temperatures during shaping and molding.
Packaging & Shipping
1. Packaging:
1) Small size: in bundles
2)Big size: in bulk
3)in plastic packing or as per customer requirement
2. Delivery time:
1) Normal size: within 7days send from warehouse directly
2) Special size: with 25-30days customer made for you
3. Trade terms:FOB/CFR/CIF
4. Shippment:
1) length:≤5.8m loaded in 20FT Container with 25-27tons
2) length:≤11.8m loaded in 40FT Container with 25-27tons
3) lengnth:≥12m shipped by bulk vessel, FILO terms
Steel Billet Images






Processing
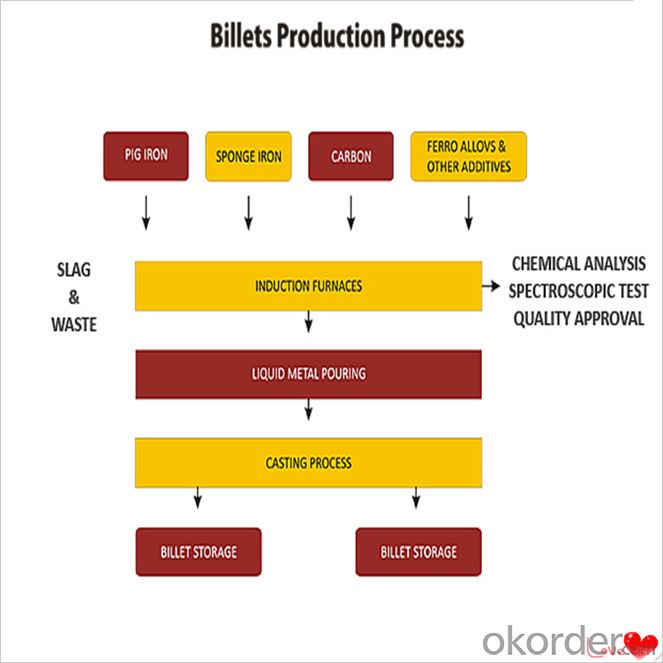
Usage-Billet Steel
Used for the plant, the bridge,shipment building high-rise building construction,lifting and transportation machinery, equipment manufracturing base building the support foundation pile manufacturing.
Billets, or ingots (as they sometimes referred to), are not of practical use until they have been formed into more functional shapes and sizes. While they have already been put in the furnace, they still require a series of shaping and molding procedures such as hot and cold working, milling and cutting before they are sold in hardware stores, or used for different applications. The unformed billets, however, can be used in striking currency such as coins and as reserves, similar to gold bars.
FAQ-Billet Steel
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1) How about your company?
A world class manufacturer & supplier of castings forging in carbon steel and alloy steel,is one of the large-scale professional investment casting production bases in China,consisting of both casting foundry forging and machining factory. Annually more than 8000 tons Precision casting and forging parts are exported to markets in Europe,America and Japan. OEM casting and forging service available according to customer’s requirements.
2) How to guarantee the quality of the products?
We have established the international advanced quality management system,every link from raw material to final product we have strict quality test;We resolutely put an end to unqualified products flowing into the market. At the same time, we will provide necessary follow-up service assurance.
3) How long can we receive the product after purchase?
In the purchase of product within three working days, We will arrange the factory delivery as soon as possible. The pecific time of receiving is related to the state and position of customers.Commonly 7 to 10 working days can be served.
4)Do you have your own QC department?
Yes, we have, our QC department will inspect the goods during the process of mass production and after completion of production.
hot sale!!! Cast Steel Grades/ mild steel bar/ billet steel
(1): High quality steel with reasonable price.
(2): Wide excellent experiences with after-sale service.
(3): Every process will be checked by responsible QC which insures every product's quality.
(4): Professional packing teams which keep every packing safely.
(5): Trial order can be done in one week.
(6): Samples can be provided as your requirements.
- Q: What are the factors that affect the price of steel billets?
- The price of steel billets can be affected by several factors. 1. Raw material costs have a significant impact on the price of steel billets. Fluctuations in the cost of iron ore, coal, and other raw materials used in steel production directly influence the price of steel billets. 2. The supply and demand dynamics of steel billets play a crucial role in determining their price. An increase in demand for steel products, such as construction materials or automotive parts, can drive up the price of steel billets. Conversely, an oversupply can lead to a decrease in price. 3. Energy costs required for steel production can impact the price of steel billets. Fluctuations in energy prices affect the overall production cost and, subsequently, the price of steel billets. 4. Currency exchange rates can have a significant impact on the price of steel billets. If the currency of the country producing steel billets weakens against other currencies, it can make the product more affordable and potentially increase demand. 5. Government regulations, trade policies, and tariffs imposed on steel billets can influence their price. Tariffs can increase the cost of imported steel billets, making domestically produced steel billets relatively more competitive and potentially leading to higher prices. 6. The overall state of the economy, both locally and globally, can impact the price of steel billets. During periods of economic growth, there is typically higher demand for steel products, which can drive up the price. Conversely, during economic downturns, demand may decrease, resulting in lower prices. 7. Technological advancements in steel production can impact the price of steel billets. Innovations that increase efficiency and reduce production costs can potentially lead to lower prices, while new technologies that improve the quality or properties of steel billets may command a higher price. It is important to note that these factors are interconnected and can influence each other. Therefore, understanding the complex relationship between these factors is essential in analyzing and predicting the price of steel billets.
- Q: What are the different grades of steel used for producing billets?
- The different grades of steel used for producing billets vary depending on the specific requirements and applications. Some common grades include mild steel, low carbon steel, medium carbon steel, high carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel. Each grade offers different mechanical properties, such as strength, durability, and corrosion resistance, to meet the desired characteristics for the final product.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of construction formwork?
- Steel billets are used in the manufacturing of construction formwork as they are often shaped and molded into various components, such as beams or columns, that provide essential structural support. These billets are strong and durable, ensuring the formwork can withstand the weight and pressure of poured concrete. Additionally, their malleability allows for customization, enabling the formwork to be precisely designed to meet the specific requirements of each construction project.
- Q: How do steel billets contribute to the manufacturing of textile machinery?
- Steel billets are a crucial component in the manufacturing of textile machinery due to their mechanical properties and versatility. Steel billets are essentially semi-finished steel products, typically in a rectangular or square shape, that are used as raw material in various industries, including textile machinery manufacturing. One of the primary ways steel billets contribute to the manufacturing of textile machinery is through the production of structural components. Textile machinery requires sturdy and durable frames, supports, and other structural elements to ensure stability and efficient functioning. Steel billets, with their high strength and rigidity, serve as an ideal material for these components. They can be easily shaped, machined, or welded to create intricate and complex structures that can withstand the heavy loads and vibrations associated with textile machinery. Additionally, steel billets are often used to produce shafts, gears, and other moving parts in textile machinery. These components need to have excellent wear resistance, high tensile strength, and good machinability to ensure smooth operation and a long service life. Steel billets, through various processes such as forging, rolling, or machining, can be transformed into these critical parts, providing the necessary mechanical properties and precision required for textile machinery. Moreover, steel billets are utilized in the manufacturing of tooling and molds used in textile machinery production. These tools and molds are essential for shaping and forming various components or parts of the machinery. Steel billets, when subjected to heat treatment and precise machining processes, can be transformed into high-quality tooling and molds that offer exceptional dimensional accuracy and durability. This contributes to the overall efficiency and quality of textile machinery production. In summary, steel billets play a pivotal role in the manufacturing of textile machinery by providing the raw material for structural components, moving parts, and tooling. Their mechanical properties, versatility, and ease of fabrication make them an indispensable material for the industry. Steel billets ensure the durability, precision, and functionality of textile machinery, ultimately contributing to the overall performance and reliability of the equipment.
- Q: the ear has burrs, is it the billet problem or the rolling mill problem, will it be caused by the blowhole of the billet?
- Billet sent from the steelmaking plant, first into the furnace, then after rolling mill rolling
- Q: What are the main challenges in the supply chain management of steel billets?
- Supply chain management of steel billets presents several key challenges. These challenges encompass demand fluctuations, transportation and logistics, supply chain visibility, quality control, and sustainability concerns. Firstly, demand fluctuations pose a significant obstacle due to the steel industry's susceptibility to economic cycles and shifts in global demand. These fluctuations often result in imbalances within the supply chain, leading to excessive inventory or shortages of steel billets. Consequently, accurately forecasting demand and optimizing production and inventory levels becomes a challenging task for supply chain managers. Secondly, transportation and logistics prove to be major hurdles in the management of steel billets. The heavy and bulky nature of these billets necessitates the establishment of efficient transportation networks to ensure timely delivery. Moreover, the handling and storage of steel billets require specialized equipment and facilities, adding complexity and cost to the supply chain. Thirdly, supply chain visibility is crucial for mitigating inefficiencies and delays. Supply chain managers must have real-time information regarding inventory levels, production status, and transportation schedules. This enables them to make informed decisions and address any potential disruptions promptly. Next, quality control plays a vital role in maintaining consistent billet quality throughout the supply chain. Since steel billets are often produced by different manufacturers, variations in quality can arise. Consequently, supply chain managers need to implement robust quality control processes, including regular inspections, testing, and adherence to industry standards, to ensure the delivery of high-quality billets to customers. Finally, sustainability and environmental concerns add another layer of complexity to the supply chain management of steel billets. The steel industry faces mounting pressure to reduce its carbon footprint and adopt sustainable practices. As a result, supply chain managers must navigate the challenge of implementing environmentally friendly processes and sourcing billets from suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices. This involves evaluating the environmental impact of transportation methods, optimizing energy consumption during production, and ensuring responsible sourcing of raw materials. In summary, effectively managing the supply chain of steel billets requires addressing challenges related to demand fluctuations, transportation and logistics, supply chain visibility, quality control, and sustainability concerns. Overcoming these obstacles necessitates effective planning, collaboration with suppliers and customers, and the utilization of advanced technologies to enhance visibility and optimize processes.
- Q: What are the different surface finishes available for alloy steel billets?
- Alloy steel billets offer a variety of surface finishes to cater to specific requirements and applications. Among the most commonly used surface finishes are: 1. Hot rolled: The prevalent surface finish, obtained by subjecting the steel billet to high temperatures during the rolling process. This results in a rough and scaled surface. 2. Cold drawn: Achieved by pulling the steel billet through a die at room temperature. It yields a smooth and polished surface, enhancing dimensional accuracy and surface quality. 3. Peeled: Involves removing a layer of material from the steel billet's surface using a peeling tool. This process produces a smooth and shiny surface finish, improving both surface quality and dimensional accuracy. 4. Ground: Accomplished by grinding the surface of the steel billet using abrasive wheels or belts. It delivers a smooth and even surface finish, enhancing both surface quality and dimensional accuracy. 5. Turned: In this process, a cutting tool is used to rotate the steel billet, removing material from the surface and creating a smooth and polished finish. It is particularly useful for high precision applications that require a smooth surface finish. 6. Polished: Achieved by polishing the steel billet using abrasive compounds and buffing wheels. This method provides a mirror-like finish, enhancing aesthetic appeal and corrosion resistance. It is crucial to carefully select the appropriate surface finish based on specific requirements such as dimensional accuracy, surface quality, aesthetic appeal, and corrosion resistance.
- Q: Can steel billets be used for artistic purposes?
- Yes, steel billets can be used for artistic purposes. Steel is a versatile material that can be shaped, welded, and manipulated to create various artistic sculptures, structures, and decorative pieces. It offers strength, durability, and a modern aesthetic, making it a popular choice among artists and designers. Additionally, steel can be painted, polished, or oxidized to create different visual effects, allowing artists to experiment and showcase their creativity.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of pressure vessel components?
- Steel billets are used in the manufacturing of pressure vessel components by being melted and formed into the desired shape through processes like casting, forging, or extrusion. These billets serve as the raw material for creating various components such as shells, heads, and nozzles, which are then further processed, machined, and assembled to construct the pressure vessel.
- Q: Charcoal is how to
- Now, there is a method of using sawdust and other waste materials to process the charcoal, which is formed by pressing the waste materials into the furnace and heating them indirectly. The raw materials are carbonized into charcoal.The quality of charcoal can only be raised according to different uses.
Send your message to us
Square Steel Billets Q235,Q255,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 20 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords

































