Hot Rolled unequal Angle Steel for Telecommunication Tower
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 12000 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 300000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
Product Description:
Specifications of Hot Rolled unequal Angle Steel for Telecommunication Tower
1.Standards:GB,ASTM,BS,
2. Invoicing on theoretical weight or actual weight as customer request3.Material:GBQ235B,Q345BorEquivalent;ASTMA36;EN10025,S235JR.
4. Payment terms:
1).100% irrevocable L/C at sight.
2).40% T/T prepaid and the balance against the copy of B/L.
3).40% T/T prepaid and the balance against L/C
5.Sizes:
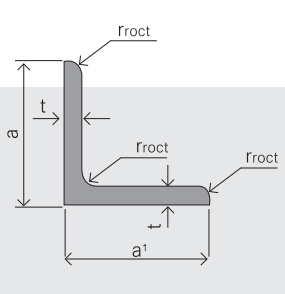
EQUAL ANGLES SIZES |
| ||
a(mm) | a1(mm) | thickness(mm) | length |
120 | 120 | 8.0-12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
125 | 125 | 8.0---12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
130 | 130 | 9.0-12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
140 | 140 | 10.0-16.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
150 | 150 | 10---15 | 6M/9M/12M |
160 | 160 | 10---16 | 6M/9M/12M |
Usage & Applications Hot Rolled Angle Steel
According to the needs of different structures, Angle can compose to different force support component. It is widely used in various building structures and engineering structures such as transport machinery, ships, industrial furnaces, reaction tower, container frame etc.



Packaging & Delivery
1. With bundles and load in container, also we could do as customer's request.
- Q: Can steel angles be used in load-bearing columns?
- Load-bearing columns can indeed utilize steel angles. Construction frequently incorporates steel angles due to their robustness and longevity. These angles offer structural reinforcement and support for load-bearing columns. Compared to alternative materials, the angle shape of steel enhances stability and load-bearing capacity. In the construction industry, steel angles find widespread application in buildings, bridges, and various structures necessitating load-bearing columns.
- Q: How do steel angles behave under seismic forces?
- The behavior of steel angles under seismic forces varies depending on their design, size, and connection details. Generally, steel angles are commonly utilized in seismic-resistant structures because they can dissipate energy and withstand lateral forces. Here are several important characteristics regarding the behavior of steel angles under seismic forces: 1. Ductility: Steel angles possess a high level of ductility, allowing them to undergo significant deformations without failure. This characteristic is crucial in seismic design as it enables the structure to absorb and dissipate energy during an earthquake, thereby preventing sudden collapse. 2. Flexibility: Steel angles have the ability to flex and bend when subjected to seismic forces, which enables them to absorb energy and minimize the impact on the overall structure. This flexibility aids in distributing the seismic forces evenly throughout the structure, reducing localized damage. 3. Connection behavior: Proper connection design is vital to ensure the performance of steel angles under seismic forces. The connections must be designed to allow for rotation and accommodate the anticipated displacements during an earthquake. Adequate connections prevent the angles from becoming brittle or failing prematurely. 4. Buckling resistance: Steel angles are prone to buckling under compression forces. To enhance their resistance to buckling, lateral bracing or stiffeners are often utilized. These components offer additional support to the angles and help prevent buckling during seismic events. 5. Strength and stiffness: Steel angles possess high strength and stiffness, enabling them to withstand the lateral forces induced by an earthquake. The strength of steel angles can be enhanced by selecting appropriate materials, such as using higher-grade steel with greater yield strength. In conclusion, steel angles are well-suited for seismic-resistant structures due to their ductility, flexibility, and strength. However, their behavior under seismic forces is heavily dependent on proper design, connection details, and adherence to seismic codes and standards. It is crucial to consult with structural engineers and follow best practices to ensure the optimal performance of steel angles in seismic design.
- Q: Are steel angles suitable for mezzanine floor construction?
- Indeed, steel angles prove to be suitable for the construction of mezzanine floors. Mezzanine floor construction commonly incorporates steel angles due to their robustness and long-lasting nature. They offer exceptional support and stability, thereby making them an ideal choice for bearing the weight of the mezzanine floor and any additional loads placed upon it. By simply bolting or welding steel angles together, a sturdy framework can be easily created for the mezzanine floor. Moreover, steel angles can be tailored to meet specific design requirements, thereby allowing for flexibility in mezzanine floor construction. In summary, steel angles provide a dependable and cost-effective solution for the construction of mezzanine floors.
- Q: What are the different types of steel angle connections?
- There are several different types of steel angle connections commonly used in construction and engineering projects. Some of the main types include: 1. Welded connections: This is one of the most common and traditional methods of connecting steel angles. In this type of connection, the two angles are joined together by welding them at the point of contact. Welded connections provide excellent strength and rigidity, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. 2. Bolted connections: Bolted connections involve using bolts and nuts to fasten the steel angles together. This method allows for easy disassembly and reassembly of the structure if needed. Bolted connections are often used in situations where frequent adjustments or modifications are required. 3. Riveted connections: Riveted connections involve using rivets to join the steel angles together. Rivets are metal fasteners that are inserted through pre-drilled holes in the angles and then hammered or pressed to secure them. Riveted connections were widely used in older structures and are still occasionally used in certain applications today. 4. Clipped connections: Clipped connections are a type of bolted connection where the angles are connected using special clip angles. These clip angles are bolted to the main angles, providing a secure and rigid connection. Clipped connections are commonly used in steel trusses and frameworks. 5. Gusset plate connections: Gusset plate connections involve using a steel plate, known as a gusset plate, to connect two or more steel angles. The gusset plate is usually bolted or welded to the angles, providing additional strength and stability. This type of connection is often used in structures subjected to heavy loads or dynamic forces. Each type of steel angle connection has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of connection method depends on various factors such as the load requirements, structural design, and project specifications.
- Q: Can steel angles be used for column supports?
- Yes, steel angles can be used for column supports. Steel angles are commonly used in construction as they provide structural support and stability, making them suitable for column supports. They offer excellent strength and load-bearing capacity, making them a reliable choice for supporting vertical loads.
- Q: How do steel angles contribute to energy-efficient construction?
- There are multiple ways in which steel angles play a role in energy-efficient construction. To begin with, steel angles are frequently utilized as structural elements in buildings, particularly for framing walls, roofs, and floors. Their excellent strength-to-weight ratio enables the construction of lighter and more efficient structures. This means that less steel is required to support the building, resulting in reduced overall weight and material usage. Consequently, this leads to a decrease in the energy needed for construction and transportation. Furthermore, steel angles can be easily prefabricated off-site, which allows for quicker construction times and lower labor costs. This not only saves time and money but also reduces energy consumption during the construction process. Moreover, steel is an incredibly durable and long-lasting material, which reduces the necessity for frequent maintenance and repairs. This durability translates into energy savings throughout the building's lifespan, as less energy is required for ongoing maintenance and replacements. Additionally, steel angles can be recycled when they reach the end of their life cycle. This reduces the demand for new materials and minimizes the environmental impact of construction. The recycling process requires less energy compared to the production of new steel, resulting in energy savings and reduced greenhouse gas emissions. Lastly, steel angles can be integrated into energy-efficient building systems, such as insulation, HVAC ductwork, and renewable energy installations. The versatility of steel allows for the creation of systems that optimize energy performance, such as efficient heating and cooling systems or solar panel installations. In conclusion, steel angles contribute to energy-efficient construction through their strength and stability, reduced material usage, faster construction times, minimized maintenance needs, recycling capabilities, and integration with energy-efficient building systems.
- Q: What is the corresponding length of the root weight in the angle standard?
- General fixed length delivery without weighing, no fixed length delivery is generally applied to weighing sales. Profile fixed length is generally divided into 6 meters, 9 meters and 12 meters, special sizing must be large quantities, consultation with the steel supply.
- Q: How do steel angles perform under dynamic or cyclic loading conditions?
- Steel angles are commonly used in structural applications where they are subjected to dynamic or cyclic loading conditions. Under such loading conditions, steel angles exhibit excellent performance due to their inherent properties. Firstly, steel angles possess high strength and stiffness, which enables them to withstand the varying loads and maintain their structural integrity. This ensures that the angles do not deform or fail prematurely under cyclic loading conditions. Furthermore, steel angles have good fatigue resistance, meaning they can endure repeated loading and unloading cycles without experiencing significant degradation in their mechanical properties. This is due to the material's ability to distribute and dissipate stress, preventing the accumulation of fatigue damage. Additionally, steel angles have the advantage of being able to absorb and distribute energy effectively. This helps in reducing the impact of dynamic loads, such as vibrations or sudden impacts, and prevents localized stress concentrations that could lead to failure. Moreover, steel angles have a high ductility, which allows them to undergo plastic deformation without fracturing. This characteristic is crucial in dynamic loading conditions as it enables the angles to absorb energy and undergo deformation, thereby dissipating the applied loads and reducing the risk of sudden failure. In conclusion, steel angles perform exceptionally well under dynamic or cyclic loading conditions. Their high strength, stiffness, fatigue resistance, energy absorption capacity, and ductility make them reliable and durable structural elements in various applications where they are subjected to dynamic or cyclic loads.
- Q: What is the lifespan of steel angles?
- The lifespan of steel angles can vary depending on several factors such as the quality of the steel, the environmental conditions it is exposed to, and the level of maintenance it receives. However, with proper care and maintenance, steel angles can last for several decades or even longer.
- Q: How are steel angles measured and specified?
- Steel angles are measured and specified based on their dimensions, which include the length of the legs and the thickness of the angle. This is typically provided in millimeters or inches. The dimensions are presented in a specific order, such as leg length × leg length × thickness. Additionally, the angle's weight per unit length or its cross-sectional area may also be specified to provide further information about its size and strength.
Send your message to us
Hot Rolled unequal Angle Steel for Telecommunication Tower
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 12000 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 300000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























