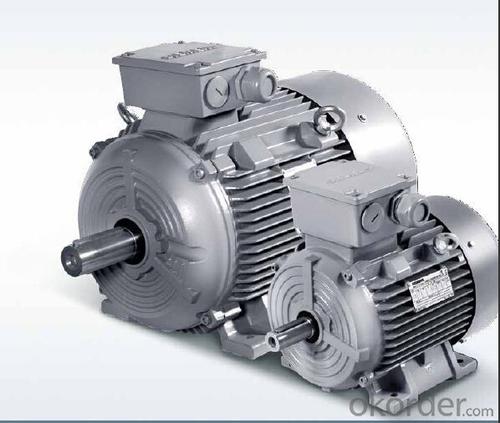
Siemens ILE0001 Series Low Voltage AC Motor
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like
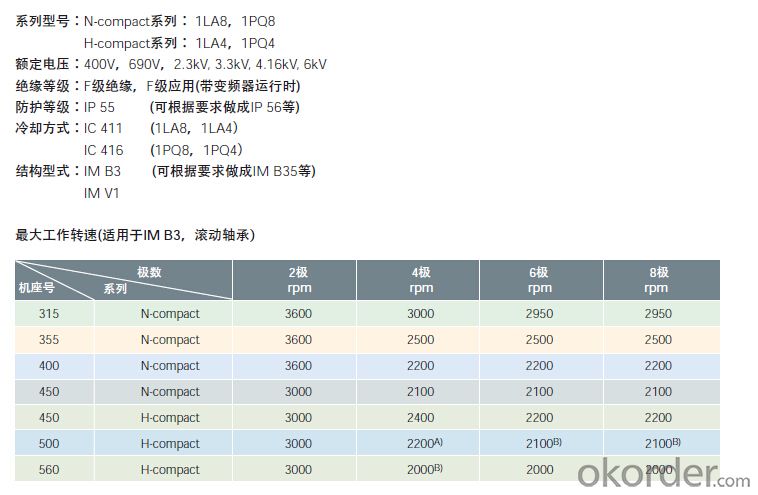
| part name | brand | model | Voltage | protection | cooling | |
| motor | Siemens | 1LA8 | 1PQ8 | 400V,690V,2.3KV,4.16KV,6KV | IP55 | IC411 (1LA8,1LA4) |
| IC416 (1PQ8,1PQ4) | ||||||



- Q: and when i turn it on it will move like a common motor(i am talking about electric motors or magnetic motors)
- An electric servo motor with an integrated electric brake will behave like that. When the motor is disengaged, the brake will hold the motor in its last position, and the brake must be disengaged to move the motor.
- Q: IHow can I install Automatic Reverse / Forward after some time interval to 3 Phase Ac Motorand Timer to stop it
- What type of a device are you using to select the forward/reverse change automatically. Your easiest method will be to use a small PLC, with a 4-position switch (Off/Forward/Reverse/Auto -not necessarily in that order) with inputs to the PLC and an input from the device which automatically selects forward or reverse. The logic will be fairly simple with a PLC, which will include the timers to allow the motor to stop completely after a stop signal, before allowing the motor to reverse directions. The PLC will be used in conjunction with the forward/reverse motor starter contactors. The use of interlocks between starters is high recommended. Email me if you need additional help. TexMav
- Q: I have it all disconnected and out of the unit. I am having trouble getting the blades off of the rusted shaft. (two rusted set screws) Any tricks out there on how to loosen them without damage to set screws? Any other advice would also be helpful...first time at this.
- If okorder . No matter what you decide to use, you may have to be patient and let it soak overnight. If the fan blades are badly rusted to the shaft, you Will need a puller, otherwise you will trash everything. One more option to get the blades off without damage is to cut the shaft (behind the fan blade) with a hack saw, then carefully set the hub (set-screw portion) of the fan blade assembly up against a large deep-well socket
- Q: It's a 1kW single phase AC pump motor with a 100v supply. This is for a theory question btw. :)
- use a potentiometer.
- Q: The coils in a motor are being magnetized when we supply AC current to it and thus the motor runs.What is the magnetic power produced in the coils in terms of quot;Teslasquot; when the motor is being run in full speed?
- The magnetic field strength does not change for AC motor,because power is applies to its field coils (do not mix it up with AC-DC series motor,field strength changes follow the load). To measure the AC magnestic field strength is quite difficult because the field polarization keep on changing according to the frequency. A hard way to find out is counting how turns of coil and the size of steel area,then calculate it.
- Q: It uses deepers for soft starting
- To control motor speed.
- Q: 4.5 amp 120 VAC 60hz MOTOR SPEED CONTROL SWITCH? help!?
- Most AC motors are not suitable for simple speed controls. Generally, you should contact a motor manufacturer's tech support to see which (if any) speed controls are suitable for a particular motor. Split phase motors are unlikely to start at a low speed setting and will burn out.
- Q: I just got charged $889 to install a new motor and capacitor. Plus $89 to add frion.
- You should specify what size unit and what size motor, where was it? Was it easy to get to or hard.Was this a question or are you just letting off steam? Every one on here just blurts out questions that do not contain enough real information to answer. The only thing I will say is if this a residential home and there were no other issues and the unit was not variable speed. You got jacked,,, sorry If this was a newer variable speed unit he got jacked...And you got a good price. Give more info..
- Q: Will the motor work fine?Not work at all? Work but not efficiently?
- It depends on it's internal structure of stator and rotor.A very important part of a DC motor is it's brushes and commutate system.A DC motor need them to have a continuous rotation and torque. But if you use an electronic brushing system for ac motor maby you can have a dc motor too. but not originally.as I told the reluctance many other things are important. according this explanation most of the time you won't be able to drive an AC motor by DC supply.
- Q: AC motors are designed to operate at +/- ____ Percent of their rated potential difference, and +/- _____ percent of their rated frequency?
- To approach the question the way it is asked would be to say few. Only synchronous A/C motors operate at a fixed speed based on the number of poles and the frequency of the power supply. A synchronous speed can be in increments of 3600 RPM or 2500 RPM depending on the frequency. Induction A/C motors will operate at the synchronous speed when there is no applied load and will begin to slow down slightly as load is applied. That slip is usually around 2- 3% when the nominal design horsepower is produced. . For example, an 1800 RPM synchronous motor will operate at 1800 RPM when fully loaded. A common induction motor will operate between 1800 and 1750 RPM. Most motors are manufactured to specific horsepower ratings at their design speeds and so cataloged. When a device needs a motor and it's design horsepower is known, the motor selected will be the next larger size. For instance a direct drive pump may be rated at 17.5 horsepower non-overloading (maximum) at 1750 RPM. There are no standard motors made to that specific horsepower so a 20 horsepower motor will be selected and will run efficiently at that partial load. Depending on the motor cooling system and the motor wiring insulation design, some will have transient service factors of 10-15% above the full load rating, but prolonged operation in an overloaded condition will shorten the motor life. In the larger sizes, motors can be custom built to closely match a non-standard horsepower within the normal speed range.
Send your message to us
Siemens ILE0001 Series Low Voltage AC Motor
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords























