Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry:Mullite Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or L/C
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 MT m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
General Information of Mullite Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
ALRE mullite based mortar for hot blast stove made as per international standards, is known for its low thermal conductivity, high refractoriness, and excellent thermal shock resistance.
Technical data of Mullite Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
Item | High Alumina Mortar | |
Al2O3(%)≥ | 70 | |
M.O.R. (MPa) ≥ | 110℃×24h | 4 |
1200℃×3h | — | |
1300℃×2h | 6 | |
1400℃×2h | — | |
1500℃×2h | — | |
Grain size(%) | 110℃×24h (≤) | 1 |
1200℃×3h (≥) | 50 | |
Refractoriness (℃) ≥ | 1790 | |
Refractoriness Under Load(℃) ≥ | 1550 | |
Adhesive Time(min) | 1-2 | |
Production line and Packing of Mullite Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove


Feature of Mullite Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
Excellent thermal shock resistance
Excellent mechanical strength
Low thermal conductivity
High refractoriness
Application of Mullite Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
ALRE tmullite based mortar for hot blast stove can be used widely for same material masonry.
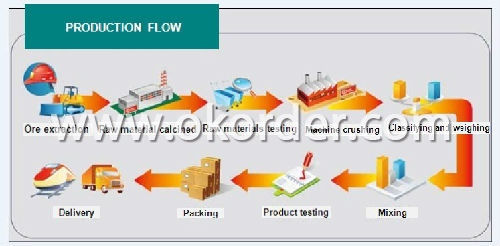
Production Flow of Mullite Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
- Q: How do monolithic refractories resist chemical corrosion in iron and steel applications?
- Monolithic refractories resist chemical corrosion in iron and steel applications through their inherent properties and composition. They are designed to have high chemical stability and resistance to react with molten metals, slag, and other corrosive substances present in these applications. Additionally, monolithic refractories are usually formulated with specific additives and binders that enhance their resistance to chemical attack. This combination of properties and composition allows them to withstand the aggressive environment of iron and steel applications without significant degradation or corrosion.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the overall safety of iron and steel operations?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in ensuring the overall safety of iron and steel operations. These refractories are designed to withstand extreme temperatures, chemical reactions, and mechanical stresses, providing a protective barrier to the furnaces, ladles, and other equipment used in these operations. By maintaining the integrity of the refractory lining, monolithic refractories prevent leaks, minimize the risk of thermal shock, and reduce the chances of equipment failure or accidents. This helps to safeguard the workers, prevent damage to the infrastructure, and ensure the uninterrupted production of iron and steel, thus contributing to the overall safety of the operations.
- Q: What are the key differences between acidic and basic monolithic refractories?
- The key differences between acidic and basic monolithic refractories lie in their chemical compositions and their behavior in different environments. Acidic monolithic refractories are primarily composed of acidic oxides such as silica (SiO2) or alumina (Al2O3). These materials have a high resistance to acidic environments and are commonly used in industries where they come into contact with acidic gases or liquids. Acidic refractories are characterized by their ability to withstand high temperatures and resist chemical erosion. They are generally not suitable for use in basic or alkaline conditions, as they can react with basic compounds and lose their effectiveness. On the other hand, basic monolithic refractories are composed of basic oxides such as magnesia (MgO) or dolomite (MgO-CaO). These materials have a high resistance to basic or alkaline environments and are commonly used in industries where they come into contact with basic compounds such as lime or cement. Basic refractories are characterized by their ability to withstand high temperatures and resist chemical erosion from basic compounds. They are generally not suitable for use in acidic conditions, as they can react with acidic compounds and lose their effectiveness. In terms of their physical properties, acidic monolithic refractories tend to have higher melting points and better thermal shock resistance compared to basic monolithic refractories. This is due to the higher melting points of acidic oxides and their ability to form stable silicate or aluminate structures at high temperatures. On the other hand, basic monolithic refractories generally have higher density and better resistance to penetration by molten materials. In conclusion, the key differences between acidic and basic monolithic refractories lie in their chemical compositions and their behavior in different environments. Acidic refractories are suitable for acidic conditions, have higher melting points, and better thermal shock resistance, while basic refractories are suitable for basic conditions, have higher density, and better resistance to penetration by molten materials.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories perform in reheating furnace applications?
- Due to their exceptional thermal stability, strength, and resistance to thermal shock, monolithic refractories are highly effective in reheating furnace applications. These refractories are specifically designed to withstand the harsh operating conditions commonly found in reheating furnaces, including high temperatures and rapid temperature changes. One major advantage of using monolithic refractories in reheating furnace applications is their ability to provide a seamless lining. Unlike traditional brick refractories that require extensive installation and joints, monolithic refractories can be easily applied as a single, homogeneous layer. This eliminates the risk of thermal stress and cracking at joints, ensuring a more reliable and durable lining. Furthermore, monolithic refractories offer excellent thermal insulation properties, which help conserve energy and reduce heat loss in the reheating furnace. This not only improves overall furnace efficiency but also reduces operational costs. In addition to their insulation properties, monolithic refractories exhibit high mechanical strength, allowing them to withstand the mechanical stress and abrasion caused by the movement of the furnace charge. They also have good resistance to chemical attack from gases, slags, and molten metals commonly encountered in reheating furnace operations. Another advantage of monolithic refractories is their ease of repair and patching, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous furnace operation. They can be easily shaped and molded to fit various furnace geometries, making them highly versatile and adaptable to different reheating furnace designs. In summary, monolithic refractories offer exceptional performance in reheating furnace applications by providing superior thermal stability, strength, and resistance to thermal shock. Their seamless lining, thermal insulation properties, and resistance to mechanical and chemical stress make them an ideal choice for ensuring reliable and efficient furnace operation.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories prevent slag penetration?
- Monolithic refractories prevent slag penetration through several mechanisms. Firstly, monolithic refractories are made up of high-quality materials that have excellent resistance to slag attack. These materials, such as alumina, silica, and magnesia, have a high melting point and can withstand the corrosive nature of the slag. Secondly, monolithic refractories are designed with a dense and compact structure that minimizes the porosity. Slag penetration occurs when the molten slag infiltrates the pores and cracks of the refractory material. By reducing the porosity, monolithic refractories create a barrier that restricts the entry of slag into the refractory lining. Additionally, monolithic refractories can be chemically bonded to the substrate, forming a strong and impermeable bond. This bond further enhances the resistance to slag penetration by preventing any gaps or weak points where the slag can penetrate. Moreover, monolithic refractories can be designed with a high thermal shock resistance. Slag penetration is often intensified by thermal cycling, where the refractory material undergoes rapid temperature changes. Monolithic refractories with high thermal shock resistance can withstand these temperature fluctuations without cracking or spalling, thus reducing the risk of slag penetration. Furthermore, the proper installation and maintenance of monolithic refractories play a crucial role in ensuring their effectiveness against slag penetration. The refractory lining needs to be properly designed, using appropriate thickness and geometry, to provide maximum protection against slag attack. Regular inspection and repair of any damaged or worn-out areas can also prevent slag penetration. In conclusion, monolithic refractories prevent slag penetration through their excellent resistance to slag attack, dense structure, chemical bonding, high thermal shock resistance, and proper installation and maintenance. These factors work together to create a strong and impermeable barrier that protects the underlying substrate from the corrosive effects of slag.
- Q: What are the considerations for selecting monolithic refractories for ladles and tundishes?
- When selecting monolithic refractories for ladles and tundishes, there are several important considerations to keep in mind. 1. Temperature resistance: Ladles and tundishes are exposed to extremely high temperatures in metal casting processes. It is crucial to choose monolithic refractories that can withstand and maintain their strength and integrity at these elevated temperatures. 2. Thermal shock resistance: Ladles and tundishes are subjected to rapid temperature changes, especially during the pouring and cooling processes. Monolithic refractories with good thermal shock resistance can prevent cracking and spalling, ensuring the longevity and performance of the ladles and tundishes. 3. Erosion and corrosion resistance: Molten metal, slag, and other corrosive substances can cause erosion and chemical attack on refractory linings. Selecting monolithic refractories with excellent erosion and corrosion resistance can prolong the service life of ladles and tundishes, reducing maintenance and downtime. 4. Mechanical strength: Ladles and tundishes are frequently handled, transported, and subjected to mechanical stresses. Monolithic refractories with adequate mechanical strength can withstand these forces without cracking or breaking, ensuring the structural integrity of ladles and tundishes. 5. Application method: The method of applying monolithic refractories is another consideration. Depending on the size and shape of the ladles and tundishes, as well as the available equipment and expertise, different application methods such as gunning, casting, ramming, or spraying may be used. The selected monolithic refractories should be compatible with the chosen application method. 6. Thermal conductivity: The thermal conductivity of monolithic refractories can affect heat transfer in ladles and tundishes. Low thermal conductivity refractories can help minimize heat loss and improve energy efficiency. 7. Cost-effectiveness: While performance and durability are essential, it is also important to consider the cost-effectiveness of the selected monolithic refractories. This includes factors such as the initial cost of the refractories, installation and maintenance costs, as well as the expected service life. Balancing performance with cost can help optimize the overall investment in ladles and tundishes. Overall, the considerations for selecting monolithic refractories for ladles and tundishes involve a combination of temperature resistance, thermal shock resistance, erosion and corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, application method compatibility, thermal conductivity, and cost-effectiveness. By carefully evaluating these factors, one can choose the most suitable monolithic refractories that meet the specific requirements of ladles and tundishes in metal casting processes.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories prevent thermal shock in the iron and steel industry?
- The iron and steel industry heavily relies on monolithic refractories to prevent thermal shock. These refractories offer exceptional thermal insulation and resistance to extreme temperatures, playing a vital role in maintaining the integrity of the refractory lining. Thermal shock occurs when there is a sudden and significant change in temperature, leading to stress and cracks in the refractory lining. Given the extremely high temperatures that can be reached in the iron and steel industry, the risk of thermal shock is particularly pronounced. To combat this, monolithic refractories possess a low thermal conductivity, enabling them to effectively insulate against rapid temperature fluctuations. This insulation property allows them to endure the extreme temperatures involved in the iron and steel production process without compromising their structural integrity. Moreover, monolithic refractories are specifically engineered to exhibit high thermal shock resistance. This means they can effectively absorb and distribute the thermal stresses caused by temperature variations, thereby minimizing the likelihood of cracking or spalling. Aside from their exceptional thermal insulation and shock resistance, monolithic refractories also demonstrate outstanding corrosion and erosion resistance. This is especially important in the corrosive environment of the iron and steel industry, where molten metals, slag, and gases are present. By providing a dependable and long-lasting lining in furnaces, ladles, and other equipment utilized in the iron and steel industry, monolithic refractories ensure that thermal shock is mitigated. Consequently, this helps to maintain the efficiency and productivity of the production process while extending the lifespan of the equipment.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the reduction of heat loss in ladles and tundishes?
- The use of monolithic refractories is crucial in reducing heat loss in ladles and tundishes. These refractories are designed to have excellent thermal insulation properties, which effectively minimize the transfer of heat from the molten metal to the surrounding environment. Conduction is a key factor that contributes to heat loss in ladles and tundishes. It occurs when heat is transferred through direct contact with the refractory lining. However, monolithic refractories are specifically engineered to have low thermal conductivity, making them efficient in reducing heat transfer through conduction. This, in turn, helps to maintain the desired temperature of the molten metal for longer periods, resulting in lower energy consumption and improved process efficiency. Additionally, monolithic refractories also aid in reducing heat loss through radiation. They have high emissivity, meaning they emit a significant amount of thermal radiation. This emitted radiation creates a heat shield around the molten metal, preventing heat loss to the surroundings. By effectively trapping the radiant heat, monolithic refractories contribute to maintaining the desired temperature in ladles and tundishes, minimizing heat loss. Apart from their thermal insulation properties, monolithic refractories also offer excellent resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress. This ensures that they remain intact and functional even in the harsh operating conditions of ladles and tundishes. The durability of these refractories further contributes to the reduction of heat loss by preventing any cracks or gaps in the refractory lining that could facilitate heat transfer. To summarize, monolithic refractories play a significant role in reducing heat loss in ladles and tundishes by minimizing heat transfer through conduction and radiation. Their thermal insulation properties, combined with their resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress, help to maintain the desired temperature of the molten metal, improve energy efficiency, and enhance the overall performance of these metallurgical vessels.
- Q: What are the latest advancements in monolithic refractories for the iron and steel industry?
- One of the latest advancements in monolithic refractories for the iron and steel industry is the development of high-performance castables with enhanced properties. These castables are designed to withstand the extreme temperatures and harsh conditions of iron and steel production processes. One major advancement is the use of advanced bonding systems that provide excellent strength and resistance to thermal shock. These bonding systems, such as nano-bonding technology, help improve the overall performance and durability of monolithic refractories. Another significant development is the introduction of low cement castables. These castables contain a reduced amount of cement, resulting in improved high-temperature strength and erosion resistance. This advancement is particularly beneficial for applications in the iron and steel industry where thermal cycling and mechanical stress are common. Additionally, there have been advancements in the composition of monolithic refractories. The use of advanced raw materials, such as high-quality aggregates and additives, has led to improved thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and thermal insulation properties. These developments allow for more efficient and sustainable iron and steel production processes. Furthermore, recent advancements have focused on the development of self-flow castables. These castables have excellent flowability, allowing for easy installation and maintenance of refractory linings. This advancement helps reduce installation time and costs while also ensuring improved lining performance. Overall, the latest advancements in monolithic refractories for the iron and steel industry have resulted in improved performance, durability, and efficiency. These advancements enable the industry to enhance its production processes, reduce downtime, and increase overall productivity.
- Q: What are the specific requirements of monolithic refractories for continuous casting applications?
- The specific requirements of monolithic refractories for continuous casting applications include high thermal shock resistance, excellent erosion resistance, good thermal conductivity, low shrinkage, and high refractoriness. These refractories must also have good flowability and workability to ensure easy installation and maintenance. Additionally, they should have a high degree of chemical stability to withstand the harsh conditions of molten metal and slag in continuous casting processes.
1. Manufacturer Overview
| Location | Henan, China |
| Year Established | 2007 |
| Annual Output Value | Above US$ 200 Million |
| Main Markets | North America;Asia;Western Europe;Africa;Russia;Middle East |
| Company Certifications | ISO 9001:2008 |
2. Manufacturer Certificates
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period |
3. Manufacturer Capability
| a) Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | Tianjin |
| Export Percentage | 20% - 30% |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | 10-20 People |
| Language Spoken: | English; Chinese |
| b) Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | Above 150,000 square meters |
| No. of Production Lines | Above 10 |
| Contract Manufacturing | Installation guide, OEM Service Offered |
| Product Price Range | High; Average |
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry:Mullite Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or L/C
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 MT m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords