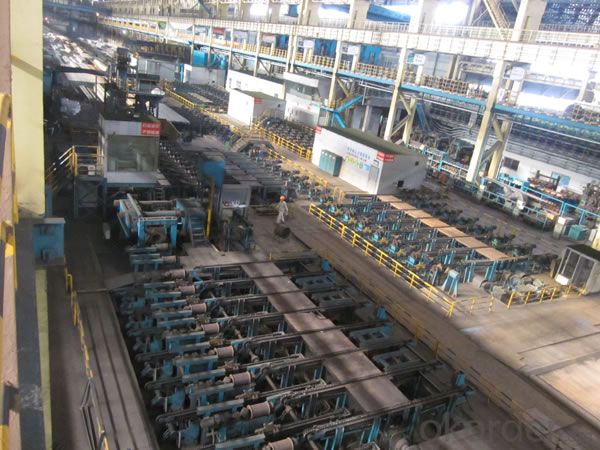
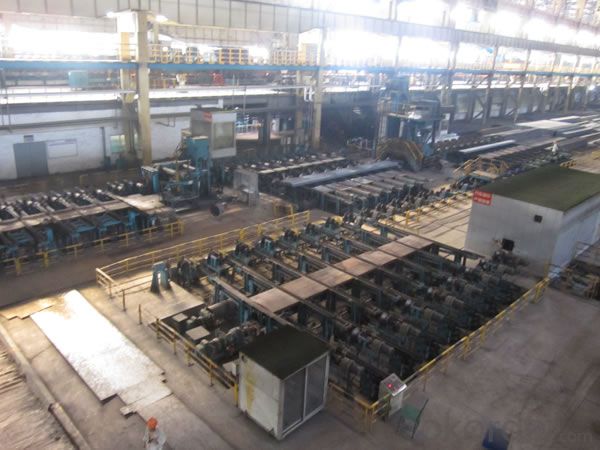
Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 105mm
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 105mm
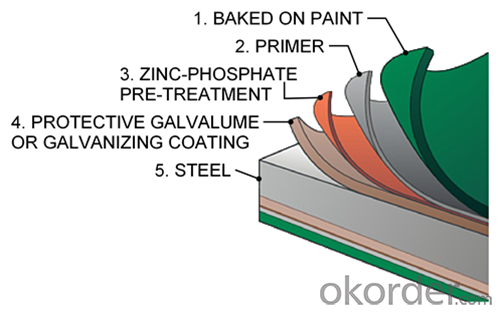
Description of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 105mm
Prepainted Rolled steel Coil is a kind of coated steel coil/sheet. With the cold rolled steel of different strength and thickness as substrate, it is produced through applying Al-Zn coat on both faces by hot dip process. In its coating, Al accounts for about 55%, Si 1.6%, while the remaining is Zn. Aluminum zinc coils enjoys both the physical protective feature and durability of Al and the electrochemical protective property of Zn. And its surface has bright silver color and regular embossed-like figure, which are highly decorative. RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing
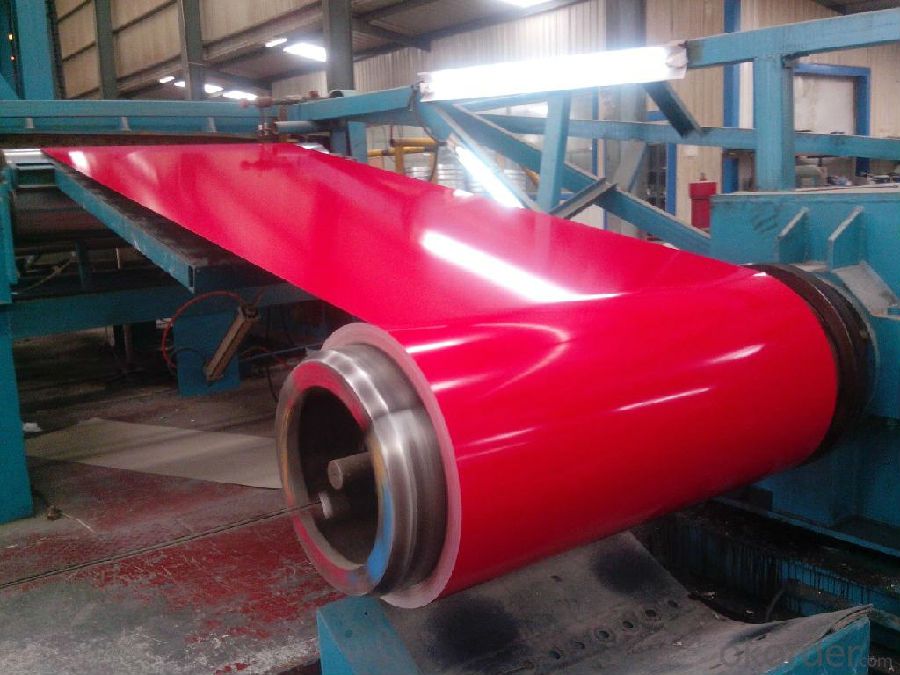

Main Feature of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 105mm
1.Corrosion resistance: It mainly depends on the zinc protection. When the zinc being worn,
2. Heat resistance: steel sheet has excellent heat resistance, can withstand high temperatures over 300 centigrade, and is similar with aluminized steel high temperature oxidation resistance. It often used in chimney pipes, ovens, fluorescent lighting device and the device cover.
3. Heat reflective: Galvanized steel plate heat-reflective high rate is twice as galvanized steel, often used to make insulation materials. RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing
Applications of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 105mm
1. Construction and building: roofing; ventilating duct; handrail; partition panel;etc.
2. Electric appliance: refrigerator; washing machine; refrigerator; DVD;etc.
3.Transportation: oil tank; gas tank;road sign; etc.
4.Agriculture constructions :barn; etc.RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing
5.Others:vending machine; game machine; auto parts spare parts etc.
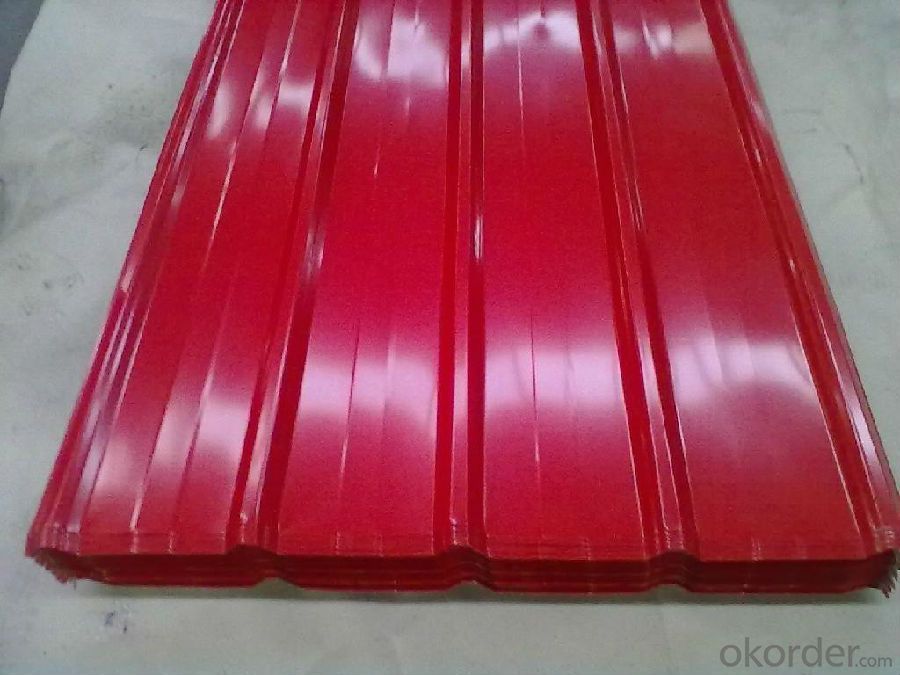

Specifications of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 105mm
Product | Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 105mm |
Material Grade | SGCC / SGCH / DX51D+AZ, etc |
Thickness | 0.5-3.0mm |
Width | 700-1500mm |
Tolerance | Thickness: +/-0.02mm , Width:+/-2mm |
Zinc-coating | AZ30-150g/m2 |
Technique | Raw material: Hot rolled steel coil --> Cold rolled_>hot dipped galvalume |
Surface | Dried, Chromated, Unoiled,RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing |
Spangle | Regular spangle , small spangle, zero spangle |
ID | 508MM 610MM |
Coil weight | 25MT max |
Export package | Cardboard inner sleeves, Waterproof paper, galvanized steel covered and steel strip packed |
FAQ of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 105mm
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1. What is the minimum order quantity ?
Our MOQ is 100 mt for each size each specification. Usually we can offer discount if can buy large QTY once. RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing
2. How long can we receive the product after ordering?
Our general delivery time is 30 days after confirmation, but so some special orders, we have offer special delivery time
3. How to guarantee the quality of the products?
We have established the international advanced quality management system ,every link from raw material to final product we have strict quality test;We resolutely put an end to unqualified products flowing into the market. At the same time, we will provide necessary follow-up service assurance.
4. What is the payment?
We accept T/T, L/C
- Q: How is the surface condition of steel billets checked?
- The surface condition of steel billets is typically checked through visual inspection and various non-destructive testing methods. Visual inspection involves thoroughly examining the surface of the billets for any visible defects such as cracks, pits, dents, or scratches. This is usually done by trained inspectors who have a keen eye for detecting surface imperfections. In addition to visual inspection, various non-destructive testing techniques are employed to assess the surface condition of steel billets. These techniques include magnetic particle testing, liquid penetrant testing, ultrasonic testing, and eddy current testing. Magnetic particle testing involves applying a magnetic field to the billet's surface and then applying fine iron particles. If there are any surface defects, such as cracks or inclusions, the magnetic particles will be attracted to these areas and form visible indications. Liquid penetrant testing involves applying a liquid dye to the surface of the billet. The dye penetrates any surface defects, and after a certain period of time, excess dye is removed, and a developer is applied. The developer draws out the dye from any surface defects, making them visible and easy to detect. Ultrasonic testing utilizes high-frequency sound waves to detect surface and subsurface defects. A transducer is used to generate sound waves that penetrate the billet's surface. If there are any defects, such as cracks or voids, the sound waves will reflect back, and by analyzing the reflected waves, any surface or subsurface flaws can be identified. Eddy current testing involves passing an alternating current through a coil placed near the billet's surface. Any surface defects or variations in the material's conductivity will cause changes in the current flow, which can be detected and analyzed to determine the surface condition. These non-destructive testing methods provide accurate and reliable information about the surface condition of steel billets, helping to ensure their quality and integrity before further processing or usage.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of wire rods?
- Steel billets are used in the manufacturing of wire rods as they are heated and then rolled into thin, long cylindrical shapes. These billets undergo a series of processes such as hot rolling, cooling, and wire drawing to transform them into wire rods of various sizes. The wire rods are then utilized in various industries for applications like construction, automotive parts, and electrical wiring.
- Q: Can steel billets be painted or coated for decorative purposes?
- Yes, steel billets can be painted or coated for decorative purposes. Painting or coating steel billets not only enhances their appearance but also provides protection against corrosion and other environmental factors. Various types of paints and coatings can be used, such as epoxy, powder coating, or metallic finishes, to achieve the desired decorative effect. These coatings can be applied to steel billets through processes like spray painting, electrostatic coating, or hot-dipping. It is important to properly prepare the surface of the steel billets before applying the paint or coating to ensure good adhesion and longevity of the decorative finish.
- Q: How are steel billets cut into desired lengths?
- Steel billets are typically cut into desired lengths using a process called sawing or shearing. This involves using specialized machinery, such as band saws or circular saws, to cut through the steel billet along the desired length. The saw blades are designed to withstand the hardness of the steel and make precise cuts. This process allows for accurate and efficient production of steel billets in varying lengths as per the requirements of different industries.
- Q: Can steel billets be used for making architectural components?
- Architectural components can indeed be made using steel billets. Steel billets are semi-finished products commonly utilized in the production of various steel items, including architectural components. These billets undergo heating and are subsequently transformed into the desired shape through processes such as forging, extrusion, or rolling. Among the architectural components that can be created are structural elements like beams, columns, and trusses, as well as decorative elements like handrails, facades, and ornamental fixtures. Steel is a highly preferred material for architectural components due to its exceptional strength, durability, and versatility. It can be easily shaped into intricate forms, enabling architects and designers to construct distinctive and visually appealing structures. Moreover, steel exhibits remarkable resistance to weathering, corrosion, and fire, further enhancing its suitability for architectural purposes.
- Q: How do steel billets contribute to energy efficiency?
- Steel billets have a significant impact on energy efficiency in various ways: 1. Enhanced production efficiency: Steel billets serve as the initial form of steel utilized in different manufacturing processes. Employing steel billets as the starting material allows manufacturers to achieve higher production efficiency. The uniform size and shape of billets facilitate easier handling, cutting, and shaping, thereby reducing energy consumption during manufacturing. 2. Optimized resource utilization: Steel billets are commonly produced from recycled steel scrap. By employing recycled steel as the raw material, manufacturers minimize the need for extracting and processing virgin iron ore, a highly energy-intensive procedure. This conservation of natural resources helps in reducing overall energy consumption related to steel production. 3. Efficient heat recovery: The manufacturing of steel billets necessitates high temperatures for melting and shaping the steel. However, modern steel plants are equipped with advanced technologies that enable efficient heat recovery. The excess heat generated during the process can be captured and utilized for various purposes, such as generating steam or heating other areas of the plant. This heat recovery system effectively reduces energy wastage and enhances overall energy efficiency. 4. Employment of energy-efficient equipment: Steel billet production often involves the use of heavy machinery and equipment. Manufacturers are increasingly investing in energy-efficient technologies and equipment to minimize energy consumption. For instance, the utilization of more efficient electric arc furnaces or induction heating systems can significantly reduce energy requirements compared to traditional methods. These technological advancements contribute to the overall energy efficiency of steel billet production. In conclusion, steel billets play a pivotal role in enhancing energy efficiency in the steel industry. Their impact is evident in production efficiency, resource optimization, heat recovery, and the utilization of energy-efficient equipment. By minimizing energy consumption, the use of steel billets promotes a more sustainable steel manufacturing process.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of bars?
- Steel billets are used in the manufacturing of bars by being heated and then rolled or forged into specific shapes and sizes. This process ensures the bars have the desired strength, durability, and dimensional accuracy required for various applications in industries such as construction, automotive, and infrastructure.
- Q: What are the different types of steel used in manufacturing steel billets?
- Steel billets are manufactured using various types of steel, including carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, and tool steel. 1. Carbon Steel: The most commonly used steel for manufacturing steel billets is carbon steel. It contains a small percentage of carbon (typically 0.05% to 0.25%), which provides it with strength and durability. Carbon steel is versatile and can be used in a wide range of applications. 2. Stainless Steel: Stainless steel is highly regarded for its corrosion resistance and high strength. It contains chromium, which forms a protective oxide layer on the surface, preventing rust and corrosion. Stainless steel is commonly used in applications where resistance to moisture and chemicals is necessary, such as in the construction of bridges and buildings. 3. Alloy Steel: Alloy steel is created by adding different alloying elements to carbon steel, including manganese, nickel, chromium, and molybdenum. These elements enhance the steel's properties, such as its strength, hardness, and resistance to wear and tear. The automotive and aerospace industries frequently employ alloy steel. 4. Tool Steel: Tool steel is specifically designed to possess high hardness, resistance to abrasion, and the ability to withstand high temperatures. It is frequently utilized in the production of cutting tools, molds, and dies. Tool steel typically comprises a combination of alloying elements, such as tungsten, vanadium, and cobalt. These examples represent a few of the diverse types of steel employed in the manufacturing of steel billets. The selection of the specific steel type relies on the desired properties and intended application of the steel billets.
- Q: Does anyone know how much it costs to refine a ton of steel? What are the expenses involved?
- Electricity, water, wages, raw materials, raw materials loss, charges, oxygen, according to their own circumstances, as well as freight and other expenses, now the steel profits are not as good as before, a ton of net profit is about 100 yuan
- Q: What industries use steel billets?
- Several industries use steel billets, including automotive, construction, manufacturing, and infrastructure. Steel billets are commonly used as raw material in the production of various metal products such as pipes, rods, bars, wires, and sheets. They are also utilized in the construction of bridges, buildings, and other structural components. The automotive industry uses steel billets for manufacturing parts like engine blocks, chassis, and suspension components. Additionally, steel billets find applications in the energy sector, machinery production, and shipbuilding.
Send your message to us
Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 105mm
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords
































