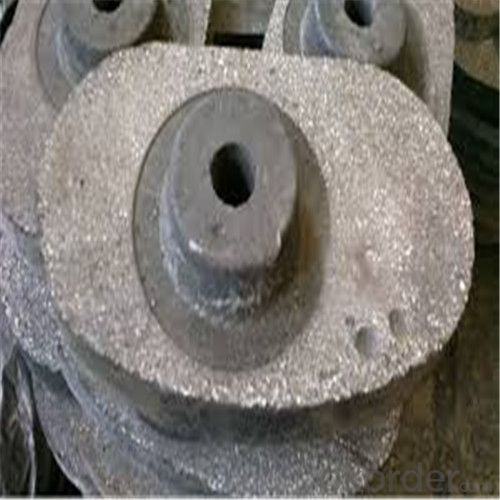
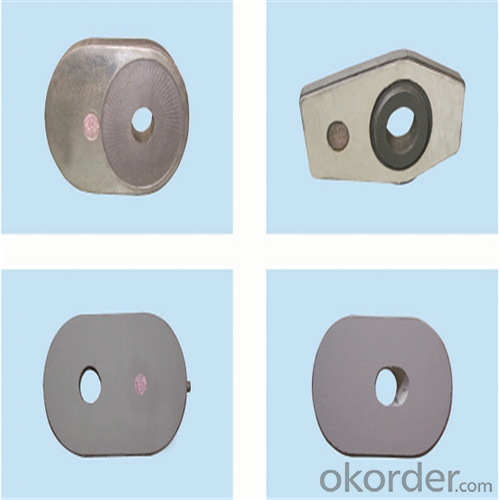
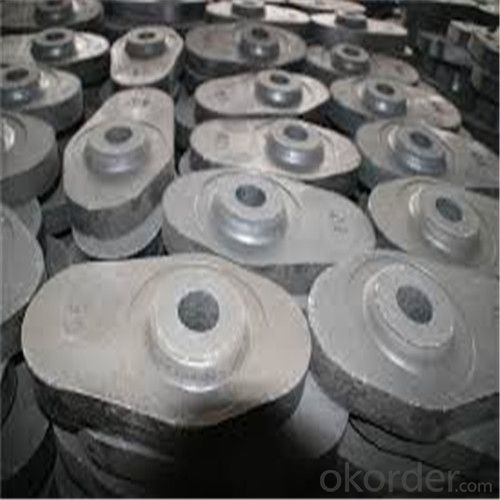
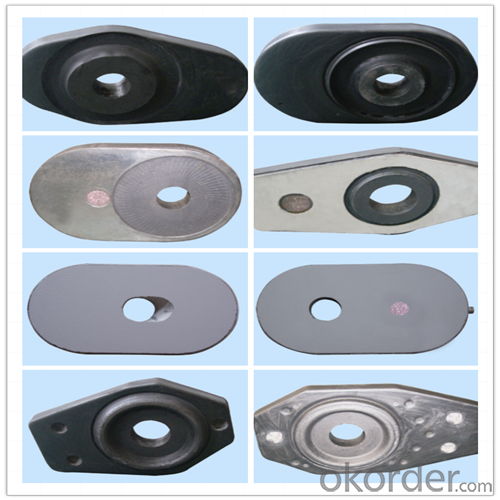
Monolithic Refractories High Temperature Ladle Sliding Gate for Iron and Steel Industry 2024
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for High Performance Refractory Ladle Slide Gate
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Shape: | Plate | Material: | Alumina Block |
| SiO2 Content (%): | N/A | Al2O3 Content (%): | 80-90% | MgO Content (%): | N/A |
| CaO Content (%): | N/A | Refractoriness (Degree): | 1770°< Refractoriness< 2000° | CrO Content (%): | N/A |
| SiC Content (%): | N/A | Model Number: | CS80 | Brand Name: | |
| Product name: | High performance refractory ladle slide gate | Model No.: | cs80 | Brand name: | CMAX |
| Quality: | Al-C or Al-Zr-C | Service life: | 4-6 heats | Apparent porosity: | 7% Max |
| Bulk density:: | 3.1 MIN | C.C.S: | 120MPA | MOQ: | 100 pcs for trial |
| Delivery time: | 60 working days upon receipt of deposit |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Inner carton packing, outer wooden case suitable for long term sea shipping |
| Delivery Detail: | three months working days upon receipt of deposit |
Specifications
Surface flatness less than 0.05mm
High mechanical strength
Erosion resistance
Oxidation resistance
Thermal shock stability
General Chemical Analysis for refractory ladle slide gate :
slide gate plate widely including Alumina carbon and Alumina Zirconia Carbon slide gate plate, MgO and MgO-spinel slide gate plate,nonoxides bonding slide gate plateand unburned slide gate plate.
Alumina -Zirconia-Carbon material
| Al-Zr-C Material | |||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) |
| 85 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
Composite type: Al-Zr-C for working line, outer Al-C material
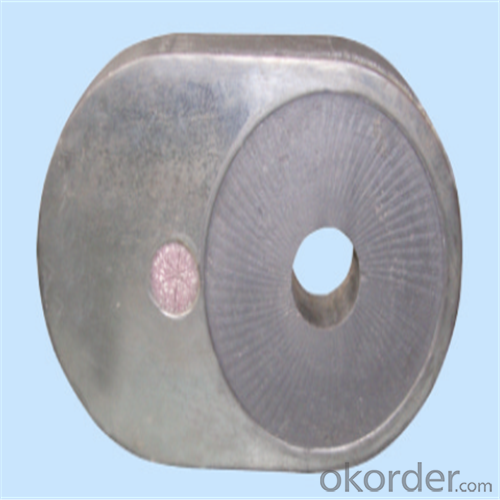
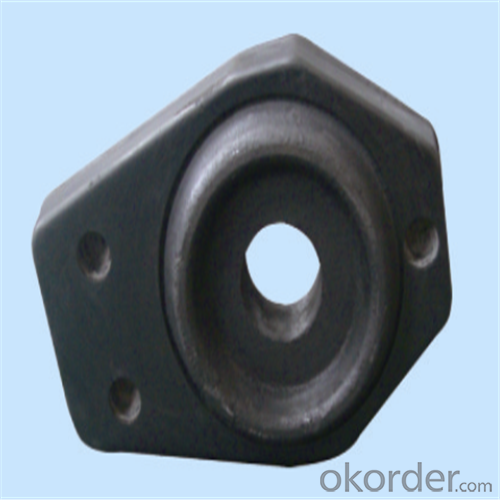
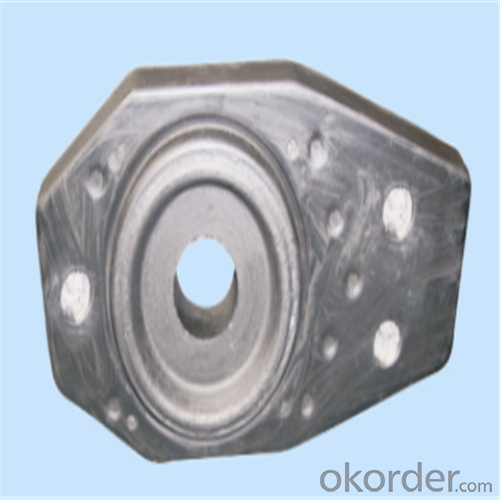



| Al-Zr-C & Al-C Material | ||||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S | |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) | |
| Inner side (Working face) | 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| Outside | 90 | 3 | 0 | 9 | 3 | |
Using the raw materials of tabular alumina, zirconia-corundum, carbon and other high-grade additives, after sintering to obtain characteristics of oxidation resistance, scour strength, erosion resistance, thermal shock resistance, shape stable and long service life, made our products the preferred materials for the large and medium-sized steel ladle, refining ladle, series of alloy steel ladle, and tundish. Our high performance sintering sliding gates include alumina carbon , Al2O3-ZrO2-C, etc, can meet the needs of different steel grade.
Other Products

About us


Sample is on your request.
Welcome to visit our factory~
- Q: How are monolithic refractories used in the repair and maintenance of ladle and tundish covers?
- Monolithic refractories are used in the repair and maintenance of ladle and tundish covers by providing a durable and heat-resistant lining. These refractories are applied as a single, seamless layer, eliminating the need for multiple bricks or tiles. They can be easily shaped and molded to fit the specific contour of the ladle or tundish cover, ensuring a tight and secure seal. Monolithic refractories also offer excellent thermal insulation properties, preventing heat loss and reducing energy consumption. Additionally, they have high resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, extending the lifespan of the ladle and tundish covers and minimizing the need for frequent repairs.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories enhance the performance of ladles and tundishes?
- Monolithic refractories enhance the performance of ladles and tundishes by providing superior thermal insulation, high resistance to thermal shock, and excellent chemical resistance. This improves their durability, reduces heat loss, and minimizes the risk of refractory failure, resulting in increased operational efficiency and extended service life of ladles and tundishes.
- Q: What are the considerations for repairing and patching monolithic refractories?
- Considerations for repairing and patching monolithic refractories include assessing the extent of the damage, identifying the cause of the damage, selecting the appropriate repair material, ensuring proper bonding and curing, and following manufacturer's instructions and recommended procedures. Additionally, factors such as temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress should be taken into account to ensure the repaired refractory maintains its performance and longevity.
- Q: What are the factors affecting the thermal conductivity of monolithic refractories?
- The factors affecting the thermal conductivity of monolithic refractories include the composition and structure of the refractory material, the porosity and density of the material, the presence of any impurities or defects, the temperature at which the material is being used, and the presence of any external factors such as pressure or moisture.
- Q: What are some common applications of monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry?
- Some common applications of monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry include lining of ladles, tundishes, and converters, as well as repairs and maintenance of furnaces, kilns, and other high-temperature equipment. They are also used for the construction of runners, troughs, and spouts in continuous casting processes.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the quality of iron and steel products?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in the production of high-quality iron and steel products. They provide superior resistance to extreme temperatures, chemical reactions, and mechanical stress in the production process. By maintaining the integrity of furnaces, ladles, and other equipment, monolithic refractories ensure consistent heat distribution and prevent contamination, resulting in improved product quality. Additionally, their ability to withstand thermal shock and erosion prolongs the lifespan of the refractory linings, reducing downtime and enhancing overall efficiency.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories resist corrosion and erosion in the iron and steel industry?
- Monolithic refractories resist corrosion and erosion in the iron and steel industry through their unique composition and properties. They are made of a single material structure, which eliminates joints and seams, reducing the likelihood of corrosion. Additionally, these refractories are designed to have high density and low porosity, making them resistant to penetration by corrosive elements. The refractories also have excellent thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength, which helps them withstand the harsh conditions of the iron and steel industry. Overall, the combination of their composition, density, and strength enables monolithic refractories to effectively resist corrosion and erosion in this industry.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to energy efficiency in iron and steel manufacturing?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in enhancing energy efficiency in iron and steel manufacturing processes. These refractories are made of a single material, typically a combination of high-quality aggregates, binders, and additives, which allows for easy installation and repair. One of the main ways monolithic refractories contribute to energy efficiency is by reducing heat loss. These materials have excellent insulation properties, which help to maintain high temperatures within the furnace or kiln. By minimizing heat loss, the energy required to maintain the desired temperature is significantly reduced, leading to lower energy consumption and cost savings. Moreover, monolithic refractories are designed to have high thermal conductivity. This property ensures efficient heat transfer from the hot gases or flames to the iron and steel being processed. By facilitating efficient heat transfer, monolithic refractories enable faster heating rates and reduce the overall processing time. This time reduction translates into energy savings and increased production capacity. Another significant advantage of monolithic refractories is their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and harsh operating conditions. These materials have excellent resistance to thermal shock, corrosion, and erosion, which extends their lifespan and reduces the need for frequent repairs or replacements. Consequently, the use of monolithic refractories leads to less downtime, allowing for continuous operation and improved energy efficiency. Furthermore, monolithic refractories offer design flexibility, which enables the optimization of furnace and kiln geometries. By tailoring the shape and dimensions of the refractory linings, heat distribution can be improved, ensuring more uniform heating and reducing energy wastage. The ability to customize the refractory linings also facilitates the implementation of advanced combustion technologies, such as regenerative burners or oxy-fuel burners, which further enhance energy efficiency. In summary, monolithic refractories contribute to energy efficiency in iron and steel manufacturing by reducing heat loss, enhancing heat transfer, withstanding extreme conditions, optimizing furnace geometries, and allowing for the implementation of advanced combustion technologies. By utilizing these refractories, the industry can achieve significant energy savings, cost reductions, and environmental benefits.
- Q: What are the specific requirements of monolithic refractories for ladle transfer applications?
- Monolithic refractories for ladle transfer applications need to have high thermal shock resistance, excellent corrosion resistance, and good thermal conductivity. They should also have low porosity to prevent molten metal penetration and maintain their structural integrity. Additionally, these refractories should possess good erosion resistance and be able to withstand the mechanical stresses of ladle transfer operations.
- Q: What are the factors affecting the lifespan of monolithic refractories?
- There are several factors that can significantly affect the lifespan of monolithic refractories. 1. Temperature: One of the most critical factors is the operating temperature. Monolithic refractories are designed to withstand high temperatures, but prolonged exposure to extreme temperatures can cause thermal shock and lead to premature failure. 2. Thermal cycling: Frequent temperature fluctuations, known as thermal cycling, can also shorten the lifespan of monolithic refractories. The expansion and contraction of the refractory material can create stress, resulting in cracking and degradation over time. 3. Chemical environment: The chemical environment in which the monolithic refractories are used plays a crucial role in their lifespan. Exposure to corrosive gases, acids, alkalis, or molten metals can cause chemical reactions that degrade the refractory material. 4. Mechanical stress: Mechanical stress, such as abrasion, impact, and vibration, can weaken monolithic refractories and shorten their lifespan. This is especially relevant in industries with high mechanical activity, such as steelmaking or cement production. 5. Installation and maintenance: Proper installation and regular maintenance are essential for maximizing the lifespan of monolithic refractories. Poor installation techniques or neglecting maintenance can result in weak joints, inadequate anchoring, or the growth of cracks, leading to premature failure. 6. Quality of refractory material: The quality and composition of the monolithic refractory material can significantly impact its lifespan. Higher-quality materials with better resistance to temperature, chemical attacks, and mechanical stress tend to have longer lifespans. 7. Design and engineering: The design of the refractory lining and its engineering considerations, such as thickness, shape, and reinforcement, also influence the lifespan of monolithic refractories. Proper design can distribute stress more evenly, reduce thermal gradients, and improve overall performance and durability. 8. Operating conditions: The way monolithic refractories are operated and handled can affect their lifespan. Factors such as rapid temperature changes, improper cooling or heating procedures, or excessive thermal cycling can all contribute to premature failure. In summary, the lifespan of monolithic refractories is influenced by various factors, including temperature, thermal cycling, chemical environment, mechanical stress, installation and maintenance practices, quality of refractory material, design and engineering considerations, and operating conditions. Proper consideration and management of these factors are essential for maximizing the lifespan of monolithic refractories.
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories High Temperature Ladle Sliding Gate for Iron and Steel Industry 2024
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords