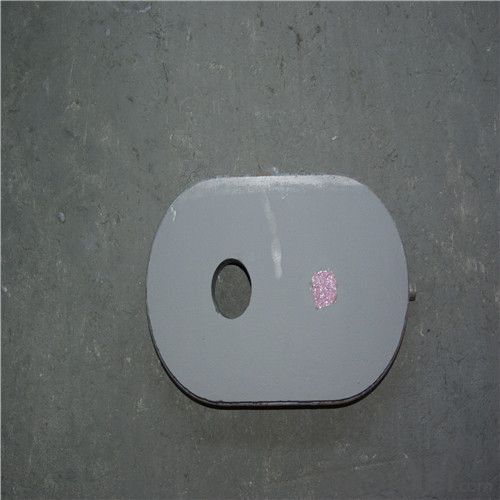
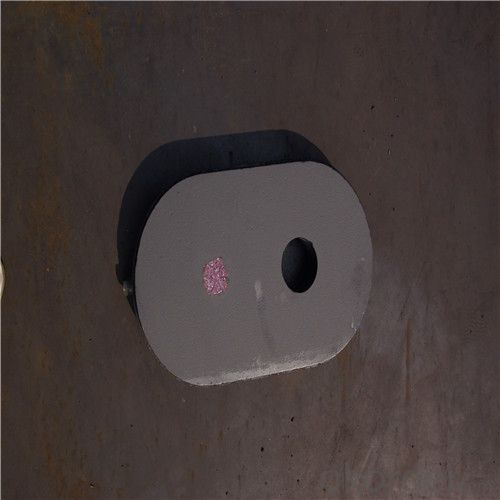
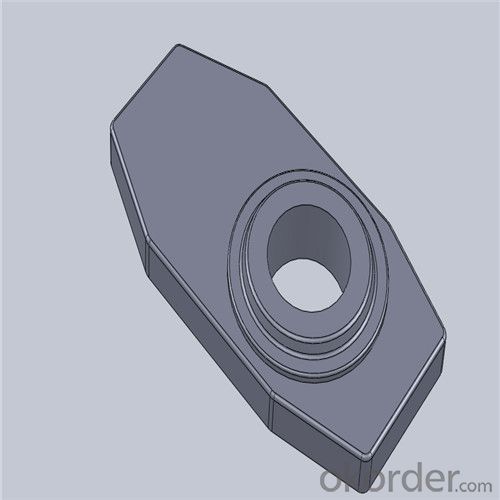
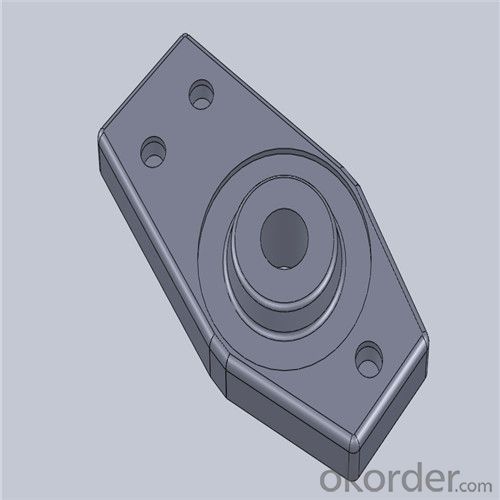
Monolithic Refractories High Temperature Ladle Sliding Gate Steel
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for High Performance Refractory Ladle Slide Gate
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Shape: | Plate | Material: | Alumina Block |
| SiO2 Content (%): | N/A | Al2O3 Content (%): | 80-90% | MgO Content (%): | N/A |
| CaO Content (%): | N/A | Refractoriness (Degree): | 1770°< Refractoriness< 2000° | CrO Content (%): | N/A |
| SiC Content (%): | N/A | Model Number: | CS80 | Brand Name: | |
| Product name: | High performance refractory ladle slide gate | Model No.: | cs80 | Brand name: | CMAX |
| Quality: | Al-C or Al-Zr-C | Service life: | 4-6 heats | Apparent porosity: | 7% Max |
| Bulk density:: | 3.1 MIN | C.C.S: | 120MPA | MOQ: | 100 pcs for trial |
| Delivery time: | 60 working days upon receipt of deposit |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Inner carton packing, outer wooden case suitable for long term sea shipping |
| Delivery Detail: | three months working days upon receipt of deposit |
Specifications
Surface flatness less than 0.05mm
High mechanical strength
Erosion resistance
Oxidation resistance
Thermal shock stability
General Chemical Analysis for refractory ladle slide gate :
slide gate plate widely including Alumina carbon and Alumina Zirconia Carbon slide gate plate, MgO and MgO-spinel slide gate plate,nonoxides bonding slide gate plateand unburned slide gate plate.
Alumina -Zirconia-Carbon material
| Al-Zr-C Material | |||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) |
| 85 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
Composite type: Al-Zr-C for working line, outer Al-C material
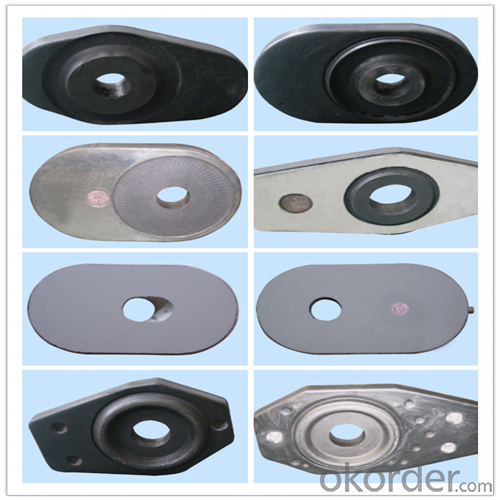

| Al-Zr-C & Al-C Material | ||||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S | |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) | |
| Inner side (Working face) | 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| Outside | 90 | 3 | 0 | 9 | 3 | |
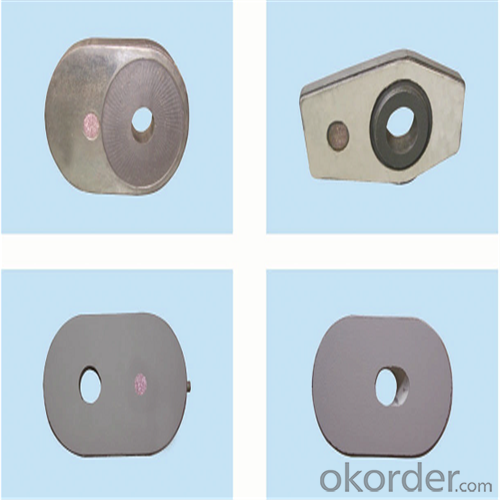

Using the raw materials of tabular alumina, zirconia-corundum, carbon and other high-grade additives, after sintering to obtain characteristics of oxidation resistance, scour strength, erosion resistance, thermal shock resistance, shape stable and long service life, made our products the preferred materials for the large and medium-sized steel ladle, refining ladle, series of alloy steel ladle, and tundish. Our high performance sintering sliding gates include alumina carbon , Al2O3-ZrO2-C, etc, can meet the needs of different steel grade.

Other Products

About us


Sample is on your request.
Welcome to visit our factory~
- Q: How do monolithic refractories protect lining in ladles and tundishes?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in protecting the lining in ladles and tundishes through their unique properties and characteristics. These refractories are composed of a single, solid piece, as opposed to traditional brick or tile linings, which consist of individual units. One of the key ways in which monolithic refractories protect the lining is through their high density and low porosity. This property ensures that the refractory material acts as an effective barrier against the penetration of molten metal and slag. By preventing the infiltration of these corrosive substances, the monolithic refractory shields the lining from chemical attack, ensuring its longevity and performance. Additionally, monolithic refractories have excellent thermal shock resistance. Ladles and tundishes are subjected to extreme temperature fluctuations during the steelmaking process, as molten metal is poured and then allowed to cool. The ability of monolithic refractories to withstand these rapid temperature changes without cracking or spalling is vital in protecting the lining from thermal damage. Furthermore, monolithic refractories offer superior strength and mechanical properties. Ladles and tundishes are subjected to various mechanical stresses, such as the weight of the molten metal, the movement of the refractory lining during pouring, and the impact of scrap or additives. The robustness of monolithic refractories allows them to withstand these forces, preventing any structural failure or damage to the lining. Another advantage of monolithic refractories is their ease of installation. Unlike brick or tile linings, which require meticulous jointing and careful placement, monolithic refractories can be applied as a single, cohesive layer. This seamless application ensures a uniform protective barrier, eliminating weak points or gaps that could compromise the lining's integrity. In summary, monolithic refractories protect the lining in ladles and tundishes by providing a dense, impermeable barrier against the penetration of molten metal and slag. Their thermal shock resistance, mechanical strength, and easy installation contribute to the overall durability and longevity of the lining, ensuring its effective performance in the demanding steelmaking environment.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories enhance the performance and longevity of furnaces?
- Monolithic refractories enhance the performance and longevity of furnaces by providing superior thermal insulation properties, excellent resistance to thermal shocks, and high mechanical strength. They create a seamless lining, eliminating joints and weak points, which reduces heat loss and prevents the penetration of molten metals or aggressive chemicals. Moreover, monolithic refractories offer flexibility in design and installation, allowing for customized shapes and sizes to maximize the efficiency of the furnace. Overall, their use enhances the overall heat transfer, reduces energy consumption, and extends the lifespan of the furnace.
- Q: What are the main factors affecting the thermal expansion of monolithic refractories?
- The thermal expansion of monolithic refractories is influenced by various factors. These factors comprise the type of refractory material, the temperature range, the chemical composition, and the physical structure of the refractory. To begin with, the thermal expansion behavior of a refractory is significantly determined by its type of material. Different types of refractories, such as alumina-based, silica-based, and magnesia-based refractories, possess varying coefficients of thermal expansion (CTE). For instance, alumina-based refractories generally exhibit a lower CTE in comparison to silica-based refractories. Consequently, the choice of refractory material holds great influence over its thermal expansion characteristics. Secondly, the thermal expansion of a refractory is affected by the temperature range to which it is exposed. As the temperature rises, the refractory material expands due to the absorption of thermal energy. However, different refractories demonstrate different expansion behaviors depending on temperature. Some refractories may exhibit a linear or near-linear expansion with temperature, while others may display non-linear or step-wise expansion. Hence, the temperature range of operation is a critical factor in determining the suitability of a refractory for a specific application. The chemical composition of the refractory also has an impact on its thermal expansion. The presence of various chemical elements and compounds in the refractory material can influence its expansion behavior. For instance, the addition of specific oxides, like magnesia or zirconia, can modify the CTE of the refractory. Similarly, impurities or variations in the chemical composition can introduce discrepancies in expansion characteristics among refractories of the same type. Lastly, the physical structure of the refractory, encompassing factors such as porosity, density, and microstructure, can influence thermal expansion. The existence of open or closed pores within the refractory can affect its ability to expand uniformly under thermal stress. The density of the refractory also plays a role, as denser refractories tend to have lower thermal expansion. Moreover, the microstructure, including grain size and orientation, can impact the overall expansion behavior of the refractory. To conclude, the primary factors influencing the thermal expansion of monolithic refractories include the type of refractory material, temperature range, chemical composition, and physical structure. A comprehensive understanding of these factors is crucial in selecting the appropriate refractory for a specific application to ensure optimal performance and durability.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand high temperatures in iron and steel production?
- Monolithic refractories are able to withstand high temperatures in iron and steel production due to their composition and unique properties. These refractories are made from a single, continuous material, which eliminates the need for joints or seams that could weaken under extreme heat. Additionally, they have high thermal conductivity and low thermal expansion, allowing them to effectively absorb and distribute the intense heat in the production process without cracking or breaking. Furthermore, monolithic refractories are highly resistant to chemical corrosion and erosion, which is crucial in the harsh environment of iron and steel production. Overall, the combination of these factors enables monolithic refractories to withstand the extreme temperatures involved in iron and steel production.
- Q: What are the environmental considerations associated with monolithic refractories?
- The environmental considerations associated with monolithic refractories primarily revolve around their production and disposal. The manufacturing process of monolithic refractories involves high energy consumption and emissions, contributing to carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, some raw materials used in their production, such as silica, can have negative environmental impacts during extraction. In terms of disposal, monolithic refractories are typically difficult to recycle due to their composition and structure. As a result, they often end up in landfills, which can contribute to pollution and waste management issues. Overall, the environmental considerations associated with monolithic refractories highlight the need for sustainable manufacturing practices, improved waste management strategies, and the development of alternative refractory materials that have less negative environmental impact.
- Q: How are monolithic refractories different from traditional refractories?
- Monolithic refractories are different from traditional refractories in terms of their composition, installation method, and performance characteristics. Firstly, monolithic refractories are composed of a single material, as the name suggests, whereas traditional refractories are typically made up of multiple materials. This single material composition of monolithic refractories allows for better control over their properties and performance. Secondly, the installation of monolithic refractories is different from traditional refractories. Traditional refractories are usually installed in the form of bricks or precast shapes, which are assembled together to form the desired lining. On the other hand, monolithic refractories are supplied in a ready-to-use form, such as a dry mix or a suspension, which is then poured, sprayed, or gunned into place. This makes the installation process of monolithic refractories faster and more efficient. Lastly, monolithic refractories offer superior performance characteristics compared to traditional refractories. Monolithic refractories have better thermal shock resistance, higher hot strength, and improved resistance to chemical attacks. Additionally, they can be more easily repaired or patched compared to traditional refractories, which often require the replacement of entire bricks or shapes. Overall, the main differences between monolithic refractories and traditional refractories lie in their composition, installation method, and performance characteristics. Monolithic refractories offer better control over properties, easier installation, and superior performance, making them a preferred choice in many industrial applications.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories mitigate heat loss in iron and steel operations?
- Monolithic refractories possess unique properties and composition that make them highly effective in reducing heat loss in iron and steel operations. Unlike other refractories, monolithic ones are made from a single, continuous material, making them resistant to cracks and gaps that could potentially allow heat to escape. One major advantage of monolithic refractories lies in their exceptional thermal conductivity and insulation properties. With their low thermal conductivity, they are able to effectively limit the transfer of heat from hot areas to cooler surroundings. This insulation characteristic helps maintain high temperatures within iron and steel operations, resulting in reduced heat loss to the environment. Another contributing factor to heat loss mitigation is the ability of monolithic refractories to form a tight seal with the metal structures they are applied to. They adhere well to surfaces and fill in any gaps or irregularities, creating a solid barrier against heat loss. By minimizing the possibility of heat escaping, these refractories ensure that the energy generated within the operations is utilized effectively. Additionally, monolithic refractories exhibit high resistance to thermal shock. In the iron and steel industry, rapid temperature fluctuations are common, which can lead to material deterioration and cracks. However, monolithic refractories possess the ability to withstand these temperature changes without compromising their structural integrity. This guarantees the longevity and effectiveness of the refractories in mitigating heat loss. In summary, monolithic refractories play a vital role in reducing heat loss in iron and steel operations through their excellent insulation, ability to form a tight seal, and resistance to thermal shock. These properties enable them to maintain high temperatures, optimize energy utilization, and enhance overall process efficiency.
- Q: What are some common applications of monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry?
- Monolithic refractories are widely used in the iron and steel industry due to their superior performance and versatility. Some common applications of monolithic refractories in this industry include: 1. Blast Furnace: Monolithic refractories are used in the lining of blast furnaces to withstand high temperatures and chemical reactions. They help in maintaining the structural integrity of the furnace and provide insulation against heat loss. 2. Ladle Lining: Monolithic refractories are used to line ladles, which are used for transferring molten iron or steel from the blast furnace to the steelmaking process. These refractories provide excellent resistance to thermal shock and erosion caused by the aggressive molten metal. 3. Tundish Lining: Tundish is an intermediate vessel used to distribute molten steel to multiple casting molds. Monolithic refractories are employed in the tundish lining to ensure proper thermal insulation and prevent contamination of the steel during casting. 4. Electric Arc Furnace (EAF): Monolithic refractories are used in the lining of EAFs to withstand the extreme temperatures and chemical reactions involved in the steelmaking process. They provide excellent resistance to high heat and erosion caused by the molten metal and slag. 5. Induction Furnace: Induction furnaces are used for melting and refining metals. Monolithic refractories are used in the lining of induction furnaces to provide insulation and protect the furnace structure from the high temperatures and chemical reactions occurring during the melting process. 6. Continuous Casting: Monolithic refractories are used in the lining of continuous casting machines to ensure smooth and consistent casting of molten steel. They provide excellent resistance to high temperatures, thermal shock, and erosion caused by the molten metal and slag. Overall, monolithic refractories play a crucial role in the iron and steel industry by providing durability, thermal insulation, and resistance to chemical reactions, thereby enhancing the overall efficiency and productivity of the manufacturing process.
- Q: What are the recommended curing and drying procedures for monolithic refractories?
- The curing and drying procedures for monolithic refractories vary depending on the specific type and composition of the material. However, there are some general guidelines that can be followed. Curing involves allowing the refractory material to set and harden. This is achieved by subjecting the material to controlled temperature and humidity conditions. The purpose of curing is to develop the desired physical and chemical properties of the refractory, such as strength and resistance to thermal shock. Drying, on the other hand, involves removing moisture from the refractory material. This is important because moisture can cause cracking or spalling when exposed to high temperatures. Drying usually takes place after the curing process. The curing and drying procedures for monolithic refractories typically involve the following steps: 1. Preheating: Before applying the refractory material, it is necessary to preheat the surface where it will be applied. This prevents rapid moisture evaporation and ensures good adhesion of the refractory. 2. Mixing and application: The refractory material should be mixed according to the manufacturer's instructions and applied to the desired surface using appropriate techniques such as gunning, casting, or ramming. 3. Initial curing: After application, the refractory should be cured at a controlled temperature and humidity for a specific duration. This allows the material to set and strengthen. The curing temperature and duration may vary depending on the specific refractory material, but it is advisable to start with a lower temperature and gradually increase it. 4. Drying: Once the initial curing is complete, the refractory should be dried to eliminate any remaining moisture. This is done by gradually increasing the temperature in a controlled manner. The drying temperature and duration may vary depending on the specific refractory material, but it is important to avoid rapid temperature changes to prevent thermal stress and cracking. 5. Final curing: After drying, the refractory should be allowed to cool gradually to room temperature. This final curing step further enhances the strength and stability of the refractory. It is crucial to follow the manufacturer's guidelines and recommendations for the specific refractory material being used, as different materials may have different curing and drying requirements. Additionally, factors such as the size and shape of the refractory installation, as well as the surrounding environment, may also affect the curing and drying procedures. It is always advisable to consult with a refractory specialist or manufacturer to ensure the proper curing and drying procedures are followed for optimal performance and longevity of the monolithic refractories.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories help in improving the quality of iron and steel products?
- Several ways exist in which monolithic refractories play a crucial role in enhancing the quality of iron and steel products. Firstly, these refractories are utilized for lining furnaces and other high-temperature equipment in the iron and steel industry. By offering excellent thermal insulation, monolithic refractories aid in maintaining a consistent and controlled temperature inside the furnace, thus ensuring efficient heating and melting of metals. Furthermore, the utilization of monolithic refractories aids in reducing heat loss, thereby enhancing the energy efficiency of the process. This not only leads to cost savings but also minimizes the environmental impact associated with high energy consumption. Additionally, the insulation properties of monolithic refractories contribute to the reduction of thermal stresses within the furnace, preventing cracks and other structural damages that could potentially affect the quality of the iron and steel products. Moreover, monolithic refractories possess exceptional resistance to chemical reactions, corrosion, and erosion caused by molten metals, slag, and other harsh substances. This resistance helps in maintaining the integrity of the refractory lining, preventing the contamination of iron and steel products by unwanted impurities. As a result, the quality of the final products, such as steel bars, sheets, or pipes, is enhanced, meeting the desired specifications and industry standards. Another advantage offered by monolithic refractories is their ability to provide a sleek and pristine lining surface. This smoothness minimizes the adherence of slag, molten metal, and other by-products, thereby reducing the risk of defects and ensuring a higher-quality finish for the iron and steel products. Additionally, the clean lining surface facilitates easy maintenance and cleaning, enabling efficient and effective operations. In conclusion, monolithic refractories significantly contribute to the improvement of iron and steel product quality through their exceptional thermal insulation, resistance to chemical reactions, erosion, and corrosion, as well as their ability to provide a sleek and pristine lining surface. By ensuring consistent temperatures, reducing heat loss, preventing structural damages, and maintaining a clean environment, monolithic refractories enhance the overall efficiency and integrity of the iron and steel production process, resulting in high-quality end products.
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories High Temperature Ladle Sliding Gate Steel
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords