Hot Rolled unequal Angle Steel for High Voltage Transmission Tower
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 20000 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
Product Description:
Specifications of Hot Rolled unequal Angle Steel for High Voltage Transmission Tower
1.Standards:GB,ASTM,
2. Invoicing on theoretical weight or actual weight as customer request3.Material:GBQ235B or Equivalent;ASTMA36;EN10025,S235JR.
3. Payment terms:
1).100% irrevocable L/C at sight.
2).30% T/T prepaid and the balance against the copy of B/L.
3).30% T/T prepaid and the balance against L/C
4.Sizes:
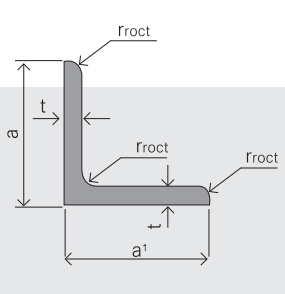
EQUAL ANGLES SIZES |
| ||
a(mm) | a1(mm) | thickness(mm) | length |
100 | 100 | 6.0---12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
120 | 120 | 8.0-12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
130 | 130 | 9.0-12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
140 | 140 | 10.0-16.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
150 | 150 | 10---15 | 6M/9M/12M |
160 | 160 | 10---16 | 6M/9M/12M |
180 | 180 | 12---18 | 6M/9M/12M |
200 | 200 | 14---20 | 6M/9M/12M |
Usage & Applications Hot Rolled Angle Steel
According to the needs of different structures, Angle can compose to different force support component. It is widely used in various building structures and engineering structures such as roof beams, hoisting machinery and transport machinery, ships, container frame and warehouse etc.
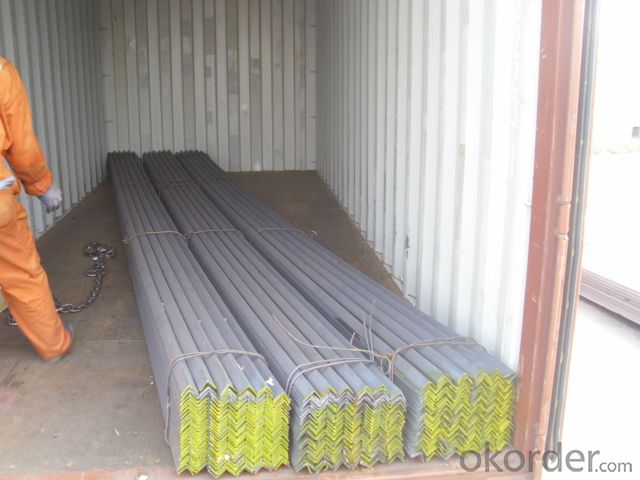



Packaging & Delivery of Hot Rolled unequal Angle Steel for High Voltage Transmission Tower
1. Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.
2. With bundles and load in container, or by bulk cargo, also we could do as customer's request.
- Q: Can steel angles be used in the construction of parking garages?
- Steel angles can indeed be utilized in the construction of parking garages. These angles are frequently employed in construction due to their robustness, durability, and versatility. They have a wide range of structural applications, including the building of parking garages. Steel angles offer support and reinforcement for crucial elements like beams and columns, as well as for framing and bracing. They play a significant role in establishing the framework for parking garage floors and walls, contributing stability and strength to the structure. Moreover, steel angles can be easily fabricated and tailored to meet the precise design and engineering specifications of a parking garage. All in all, steel angles are a favored choice for constructing parking garages because they can endure heavy loads, resist corrosion, and deliver enduring performance.
- Q: What are the common thicknesses of steel angles?
- The specific application and industry requirements determine the varying common thicknesses of steel angles. Examples of frequently utilized thicknesses for steel angles are 1/8 inch, 3/16 inch, 1/4 inch, 3/8 inch, and 1/2 inch. These thicknesses find common usage in construction, manufacturing, and structural applications. It is worth noting that thicker steel angles offer enhanced strength and durability, whereas thinner angles are suitable for lighter applications. Ultimately, the decision regarding thickness depends on the specific load-bearing requirements and considerations of the structural design.
- Q: How do you determine the required length of a steel angle for a specific application?
- In order to determine the necessary length of a steel angle for a particular application, several factors must be taken into consideration. 1. Load requirements: The first step is to calculate the maximum load that the angle will need to support. This includes the weight of the object or structure it will be holding, as well as any additional live loads like wind or snow. By determining the load requirement, you can determine the appropriate strength and size of the angle. 2. Structural analysis: Conduct a structural analysis of the intended application to determine the forces and stresses that will be applied to the steel angle. This analysis will help determine the necessary properties of the angle, such as its moment of inertia, section modulus, and bending capacity. 3. Material selection: Select the appropriate steel material for the application based on its mechanical properties, such as yield strength, tensile strength, and ductility. Different grades of steel offer varying levels of strength and durability, so it is important to choose the right material to ensure the angle can withstand the required loads. 4. Design codes and standards: Refer to relevant design codes and standards, such as those established by organizations like the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) or the Eurocode, to ensure compliance with industry regulations and guidelines. These codes provide specific formulas and procedures for calculating the required length and size of the angle based on the load and structural analysis. 5. Fabrication considerations: Take into account any limitations or constraints in the fabrication process that may affect the length of the steel angle. For instance, standard lengths of steel angles may be available, so it may be necessary to choose a length that is readily accessible or can be easily obtained through custom fabrication. 6. Consultation with professionals: If there are any uncertainties in determining the required length of a steel angle, it is recommended to seek advice from a structural engineer or a professional experienced in steel design. They can offer expert guidance and ensure that the angle is appropriately sized and designed for the specific application. By considering these factors and following a systematic approach, it is possible to determine the necessary length of a steel angle that fulfills the specific requirements of the application.
- Q: Can steel angles be used in high-temperature applications?
- Steel angles can be used in high-temperature applications depending on the specific alloy and the temperature range. Steel alloys that have been specifically designed for high-temperature applications, such as stainless steels or heat-resistant alloys, can withstand elevated temperatures without significant loss in strength or structural integrity. These alloys often contain elements like chromium, nickel, or molybdenum, which increase their resistance to corrosion, oxidation, and high temperatures. However, it is important to note that not all steel angles are suitable for high-temperature applications. Ordinary carbon steels, for example, have a limited temperature range before they start to lose strength and become susceptible to deformation or failure. The exact temperature limit for a specific steel angle will depend on factors such as the alloy composition, heat treatment, and the duration of exposure to high temperatures. In summary, steel angles can be used in high-temperature applications if they are made from appropriate alloys that are specifically designed for such conditions. It is crucial to consult with materials engineers or experts who can provide guidance on the suitable steel alloys and temperature limits for a given application to ensure safe and reliable performance.
- Q: Can steel angles be used for HVAC ductwork support?
- Yes, steel angles can be used for HVAC ductwork support. Steel angles provide structural support and stability, making them suitable for holding and securing ductwork in place.
- Q: What are steel angles?
- Steel angles are L-shaped structural components made from steel, typically used in construction and engineering projects. These angles have two perpendicular legs that provide strength and stability, making them suitable for various applications such as supporting beams, framing structures, and reinforcing corners. Steel angles come in different sizes and thicknesses to meet specific project requirements and can be easily welded, bolted, or screwed into place.
- Q: Can steel angles be drilled or punched for fastening?
- Yes, steel angles can be drilled or punched for fastening.
- Q: Which is cheaper, angle iron or steel pipe?
- Steel pipe is not only used to transport fluid and powder solid, exchange heat energy, and manufacture mechanical parts and containers, but also is an economic steel. It can reduce weight and save 20 to 40% of metal by using steel pipe to make building structure, network frame, prop and mechanical support. Moreover, it can realize factory mechanization construction. Using steel pipe to manufacture road bridge can not only save steel, simplify construction, but also greatly reduce the area of coating protective layer, save investment and maintenance cost.
- Q: What are the different types of connections used for steel angles in marine applications?
- Steel angles are commonly utilized in marine applications to provide structural support and reinforcement. To ensure their stability and strength in the harsh marine environment, various types of connections are employed. The different connection methods for steel angles in marine applications include: 1. Welded Connections: Welding is widely used to connect steel angles in marine applications. This method involves melting the base metals and allowing them to cool and solidify, resulting in strong and durable connections. Welded connections are ideal for heavy-duty marine applications due to their excellent strength and durability. 2. Bolted Connections: Another commonly used method is bolted connections, which involve securing the angles together using bolts, nuts, and washers. Bolted connections offer easy installation and allow for disassembly if needed. They are suitable when adjustments or replacements of the angles are required. 3. Riveted Connections: Riveting, an older connection method, is still employed in certain marine applications. It entails using rivets, metal pins with heads, to connect the angles. The rivets are inserted through pre-drilled holes in the angles and deformed to secure them. Riveted connections offer good strength and vibration resistance, but they can be time-consuming to install compared to other methods. 4. Adhesive Connections: Adhesive bonding is a contemporary method used to connect steel angles in marine applications. This method involves utilizing high-strength adhesives to join the angles together. Adhesive connections evenly distribute stress across the connected surfaces and eliminate the need for drilling or welding. However, they require meticulous surface preparation and curing time for optimal strength. 5. Hybrid Connections: In certain cases, a combination of different connection methods may be employed for steel angles in marine applications. For instance, a welded-bolted connection may be used to enhance strength and redundancy. Hybrid connections offer the advantages of multiple connection methods while ensuring a robust and reliable connection. The choice of connection type for steel angles in marine applications depends on factors such as load requirements, environmental conditions, and project specifications. It is crucial to consider the specific needs of the application and consult with structural engineers and marine professionals to determine the most suitable connection method.
- Q: Can steel angles be used in the construction of storage tanks?
- Yes, steel angles can be used in the construction of storage tanks. Steel angles are commonly used in the construction industry due to their strength, durability, and versatility. In the case of storage tanks, steel angles can be used as structural components to provide support and stability to the tank's framework. They are often used to create the framework for the tank's walls, roof, and base, ensuring the tank's overall strength and stability. Additionally, steel angles can also be used to reinforce corners and joints, improving the tank's structural integrity. Overall, steel angles are a reliable and cost-effective option for incorporating into the construction of storage tanks.
Send your message to us
Hot Rolled unequal Angle Steel for High Voltage Transmission Tower
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 20000 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords






























