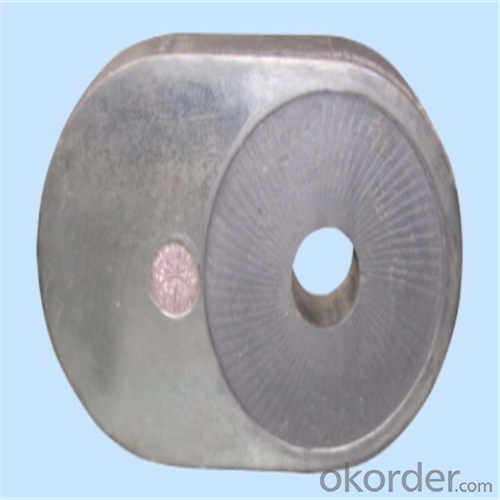
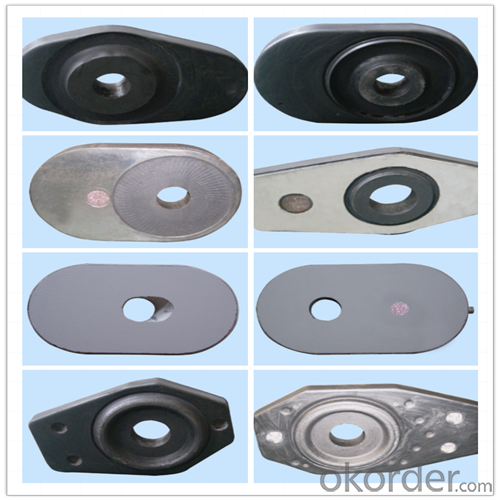
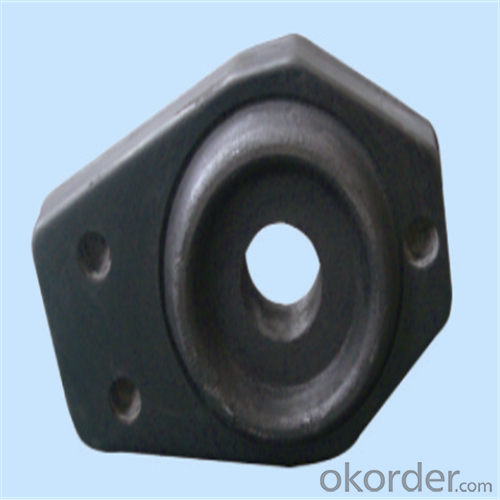
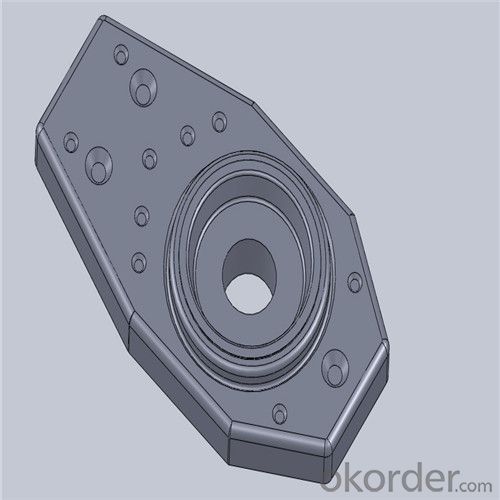
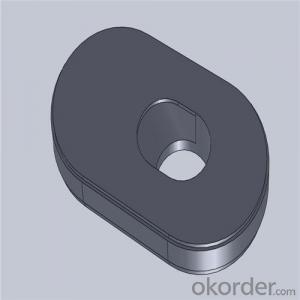
Monolithic Refractories High Performance Ladle Slide Gate for Iron and Steel Industry 2024
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for High Performance Refractory Ladle Slide Gate
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Shape: | Plate | Material: | Alumina Block |
| SiO2 Content (%): | N/A | Al2O3 Content (%): | 80-90% | MgO Content (%): | N/A |
| CaO Content (%): | N/A | Refractoriness (Degree): | 1770°< Refractoriness< 2000° | CrO Content (%): | N/A |
| SiC Content (%): | N/A | Model Number: | CS80 | Brand Name: | |
| Product name: | High performance refractory ladle slide gate | Model No.: | cs80 | Brand name: | CMAX |
| Quality: | Al-C or Al-Zr-C | Service life: | 4-6 heats | Apparent porosity: | 7% Max |
| Bulk density:: | 3.1 MIN | C.C.S: | 120MPA | MOQ: | 100 pcs for trial |
| Delivery time: | 60 working days upon receipt of deposit |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Inner carton packing, outer wooden case suitable for long term sea shipping |
| Delivery Detail: | three months working days upon receipt of deposit |
Specifications
Surface flatness less than 0.05mm
High mechanical strength
Erosion resistance
Oxidation resistance
Thermal shock stability
Using the raw materials of tabular alumina, zirconia-corundum, carbon and other high-grade additives, after sintering to obtain characteristics of oxidation resistance, scour strength, erosion resistance, thermal shock resistance, shape stable and long service life, made our products the preferred materials for the large and medium-sized steel ladle, refining ladle, series of alloy steel ladle, and tundish. Our high performance sintering sliding gates include alumina carbon , Al2O3-ZrO2-C, etc, can meet the needs of different steel grade.
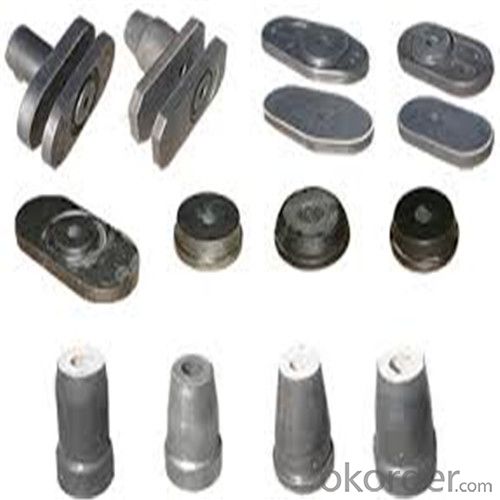


General Chemical Analysis for refractory ladle slide gate :
slide gate plate widely including Alumina carbon and Alumina Zirconia Carbon slide gate plate, MgO and MgO-spinel slide gate plate,nonoxides bonding slide gate plateand unburned slide gate plate.
Alumina -Zirconia-Carbon material
| Al-Zr-C Material | |||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) |
| 85 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
Composite type: Al-Zr-C for working line, outer Al-C material
| Al-Zr-C & Al-C Material | ||||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S | |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) | |
| Inner side (Working face) | 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| Outside | 90 | 3 | 0 | 9 | 3 | |
Other Products:


About us


Sample is on your request.
Welcome to visit our factory~
- Q: What are the quality control measures for monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry?
- To ensure the efficiency and safety of the production process in the iron and steel industry, it is crucial to implement quality control measures for monolithic refractories. These measures encompass a range of inspections and tests throughout the manufacturing and installation stages. To begin with, rigorous testing is conducted on the raw materials used for monolithic refractories. This involves analyzing the chemical composition, particle size distribution, and impurity content. These tests are essential to ensure that the ingredients meet the required specifications and are suitable for the intended application. During the production process, the focus of quality control measures lies in monitoring the mixing and blending of the materials. This ensures that a homogeneous mixture is achieved, preventing any inconsistencies in the final product. Additionally, the density and viscosity of the refractory castables or plastics are checked to maintain the desired physical properties. Once the monolithic refractories are manufactured, they undergo several performance tests. These tests involve determining properties such as cold crushing strength, modulus of rupture, and thermal conductivity. These characteristics are crucial in ensuring that the refractories can withstand the extreme temperatures and mechanical stress present in the iron and steel industry. Aside from laboratory testing, quality control measures also involve on-site inspections during installation. This includes verifying the correct application techniques, such as proper vibration, curing, and drying procedures. It is of utmost importance to ensure that the monolithic refractories are applied correctly to achieve optimal performance and longevity. Furthermore, regular sampling and monitoring of the refractories' performance are carried out during operation. This allows for the early detection of any signs of degradation or wear, enabling proactive maintenance and replacement before any significant issues arise. In conclusion, the quality control measures for monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry encompass comprehensive testing, monitoring, and inspection procedures. These measures are implemented to guarantee the reliability, durability, and efficiency of the refractories, ultimately contributing to the smooth operation of the iron and steel production processes.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to reducing emissions in iron and steel processes?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in reducing emissions in iron and steel processes by providing a more efficient and sustainable lining solution compared to traditional brick refractories. Firstly, monolithic refractories are characterized by their homogeneous structure, which allows for easier installation and repair. This feature reduces the downtime required for maintenance, resulting in increased productivity and ultimately lower emissions. In contrast, brick refractories require more extensive labor and time-consuming procedures for installation and repair, leading to longer shutdown periods and increased emissions. Moreover, monolithic refractories exhibit superior thermal insulation properties. By minimizing heat loss from the furnace or kiln, they enable higher energy efficiency and reduce the fuel consumption required for achieving the desired temperature. This reduction in fuel usage directly translates to lower emissions of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, contributing to the overall environmental sustainability of iron and steel processes. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer excellent resistance to thermal and chemical wear, enhancing the durability and lifespan of the lining. This durability reduces the frequency of refractory replacement, resulting in reduced waste generation and resource consumption. By extending the service life of the lining, monolithic refractories contribute to reducing the environmental impact associated with the production and disposal of refractory materials. Furthermore, monolithic refractories can be formulated with specialized compositions and additives to enhance their resistance to corrosion and erosion, common challenges in iron and steel processes. By minimizing the wear and tear on the refractory lining, they help maintain the integrity of the furnace or kiln, preventing the leakage of harmful gases and pollutants that would otherwise contribute to emissions. In summary, monolithic refractories contribute to reducing emissions in iron and steel processes through their ease of installation and repair, superior thermal insulation properties, increased durability, and resistance to corrosion and erosion. By optimizing energy efficiency, minimizing downtime, and reducing waste generation, monolithic refractories offer a sustainable solution for the industry, aligning with the global efforts to combat climate change and promote environmental stewardship.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories improve the efficiency of ladle and tundish preheating furnaces?
- Monolithic refractories improve the efficiency of ladle and tundish preheating furnaces by providing superior insulation and heat retention properties. These refractories are designed to withstand high temperatures and reduce heat loss, ensuring that the furnaces reach and maintain the desired preheating temperatures more efficiently. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer excellent thermal shock resistance, preventing cracks and damage that can negatively impact furnace performance. Overall, the use of monolithic refractories in ladle and tundish preheating furnaces helps to optimize energy consumption and enhance the overall efficiency of the preheating process.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories prevent slag penetration?
- Monolithic refractories prevent slag penetration through several mechanisms. Firstly, monolithic refractories are made up of high-quality materials that have excellent resistance to slag attack. These materials, such as alumina, silica, and magnesia, have a high melting point and can withstand the corrosive nature of the slag. Secondly, monolithic refractories are designed with a dense and compact structure that minimizes the porosity. Slag penetration occurs when the molten slag infiltrates the pores and cracks of the refractory material. By reducing the porosity, monolithic refractories create a barrier that restricts the entry of slag into the refractory lining. Additionally, monolithic refractories can be chemically bonded to the substrate, forming a strong and impermeable bond. This bond further enhances the resistance to slag penetration by preventing any gaps or weak points where the slag can penetrate. Moreover, monolithic refractories can be designed with a high thermal shock resistance. Slag penetration is often intensified by thermal cycling, where the refractory material undergoes rapid temperature changes. Monolithic refractories with high thermal shock resistance can withstand these temperature fluctuations without cracking or spalling, thus reducing the risk of slag penetration. Furthermore, the proper installation and maintenance of monolithic refractories play a crucial role in ensuring their effectiveness against slag penetration. The refractory lining needs to be properly designed, using appropriate thickness and geometry, to provide maximum protection against slag attack. Regular inspection and repair of any damaged or worn-out areas can also prevent slag penetration. In conclusion, monolithic refractories prevent slag penetration through their excellent resistance to slag attack, dense structure, chemical bonding, high thermal shock resistance, and proper installation and maintenance. These factors work together to create a strong and impermeable barrier that protects the underlying substrate from the corrosive effects of slag.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand the alkali attacks in cement kiln applications?
- Monolithic refractories are able to withstand alkali attacks in cement kiln applications due to their unique composition and structure. These refractories are made from a single material, which allows for a more uniform and dense structure compared to traditional brick refractories. When exposed to alkali attacks in cement kilns, monolithic refractories form a protective layer on the surface which acts as a barrier against the corrosive alkali substances. This protective layer is typically formed by reactions between the alkali substances and the refractory material, resulting in the formation of a stable compound that is resistant to further attacks. Furthermore, monolithic refractories have high chemical resistance, which enables them to withstand the aggressive conditions inside cement kilns. They are designed to have low porosity, which prevents the penetration of alkali substances into the refractory material. This reduces the chances of alkali attacks and prolongs the service life of the refractory lining. In addition, monolithic refractories are often made from materials with high melting points, such as alumina, silica, and magnesia. These materials have excellent thermal stability, allowing the refractories to withstand the high temperatures in cement kilns without significant degradation. This thermal stability is crucial in preventing the formation of cracks and spalling, which can lead to alkali penetration and subsequent damage to the refractory lining. Overall, monolithic refractories are specifically engineered to resist alkali attacks in cement kiln applications by forming a protective layer, having high chemical resistance, and exhibiting excellent thermal stability. These properties make them an ideal choice for lining cement kilns and ensuring their long-term performance and durability.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the overall efficiency of ladle cleaning operations?
- Enhancing the overall efficiency of ladle cleaning operations is a crucial role played by monolithic refractories. Composed of a single, homogeneous structure, these refractory materials offer several key advantages that contribute to improved efficiency. To begin with, monolithic refractories possess exceptional thermal insulation properties. This means they can withstand high temperatures without cracking or deteriorating, thereby allowing for more efficient and effective ladle cleaning operations. By consistently maintaining a specific temperature, these refractories minimize heat loss and ensure uninterrupted and timely completion of the cleaning process. Furthermore, monolithic refractories exhibit high resistance to chemical attacks. In steelmaking processes, ladles often come into contact with aggressive molten metals and slag that can erode and corrode the refractory lining. However, monolithic refractories are designed specifically to endure these harsh conditions, providing a longer service life and reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements. This not only saves time but also reduces the overall cost of ladle maintenance. In addition, monolithic refractories possess excellent flowability and workability. They can be easily shaped and installed in the ladle lining, enabling quick and precise application. This ease of installation results in shorter downtime during ladle cleaning operations, as the refractory lining can be swiftly repaired or replaced. Moreover, the flowability of monolithic refractories ensures better coverage and adherence to the ladle's surface, leaving no gaps or weak points. This enhances the overall effectiveness of the cleaning process and prevents potential contamination or reactivity issues. In conclusion, monolithic refractories significantly contribute to the overall efficiency of ladle cleaning operations by providing exceptional thermal insulation, high resistance to chemical attacks, and easy workability. These properties lead to reduced downtime, increased durability, and cost savings, making monolithic refractories a vital component in optimizing ladle cleaning processes.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand the mechanical impacts in ladle lip applications?
- Monolithic refractories are able to withstand the mechanical impacts in ladle lip applications due to their unique properties and composition. Firstly, monolithic refractories are made from a single, homogenous material, which provides them with a high level of structural integrity. This means that they are less vulnerable to cracking or breaking when subjected to mechanical impacts. Additionally, monolithic refractories often contain additives such as fibers or aggregates, which further enhance their resistance to mechanical stresses. These additives help to distribute the forces applied to the refractory material, reducing the concentration of stress points and increasing its overall durability. Furthermore, the application process of monolithic refractories allows for a seamless and continuous lining, eliminating the presence of joints or weak points that are susceptible to mechanical damage. This ensures a more uniform distribution of the impacts and enhances the material's ability to withstand them. Moreover, monolithic refractories can be designed with specific compositions and formulations that are tailored to resist mechanical impacts. Various binders and additives can be incorporated to enhance the material's toughness, impact resistance, and overall mechanical strength. Finally, the selection of monolithic refractories for ladle lip applications also takes into consideration the operating conditions, such as temperature and chemical exposure. By choosing refractories that are suitable for these conditions, their mechanical properties can be optimized to withstand the specific challenges posed by ladle lip applications. In summary, monolithic refractories are able to withstand mechanical impacts in ladle lip applications due to their homogenous structure, the inclusion of additives, the seamless application process, and the ability to customize their composition. These factors contribute to their ability to resist cracking, breaking, and other forms of mechanical damage, ensuring their longevity and effectiveness in ladle lip applications.
- Q: What are the key factors affecting the installation and curing of monolithic refractories?
- There are several key factors that can affect the installation and curing of monolithic refractories. These factors include the selection of the appropriate refractory material, proper surface preparation, correct mixing and application techniques, controlled drying and curing process, and adherence to manufacturer's guidelines and recommendations. Additionally, factors such as temperature, humidity, and atmospheric conditions can also impact the installation and curing of monolithic refractories.
- Q: What are the main factors affecting the erosion resistance of monolithic refractories?
- The main factors affecting the erosion resistance of monolithic refractories include the type and composition of the refractory material, the operating temperature and environment, the mechanical strength and density of the refractory, and the presence of impurities or contaminants. Additionally, the design and installation of the refractory lining, as well as the method of installation, can also influence its erosion resistance.
- Q: What are the advantages of using monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry?
- Using monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry offers several advantages. Firstly, they have excellent thermal insulation properties, allowing them to withstand and retain high temperatures. This is crucial in the manufacturing process as it ensures structural integrity, reduces the risk of failure, and maintains operational efficiency. Secondly, monolithic refractories have superior corrosion resistance. This protects equipment and structures from degradation caused by harsh chemicals and corrosive agents. It extends the lifespan of the refractories, reduces maintenance costs, and minimizes downtime. Another advantage is the versatility of monolithic refractories. Unlike traditional refractory bricks, they can be cast or sprayed into various shapes and sizes. This makes installation easier and allows for better lining design and improved performance. They can also be easily repaired or patched, minimizing production disruptions. Furthermore, monolithic refractories have excellent mechanical strength and abrasion resistance. This ensures they can withstand the constant movement and processing of materials in the industry without compromising performance. Lastly, using monolithic refractories can lead to cost savings. They require less labor and time for installation, resulting in reduced costs. Their longer lifespan, resistance to corrosion and thermal shock, also reduces the need for frequent replacements, minimizing maintenance and downtime costs. In conclusion, monolithic refractories offer advantages such as thermal insulation, corrosion resistance, versatility, mechanical strength, and cost savings. They are an ideal choice for lining furnaces, ladles, and other equipment used in the production of iron and steel.
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories High Performance Ladle Slide Gate for Iron and Steel Industry 2024
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords