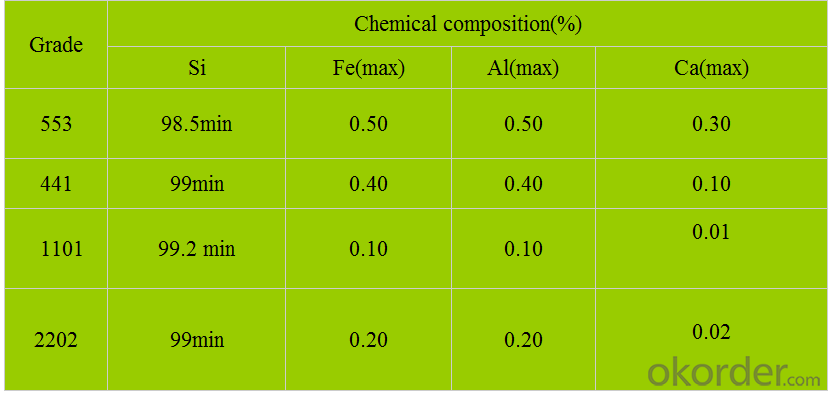
Quality safety Silicon Metal/metal silicon 553 grade
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 20 m.t
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 m.t/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description
Silicon metal is very rich in the earth's crust, rank only second to oxygen. Silicon metal can be divided into many kinds, including ferro silicon ,simn etc.Its main element is si whose content is about 98% and its impurities is Al, Fe, Ca etc. The additional product of silicon metal includes silica fume, edge leather, black silicon etc.Silica fume is widely used in the fireproofing and concrete industry
Applications of silicon metal
(1)Silicon metal can be used to make silicon crystals, silicone rubber , silicone oil etc.
(2)Silicon metal can be used in the aluminum alloy industry.
(3)Silicon metal can also be used as the basic raw material in the chemical industry.
(4)Silicon metal can make high purity semiconductor.
(5)Automobile industries use aluminum that requires a quite large industrial silicon , so the country's auto industry development has a direct effect on industrial silicon market.
(6)Silicon metal can replace pure aluminium in steelmaking.
(7)A large proportion of silicon metal will be applied in the chemical industry.


- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the overall efficiency of iron and steel production?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in enhancing the overall efficiency of iron and steel production. These refractories, which are made from a single material, provide exceptional thermal insulation, resistance to high temperatures, and excellent mechanical strength. By lining the furnaces, ladles, and other equipment used in the production process, monolithic refractories help in maintaining and regulating the required high temperatures for melting, refining, and shaping iron and steel. This insulation reduces heat loss, minimizes energy consumption, and ensures a more efficient and cost-effective production process. Additionally, the mechanical strength of monolithic refractories allows for better protection against wear and tear, resulting in increased equipment lifespan and reduced downtime for repairs and maintenance. Overall, the use of monolithic refractories significantly contributes to the efficiency, productivity, and sustainability of the iron and steel production industry.
- Q: What are the common failure mechanisms of monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry?
- Some common failure mechanisms of monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry include thermal spalling, erosion, chemical attack, and mechanical damage. Thermal spalling occurs due to rapid temperature changes, causing the refractory material to crack and break. Erosion occurs when hot gases or molten metal wear away the refractory lining. Chemical attack refers to the corrosive action of slag or other chemicals on the refractory material. Mechanical damage may occur due to physical impacts or stresses, leading to cracks and fractures in the refractory lining.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the overall efficiency of ladle slagging operations?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in improving the overall efficiency of ladle slagging operations. Ladle slagging is a process that involves the removal of impurities from molten metal in a ladle before it is poured into molds or further processed. One of the key contributions of monolithic refractories is their ability to withstand high temperatures, which is essential in ladle slagging operations. The refractory lining of the ladle needs to be able to endure the extreme heat generated by the molten metal and slag, as well as the chemical reactions occurring during the process. Monolithic refractories, with their high thermal stability, prevent the lining from cracking or deteriorating, thus ensuring the integrity of the ladle and maintaining its efficiency. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer excellent resistance to chemical erosion and corrosion. During the ladle slagging process, the molten metal and slag can contain various impurities and aggressive chemicals, such as sulfur, phosphorus, and other oxides. These substances can attack and degrade the lining of the ladle, compromising its efficiency. However, monolithic refractories are designed to resist these chemical attacks, thereby extending the lifespan of the ladle and reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements. Moreover, monolithic refractories provide good thermal insulation properties. Ladle slagging operations require precise temperature control to ensure the desired chemical reactions and efficient removal of impurities. The thermal insulation offered by monolithic refractories helps to maintain a consistent temperature within the ladle, preventing heat loss and allowing for optimized slagging conditions. This insulation also minimizes energy consumption and improves the overall energy efficiency of the ladle slagging process. In conclusion, monolithic refractories contribute significantly to the overall efficiency of ladle slagging operations. Their ability to withstand high temperatures, resist chemical erosion, and provide thermal insulation ensures the integrity and longevity of the ladle. By reducing the need for frequent repairs and allowing for precise temperature control, monolithic refractories optimize the slagging process, leading to improved productivity and cost-effectiveness.
- Q: What are the considerations for repairing and patching monolithic refractories?
- When it comes to the repair and patching of monolithic refractories, there are several key factors that must be taken into consideration. First and foremost, it is crucial to thoroughly evaluate the extent and severity of the damage or deterioration. This assessment will help determine the most appropriate repair method and materials required. Minor cracks or small damages may only necessitate a simple patch or seal, whereas larger or more serious damage may require a complete replacement or a more extensive repair process. Secondly, the type of monolithic refractory material being utilized is a critical factor to consider. Different types of monolithic refractories possess varying properties and characteristics, such as thermal conductivity, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength. Therefore, it is vital to select a repair material that is compatible with the existing refractory material, ensuring proper bonding and optimal performance. Another factor to take into account is the operating conditions and environment in which the monolithic refractory is exposed. Variables such as temperature, pressure, chemical exposure, and abrasion can significantly impact the durability and longevity of the refractory material. Understanding these conditions will assist in selecting the appropriate repair materials and techniques that can withstand and perform well under these specific circumstances. Furthermore, it is imperative that the repair process is carried out by experienced personnel who possess knowledge about refractory materials and their installation. Improper repairs can lead to further damage or diminished performance, so it is essential to have skilled professionals who can execute the repair work correctly. Lastly, regular inspection and maintenance of the monolithic refractories are crucial in order to detect any potential damage or deterioration early on. Timely repairs and patching can prevent further deterioration and prolong the service life of the refractory material. In summary, the considerations for repairing and patching monolithic refractories involve evaluating the extent of damage, selecting compatible repair materials, understanding the operating conditions, employing skilled personnel, and conducting regular inspections and maintenance. By taking these factors into account, one can ensure effective repairs and the continued performance of monolithic refractories.
- Q: What are the factors affecting the thermal expansion of monolithic refractories?
- There are several factors that influence the thermal expansion of monolithic refractories. 1. Chemical Composition: The chemical composition of the refractory material plays a significant role in its thermal expansion. Different chemical elements and compounds have different coefficients of thermal expansion. For example, materials containing high levels of silica tend to have lower coefficients of thermal expansion compared to materials with higher concentrations of alumina. 2. Particle Size: The particle size distribution of the refractory material can affect its thermal expansion. Smaller particle sizes tend to result in higher thermal expansion due to increased surface area and greater contact between particles. 3. Temperature: The temperature at which the monolithic refractory is exposed can greatly impact its thermal expansion. As the temperature increases, the kinetic energy of the particles increases, causing them to move more vigorously and expand. Different refractory materials have different temperature ranges at which they exhibit significant expansion. 4. Thermal History: The thermal history of the refractory material, including its heating and cooling cycles, can influence its thermal expansion behavior. Repeated heating and cooling cycles can induce microstructural changes in the material, affecting its thermal expansion properties. 5. Porosity: The porosity of the monolithic refractory can affect its thermal expansion. Higher porosity generally leads to higher thermal expansion due to the presence of voids and gaps within the material. 6. Binder Content: Monolithic refractories often contain binders that hold the particles together. The type and amount of binder used can impact the thermal expansion of the refractory. Different binders have different coefficients of thermal expansion, which can influence the overall expansion behavior of the material. 7. Thermal Shock: Rapid temperature changes, such as during quenching or exposure to alternating heating and cooling, can cause thermal shock in the refractory material. This can lead to cracks, spalling, and changes in the thermal expansion behavior. Understanding these factors is crucial in selecting the appropriate monolithic refractory material for specific applications, as the thermal expansion characteristics can directly impact the performance and longevity of the refractory in high-temperature environments.
- Q: What are the factors affecting the thermal conductivity of monolithic refractories?
- The factors affecting the thermal conductivity of monolithic refractories include the composition and structure of the refractory material, the porosity and density of the material, the presence of any impurities or defects, the temperature at which the material is being used, and the presence of any external factors such as pressure or moisture.
- Q: What are the limitations of monolithic refractories in high-temperature applications?
- Monolithic refractories are known for their versatility and ease of installation, making them popular in a variety of high-temperature applications. However, they do have certain limitations that need to be considered. Firstly, monolithic refractories have a limited thermal shock resistance. Rapid temperature changes, such as during startup or shutdown procedures, can cause thermal stress, leading to cracking or spalling. This can be a significant concern in applications where the refractory is subjected to frequent temperature fluctuations. Secondly, monolithic refractories have relatively lower mechanical strength compared to traditional brick or block refractories. This can result in reduced resistance to mechanical stress, such as abrasion or impact, particularly in high-temperature environments. Therefore, they may not be suitable for applications with high mechanical loading or abrasive conditions. Another limitation of monolithic refractories is their susceptibility to chemical attack. Certain aggressive chemical environments can cause chemical reactions with the refractory material, leading to deterioration or corrosion. This can be a concern in applications involving acidic or alkaline substances, where special refractory materials may be required. Furthermore, monolithic refractories can have a higher susceptibility to spalling or erosion caused by thermal cycling. The repeated expansion and contraction of the refractory material due to temperature changes can lead to the formation of cracks or gaps, making them more prone to erosion from gases or liquids. This limitation should be carefully considered in applications where long-term durability is essential. Lastly, monolithic refractories can be challenging to repair or replace compared to brick or block refractories. Once installed, it can be difficult to remove and replace a monolithic lining, especially in complex shapes or confined spaces. This limitation can result in longer downtime or increased costs for maintenance or repairs. In summary, while monolithic refractories offer several advantages in high-temperature applications, they also have limitations in terms of thermal shock resistance, mechanical strength, chemical resistance, erosion, and repairability. These limitations should be carefully evaluated to ensure the suitability of monolithic refractories for specific application requirements.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand thermal cycling in the iron and steel industry?
- Monolithic refractories are designed to withstand thermal cycling in the iron and steel industry due to their unique composition and properties. These refractories are made from a single, continuous material, unlike traditional refractory bricks that are made by stacking individual bricks together. One of the main reasons monolithic refractories are able to withstand thermal cycling is their ability to expand and contract without cracking or damage. This is due to their high thermal shock resistance, which is a measure of their ability to withstand rapid temperature changes. Monolithic refractories are specially formulated to have low thermal conductivity, allowing them to resist the transfer of heat and minimize thermal gradients within the material. In addition, monolithic refractories have excellent thermal stability, which means they can maintain their structural integrity and mechanical strength even at high temperatures. This is crucial in the iron and steel industry, where temperatures can reach extreme levels. The refractories are able to withstand repeated heating and cooling cycles without undergoing significant structural changes or degradation. Furthermore, monolithic refractories have good corrosion resistance, which is important in an environment where they come into contact with molten metal and various chemical agents. Their composition and special additives help to protect the refractory material from chemical attack, preventing erosion and prolonging their lifespan. The manufacturing process of monolithic refractories allows for easy installation and repair, as they can be applied as a liquid or a semi-liquid mixture. This reduces the risk of joints or weak points that could lead to thermal stress or failure during thermal cycling. Overall, the combination of high thermal shock resistance, low thermal conductivity, excellent thermal stability, corrosion resistance, and easy installation makes monolithic refractories highly durable and capable of withstanding the severe thermal cycling conditions in the iron and steel industry.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories improve the performance of iron and steel furnaces?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in improving the performance of iron and steel furnaces in several ways. Firstly, these refractories provide excellent thermal insulation, which helps to maintain a stable and high temperature inside the furnace. This is important because the production of iron and steel requires extremely high temperatures for efficient melting and refining processes. Secondly, monolithic refractories have high resistance to thermal shock and can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or spalling. This is particularly important in iron and steel furnaces, where the temperature can fluctuate greatly during operations. By withstanding thermal shock, these refractories ensure the longevity of the furnace lining, reducing maintenance and downtime. Furthermore, monolithic refractories have excellent resistance to chemical attacks from the molten metal and slag in the furnace. The production of iron and steel involves the use of various chemical agents that can corrode and erode the lining of the furnace. Monolithic refractories offer superior resistance to these chemical attacks, ensuring the integrity of the furnace lining and preventing contamination of the metal being produced. Additionally, monolithic refractories have excellent mechanical strength and abrasion resistance. This is important as they are subjected to mechanical stresses and wear from the movement of materials inside the furnace, such as charging and tapping operations. The high mechanical strength and abrasion resistance of these refractories ensure their durability and prolong their service life in iron and steel furnaces. Overall, monolithic refractories improve the performance of iron and steel furnaces by providing superior thermal insulation, resistance to thermal shock and chemical attacks, as well as high mechanical strength and abrasion resistance. These properties contribute to the efficient and reliable operation of the furnace, resulting in increased productivity, reduced maintenance costs, and improved product quality.
- Q: What are the factors affecting the lifespan of monolithic refractories?
- There are several factors that can affect the lifespan of monolithic refractories. These include the type of material used in the refractory, the operating conditions such as temperature and pressure, the presence of corrosive or abrasive substances, the frequency and intensity of thermal cycling, and the quality of installation and maintenance. Additionally, factors like mechanical stresses, chemical reactions, and thermal shock can also contribute to the degradation and reduced lifespan of monolithic refractories.
Send your message to us
Quality safety Silicon Metal/metal silicon 553 grade
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 20 m.t
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 m.t/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords























