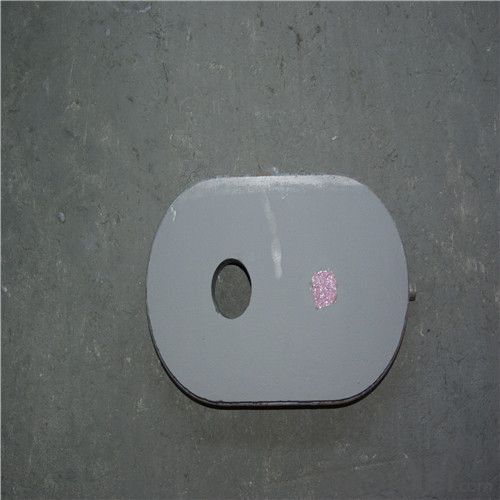
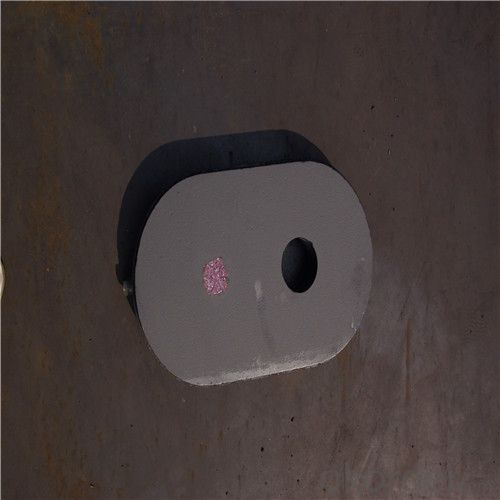
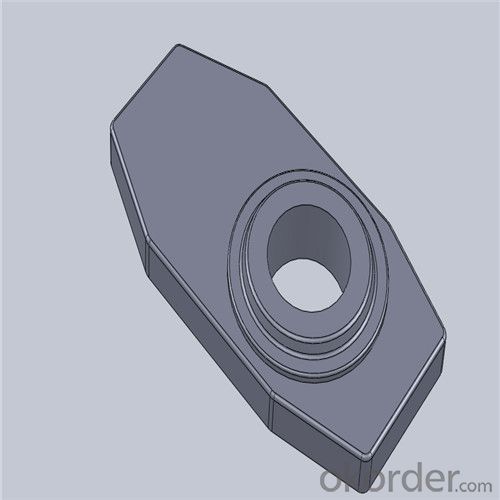
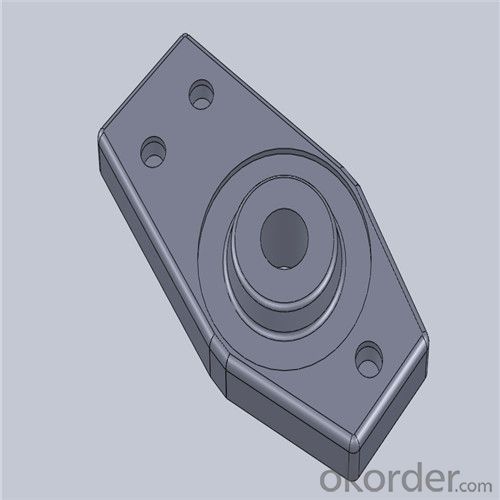
Monolithic Refractories High Temperature Ladle Sliding Gate Steel
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for High Performance Refractory Ladle Slide Gate
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Shape: | Plate | Material: | Alumina Block |
| SiO2 Content (%): | N/A | Al2O3 Content (%): | 80-90% | MgO Content (%): | N/A |
| CaO Content (%): | N/A | Refractoriness (Degree): | 1770°< Refractoriness< 2000° | CrO Content (%): | N/A |
| SiC Content (%): | N/A | Model Number: | CS80 | Brand Name: | |
| Product name: | High performance refractory ladle slide gate | Model No.: | cs80 | Brand name: | CMAX |
| Quality: | Al-C or Al-Zr-C | Service life: | 4-6 heats | Apparent porosity: | 7% Max |
| Bulk density:: | 3.1 MIN | C.C.S: | 120MPA | MOQ: | 100 pcs for trial |
| Delivery time: | 60 working days upon receipt of deposit |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Inner carton packing, outer wooden case suitable for long term sea shipping |
| Delivery Detail: | three months working days upon receipt of deposit |
Specifications
Surface flatness less than 0.05mm
High mechanical strength
Erosion resistance
Oxidation resistance
Thermal shock stability
General Chemical Analysis for refractory ladle slide gate :
slide gate plate widely including Alumina carbon and Alumina Zirconia Carbon slide gate plate, MgO and MgO-spinel slide gate plate,nonoxides bonding slide gate plateand unburned slide gate plate.
Alumina -Zirconia-Carbon material
| Al-Zr-C Material | |||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) |
| 85 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
Composite type: Al-Zr-C for working line, outer Al-C material
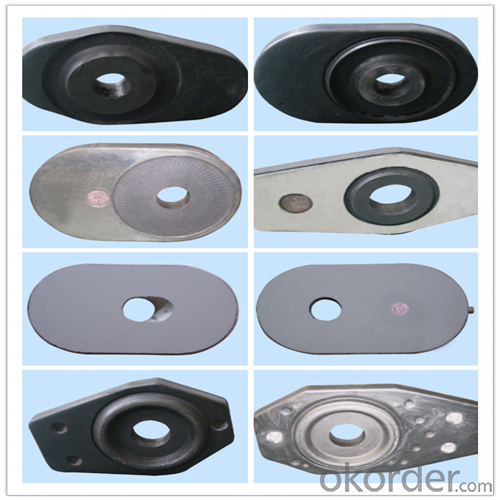

| Al-Zr-C & Al-C Material | ||||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S | |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) | |
| Inner side (Working face) | 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| Outside | 90 | 3 | 0 | 9 | 3 | |
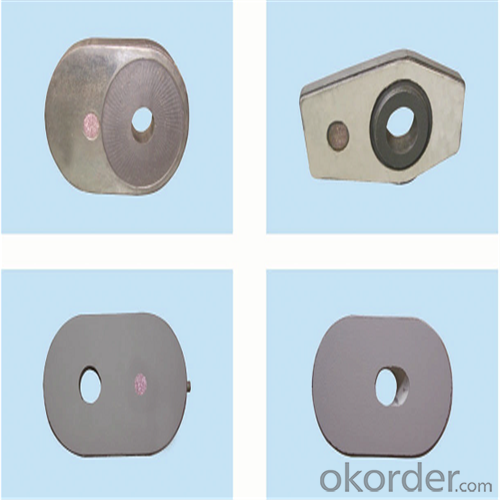

Using the raw materials of tabular alumina, zirconia-corundum, carbon and other high-grade additives, after sintering to obtain characteristics of oxidation resistance, scour strength, erosion resistance, thermal shock resistance, shape stable and long service life, made our products the preferred materials for the large and medium-sized steel ladle, refining ladle, series of alloy steel ladle, and tundish. Our high performance sintering sliding gates include alumina carbon , Al2O3-ZrO2-C, etc, can meet the needs of different steel grade.

Other Products

About us


Sample is on your request.
Welcome to visit our factory~
- Q: How do monolithic refractories improve the efficiency of reheating furnaces in steel plants?
- The efficiency of reheating furnaces in steel plants is greatly improved by the use of monolithic refractories. Specifically designed to withstand high temperatures and harsh conditions, these refractories are an ideal choice for steel plants. One important way in which monolithic refractories enhance furnace efficiency is by decreasing heat loss. With their excellent insulation properties, these refractories minimize the transfer of heat from the furnace to its surroundings. As a result, less energy is wasted and the furnace can maintain its desired temperature more effectively. Furthermore, monolithic refractories contribute to a more uniform and controlled distribution of heat within the furnace. They can be easily shaped and installed to create a seamless lining, ensuring that heat is evenly spread throughout the furnace chamber. This even distribution of heat eliminates any hotspots or cold spots, resulting in a more efficient heating process. Another crucial role of monolithic refractories is reducing downtime and maintenance requirements. Unlike traditional brick linings, which are prone to cracking and erosion, monolithic refractories offer superior resistance to wear and tear. This increased durability reduces the need for frequent repairs and replacements, allowing for uninterrupted furnace operation and increased overall efficiency. Moreover, monolithic refractories help improve energy efficiency by decreasing fuel consumption. The superior insulation properties of these refractories help retain heat within the furnace, reducing the amount of energy needed to maintain the desired temperature. This leads to significant energy savings for steel plants, as less fuel is required to achieve the same heating results. In conclusion, the efficiency of reheating furnaces in steel plants is significantly enhanced by the use of monolithic refractories. These refractories reduce heat loss, ensure uniform heat distribution, minimize downtime and maintenance, and decrease fuel consumption. By incorporating these refractories into their furnace linings, steel plants can increase productivity, reduce energy costs, and improve overall operational efficiency.
- Q: How are monolithic refractories installed and repaired in iron and steel plants?
- Monolithic refractories in iron and steel plants are typically installed through a process called gunning, where a specialized gunning machine is used to spray the refractory material onto the desired surface. The refractory material is mixed with water or a bonding agent to form a dense and durable lining. In terms of repairs, damaged or worn-out monolithic refractories are typically removed by mechanical means, such as jackhammers or pneumatic tools. The damaged area is then cleaned and prepared before new refractory material is applied using the gunning method. In some cases, patching materials may be used to repair smaller areas of damage. Overall, the installation and repair of monolithic refractories in iron and steel plants require skilled technicians and specialized equipment to ensure the optimum performance and longevity of the refractory lining.
- Q: How are monolithic refractories used in the iron and steel industry?
- Due to their exceptional performance and versatility, monolithic refractories are widely utilized in various applications within the iron and steel industry. Composed of a uniform material, these refractories serve as seamless linings in high-temperature environments. In the iron and steel industry, the significance of monolithic refractories cannot be overstated as they play a crucial role in multiple stages of the manufacturing process. A primary application is seen in the blast furnace, where the inside of the furnace is lined with monolithic refractories. This lining is exposed to exceedingly high temperatures and harsh chemical reactions. By providing excellent thermal insulation and resistance to chemical attack, monolithic refractories ensure the durability and longevity of the blast furnace. Another crucial application is witnessed in the steelmaking process, where monolithic refractories are used to line the ladles and tundish, utilized for transporting and pouring molten steel. These refractories are specially designed to withstand the corrosive nature and high temperatures of the molten steel, thus preventing contamination and guaranteeing the quality of the final product. Furthermore, monolithic refractories find application in various ancillary equipment and structures within the iron and steel industry. They are employed in furnaces, kilns, and other heat treatment systems to provide insulation and maintain high-temperature conditions. Additionally, they are used in the construction of chimneys, exhaust ducts, and other exhaust systems, where they offer thermal insulation and resistance against corrosive gases. Overall, the vital role played by monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry lies in their ability to provide high-temperature insulation, chemical resistance, and durability. They optimize the production process, enhance energy efficiency, and ensure the quality of the final product. With their exceptional performance and versatility, monolithic refractories have become an indispensable component within the iron and steel manufacturing industry.
- Q: What are the considerations for repairing and relining monolithic refractories?
- When repairing and relining monolithic refractories, there are several key considerations that need to be taken into account. First and foremost, it is crucial to assess the extent of the damage or deterioration in order to determine the appropriate repair method. Factors such as the type of refractory material, the operating conditions, and the expected service life must be considered. Additionally, it is essential to select the right refractory material for the repair or relining process. This involves evaluating the temperature range, chemical resistance, thermal conductivity, and mechanical properties of the refractory material to ensure it is compatible with the specific application. Another important consideration is the proper preparation of the surface before applying the repair material. This may involve removing any loose or damaged refractory, cleaning the surface thoroughly, and creating a suitable bonding surface to ensure optimal adhesion. Furthermore, the application technique and curing process of the repair material should be carefully followed to achieve the desired performance and durability. This may involve proper mixing, application thickness, drying time, and temperature control. Lastly, it is crucial to conduct regular inspections and maintenance to identify any signs of deterioration or damage early on. This proactive approach will help prevent major repairs or relining in the future and prolong the overall lifespan of the monolithic refractories.
- Q: Can monolithic refractories be used for the lining of continuous casting tundishes and molds?
- Indeed, tundishes and molds used in continuous casting can utilize monolithic refractories for their lining. These refractories consist of a single, uniform structure, in contrast to traditional refractories that are composed of multiple bricks or tiles. The utilization of monolithic refractories offers various advantages in the lining of tundishes and molds during continuous casting procedures. Firstly, their monolithic nature allows for convenient installation and repair, as they can be cast or gunned into place, eliminating the need for intricate brickwork. Consequently, this reduces downtime and enhances productivity. Furthermore, monolithic refractories demonstrate exceptional resistance to thermal shock, which is critical for tundishes and molds that undergo rapid and extreme temperature fluctuations throughout the casting process. Their high thermal conductivity additionally ensures efficient heat transfer, facilitating uniform cooling and solidification of the cast metal. Additionally, monolithic refractories exhibit commendable resistance to chemical attack, ensuring prolonged performance even in the presence of molten metal and slag. Their low porosity further prevents metal penetration and the formation of cracks or spalling. In summary, monolithic refractories are a practical and efficient choice for lining continuous casting tundishes and molds, offering superior performance, ease of installation, and durability in the demanding conditions of the casting process.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories improve the performance and efficiency of iron and steel production?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in improving the performance and efficiency of iron and steel production. These specialized materials are designed to withstand extreme temperatures, chemical reactions, and mechanical stresses, making them ideal for use in high-temperature industrial processes. One of the key ways in which monolithic refractories enhance performance is by providing a protective lining in furnaces, kilns, and other equipment used in iron and steel production. Due to their superior heat resistance, they protect the underlying structure from the intense heat and prevent any detrimental effects on the equipment. This results in reduced downtime, longer service life, and ultimately, increased overall efficiency. Monolithic refractories also ensure better thermal efficiency in the production process. By minimizing heat losses, these materials help to maintain a stable and uniform temperature distribution, thereby improving the energy efficiency of the system. This is particularly important in iron and steel production, where precise temperature control is crucial for achieving the desired metallurgical properties of the final product. Furthermore, monolithic refractories offer excellent resistance to chemical corrosion, erosion, and slag attacks. They act as a barrier between the molten metal and the refractory lining, preventing undesirable reactions and material degradation. This helps to maintain the integrity of the furnace lining, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements. Consequently, it leads to increased productivity and cost savings in the long run. Another advantage of monolithic refractories is their ability to be easily shaped, repaired, or replaced. Unlike traditional brick refractories, which require extensive labor and time-consuming installation, monolithic refractories can be applied in a more flexible and efficient manner. Their flexible nature allows for easy repair of damaged areas, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous production. In summary, the use of monolithic refractories significantly enhances the performance and efficiency of iron and steel production. These materials provide a protective lining, improve thermal efficiency, resist chemical corrosion, and offer easy installation and repair options. By optimizing the production process, monolithic refractories contribute to higher productivity, reduced downtime, and increased cost-effectiveness in the iron and steel industry.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories mitigate heat loss in iron and steel operations?
- Monolithic refractories are highly effective in mitigating heat loss in iron and steel operations due to their unique properties and composition. These refractories are made from a single, continuous material, making them resistant to cracks and gaps that could allow heat to escape. One key advantage of monolithic refractories is their excellent thermal conductivity and insulation properties. They have a low thermal conductivity, which means they can effectively restrict the transfer of heat from the hot areas to the cooler surroundings. This insulation property helps maintain high temperatures within the iron and steel operations, reducing heat loss to the environment. Another factor that contributes to the heat loss mitigation is the ability of monolithic refractories to form a tight seal with the metal structures they are applied to. They adhere well to the surfaces and fill in any gaps or irregularities, creating a solid barrier against heat loss. This seal minimizes the possibility of heat escaping, ensuring that the energy generated within the operations is effectively utilized. Furthermore, monolithic refractories have high resistance to thermal shock. In the iron and steel industry, extreme temperature fluctuations are common, which can lead to material deterioration and cracks. Monolithic refractories, with their high thermal shock resistance, are able to withstand these rapid temperature changes without compromising their structural integrity. This ensures the longevity and effectiveness of the refractories in mitigating heat loss. Overall, monolithic refractories play a crucial role in mitigating heat loss in iron and steel operations by providing excellent insulation, forming a tight seal, and withstanding thermal shock. These properties allow the refractories to maintain high temperatures within the operations, optimize energy utilization, and enhance the overall efficiency of the processes.
- Q: What are monolithic refractories?
- Monolithic refractories are a type of refractory material that is manufactured as a single, homogeneous unit, as opposed to being made from individual bricks or precast shapes. They are characterized by their ability to be shaped and installed in various applications without the need for joints or mortar, making them a versatile and convenient choice for lining furnaces, boilers, kilns, and other high-temperature industrial equipment. These refractories are typically composed of a mixture of refractory aggregates, binders, and additives, which are carefully selected and combined to provide the desired properties such as high temperature resistance, thermal shock resistance, and chemical durability. The aggregates used can include materials like alumina, magnesia, zirconia, and silica, while binders like clay, cement, or phosphate are added to hold the aggregates together. One of the advantages of monolithic refractories is their ability to adapt to complex shapes and designs, allowing for customized linings that can be tailored to specific equipment requirements. They are often applied by pouring, gunning, ramming, or spraying the refractory material onto the surface to be lined, allowing for quick and efficient installation. This eliminates the need for time-consuming bricklaying and jointing, reducing installation time and labor costs. Monolithic refractories are also known for their superior thermal conductivity, which enables them to withstand high temperatures and sudden temperature changes. They offer excellent insulation properties, preventing heat loss and improving energy efficiency in industrial processes. Furthermore, these refractories exhibit good resistance to chemical attack from molten metals, slags, gases, and other corrosive substances found in various industrial environments. This makes them highly suitable for applications in industries such as steel, cement, glass, petrochemical, and non-ferrous metals. In summary, monolithic refractories are a versatile and efficient solution for high-temperature applications. Their ability to be shaped and installed without joints or mortar, coupled with their excellent thermal conductivity and chemical resistance, make them a valuable choice for lining industrial equipment that operates under extreme conditions.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand chemical attack from molten metals and slag?
- Monolithic refractories are highly resistant to chemical attack from molten metals and slag due to their unique composition and structure. These refractories are typically made from a single, solid piece with no joints or seams, which minimizes the opportunity for chemical penetration. One of the key factors that enables monolithic refractories to withstand chemical attack is their high melting point. These materials are designed to have a melting point significantly higher than the temperature of the molten metal or slag they are exposed to. This prevents the refractory from melting or deforming when in contact with the hot molten substances. In addition to their high melting point, monolithic refractories are formulated with materials that have excellent chemical resistance. They are often composed of a combination of oxides, such as alumina, magnesia, and zirconia, which have a strong affinity for oxygen and form stable compounds. This allows the refractory to form a protective oxide layer on its surface when exposed to molten metals and slag, effectively shielding it from chemical attack. Furthermore, the dense and compact structure of monolithic refractories plays a crucial role in their resistance to chemical attack. The absence of joints and seams minimizes the chances of molten metals and slag infiltrating the refractory and causing chemical reactions. This dense structure also reduces the porosity of the material, making it less permeable to aggressive substances. Moreover, manufacturers often add specialized additives to monolithic refractories to enhance their chemical resistance. These additives can include fibers, binders, and corrosion inhibitors, which further improve the refractory's ability to withstand chemical attack. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are designed to withstand chemical attack from molten metals and slag through their high melting point, chemical-resistant composition, dense structure, and specialized additives. These properties allow them to maintain their integrity and performance even in the harshest environments, making them an ideal choice for applications involving high-temperature and corrosive substances.
- Q: What are the recommended storage and handling practices for monolithic refractories?
- The recommended storage and handling practices for monolithic refractories are crucial to ensure their optimal performance and longevity. Here are some key practices to follow: 1. Storage: Monolithic refractories should be stored in a clean, dry, and well-ventilated area. The storage facility should be protected from moisture, extreme temperatures, and direct exposure to sunlight. Ideally, the refractories should be stored on pallets or racks to prevent contact with the ground and minimize the risk of damage. 2. Handling: It is essential to handle monolithic refractories with care to avoid any physical damage. Refractories should be lifted and moved using appropriate lifting equipment, such as forklifts or cranes, to prevent excessive stress or strain on the material. Avoid dropping or dragging the refractories, as this can lead to cracks or fractures. 3. Packaging: If the monolithic refractories are supplied in packaging, it is important to inspect the packaging for any signs of damage or moisture before accepting the delivery. Damaged packaging can indicate potential damage to the refractory material. If any anomalies are noticed, it is advisable to inform the supplier immediately. 4. Moisture control: Monolithic refractories are susceptible to moisture absorption, which can lead to reduced performance and structural integrity. It is crucial to protect the refractories from direct contact with water or excessive humidity during storage and handling. If refractories become wet, they should be dried thoroughly before use to eliminate any absorbed moisture. 5. Stack height: When storing monolithic refractories, it is important to consider the stack height. Excessive stacking can result in pressure on the lower layers, leading to deformation or cracking. Follow the manufacturer's recommendations for maximum stack height to ensure the refractories' structural integrity. 6. Regular inspection: Regularly inspect the refractory material for any signs of damage or degradation during storage and handling. Look for cracks, spalling, or any other visible abnormalities. If any issues are identified, consult the manufacturer or a refractory expert for guidance on whether the material is still suitable for use. By following these recommended storage and handling practices, you can minimize the risk of damage to monolithic refractories and optimize their performance, ultimately extending their service life and ensuring their effectiveness in high-temperature applications.
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories High Temperature Ladle Sliding Gate Steel
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords