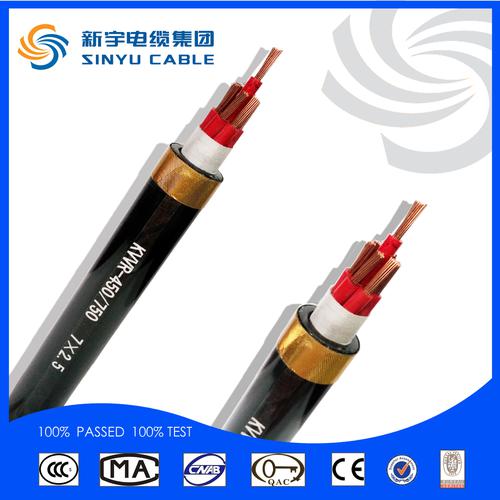
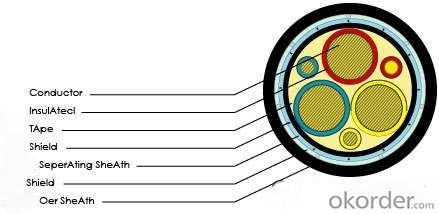
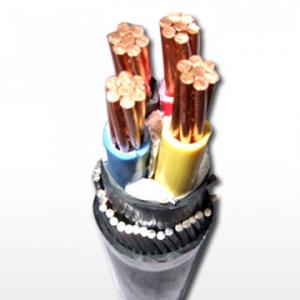
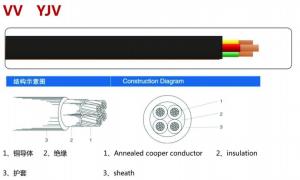
Flame retardant house wiring electrical control cable
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 1000000meters m/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Flame retardant house wiring electrical control cable
Features and Applications
The control cables are suitable for control, monitoring circuit and line protection at AC (alternating current) rated voltage 450/750V and below. The 105°C,135°Cflame-retardant PVC insulated and sheathed control cable has good anti-corrosion and aging-resistant performance when used under general condition.
Executive Standard
For PVC insulated and sheathed control cable, GB/T9330-2008 is applied
The combustion test standard for 105°C,135°C flame-retardant control cable is GB/T12666-2008
Operational Performances
1. Rated AC voltage: U0/U 450/750V.
2. Long-time allowed working temperature of cable conductor:
For PVC insulation and sheath, it is 70°C.
For flame-retardant 105°C,135°CPVC insulation and sheath,they are 105°C,135°C
3. Lowest ambient temperature:-40°C for fixed laying and-15°C for non-fixed laying
4. Allowed bending radius for laying: For cables without armored layer, it shall not be less than 6 times of cable outer diameter; for cables with armored layer or copper tape shield structure, it shall not be less than 12 times of cable outer diameter
Main Technical Data
Item | Unit | Technical Data | ||||||||||
resistance of conductor at 20°C | Ω/km | Section | 0. 5mm2 | 0.75mm2 | 1.0mm2 | 1.5mm2 | 2.5mm2 | |||||
Plating layer | No Tin- plating | Tin-plated | No Tin-plating | Tin-plated | No Tin-plating | Tin-plated | No Tin-plating | Tin-plated | No Tin-plating | Tin-plated | ||
Type AB | 36.0 | 36.7 | 24.5 | 24.8 | 18.1 | 18.2 | 12.1 | 12.2 | 7.41 | 7.56 | ||
Type R | 39.0 | 40.1 | 26.0 | 26.7 | 19.5 | 20.0 | 13.3 | 13.7 | 7.98 | 8.21 | ||
| MΩ/km | Type A | / | 0.012 | 0.011 | 0.011 | 0.01 | |||||
Type BR | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.009 | |||||||
Insulation resistance of cable at allowed max.temperature | kV/5min | 2.5 | ||||||||||
Flame-retardant character | Test shall be performed in terms of Standard No. GB/T12666.5-2008 | |||||||||||
Basic Types and Designations
1.PVC Insulated and Sheathed Control Cable
Type | Product Designation | Main Scope of Application |
KVV | Copper-core PVC insulated, PVC sheathed control | For laying in fixed sifts such as the indoor, cable ditch cable and conduit, etc. |
KVVP | Copper-core PVC insulated, PVC sheathed copper wire woven control cable | For laying in fixed sites such as the indoor, cable ditch and conduit, etc,where require shield. |
KVVP2 | Copper-core PVC insulated, PVC sheathed copper tape shield control cable | For laying in fixed sites such as the indoor, cable ditch and conduit, etc, where require shield. |
KVV22 | Copper-tort PVC insulated, PVC sheathed steel tape armored control cable | For laying in fixed sites such as the indoor,conduit bury, etc,where it can bear more mechanical external force. |
2. 105°C,135°C flame-retardant insulation & sheath control cable
Type | Product Designation | Main Scope of Application |
ZR105-KVV | Cu conductor 105°C flame-retardant PVC insulation & sheath control cable | For laying in fixed sites such as the indoor, cable ditch and conduit, etc. |
ZR105-KVVP | Cu conductor 105°C flame-retardant PVC insulation&sheath woven Cu wire shield control cable | For laying in fixed such as the indoor, cable ditch and conduit, etc, where require shield |
ZR105-KVV22 | Cu conductor 105°C flame-retardant PVC insulation&sheath steel tape armor control cable | For laying in fixed sites such as the indoor, conduit bury, etc, where it can bear more mechanical external force. |
ZR135-KVV | Cu conductor 135°C flame-retardant PVC insulation & sheath control cable | For laying in fixed sites such as the indoor,cable ditch and conduit,etc. |
ZR135-KVVP | Cu conductor 105°Cflame-retardant PVC insulation &sheath woven Cu wire shield control cable | For laying in fixed sites such as the indoor, cable ditch and conduit, etc, where require shield. |
ZR135-KVV22 | Cu conductor 105°C flame-retardant PVC insulation &sheath steel tape armor control cable | For laying in fixed sites such as the indoor ,conduit bury, etc, where it can bear more mechanical external force |





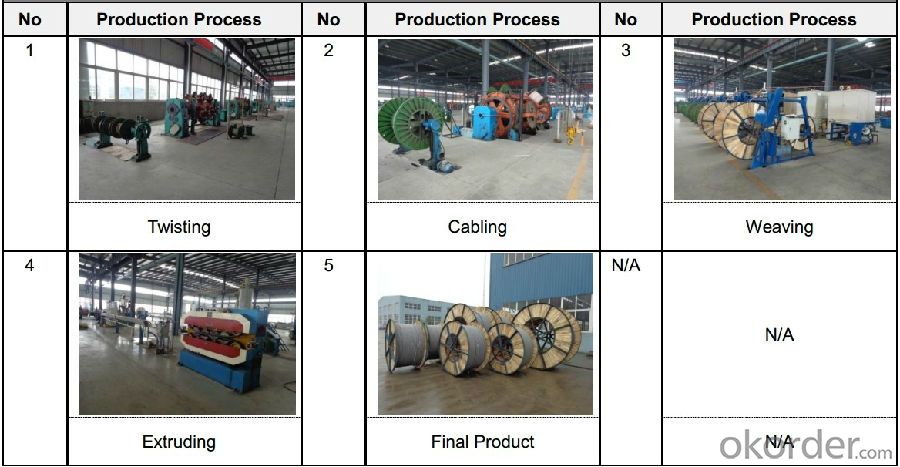

- Q: What is the difference between the power BV line and the power YJV cable?
- According to the provisions of GB-. pipes with a diameter of 15 mm can wear 3 BV-2.5 or 2 BV-4; and so on, 20 mm pipe, 3 * 4 or 4 * 2.5; 25 mm pipe, * 6 mm or 5 * 4; 32 mm tubing, wear 3 * 10 or 5 * 6; 40 mm tubing, wear 4 * 16 or 5 * 10; 50 mm tubing, wear 4 * 25 or 5 * 16 The The combination of the above, generally can be applied to all the current distribution lines of the way. As for the 35 square millimeters above the wire, the general use of cable laying, do not use PVC pipe, you can see the environment as a result of the application or wear pipe protection.
- Q: I was just wondering because I need a new power supply for my computer. It is an Acer Aspire AM3910-U4012. Is the power cable that connects to the motherboard the only power cable I need to replace or will I need to replace all the cables in my computer for it to work properly?
- If your current power supply is modular and you buy the same brand of modular power supply to replace it, then you can use most of the existing cables, if you want to. For most power supplies, all the cables are permanently attached. But there's nothing wrong with using existing cabling if it is modular. You have to be aware that different brands of power supplies use different types of modular cables, though. If you change brands of power supply, most likely you will need to replace all power cables, regardless of if they are modular or not...
- Q: its 6pin power cable on vga if we went really connect to psu if i not connect to that it ll happen something ?if i want to connect psu or mother board?
- The question was not making sense to me. 1. If you wanted to know if you wont connect any power cable to the video card will it work. No It will not work. The video card has its own power requirement hence it has to be connected to six pin PCIe power. If you don't have one of those in your power supply then then you have a molex to 6 pin power connector. 2. If you want to know if the PCI'e power connector canbe connected somewhere else the answer is no. 3. The graphic card can only be installed in PCIe X16 slot. Hope it helps Rocky :)
- Q: i cant drill a hole through the firewall because there's too much stuff in the way. so can i run the power cable to the power wire from the radio. the radio power wire is what im talking about. can i do that instead of running it to the battery? thanks
- No you can't use the radio power wire to power your amplifier. That circuit wasn't designed to carry the amount of power you'll be needing. As for getting through the firewall, generally you don't need to drill a hole. There are several holes already you can use. Find where the wire harness crosses the firewall from engine side to the cabin. Or in some cars there are circular rubber plugs in the firewall that you can run cable through. Search forums about your car to see if you can find where other people ran their power cables. In any case you need to make sure you run a dedicated, properly fused, properly sized wire. Otherwise you'll blow fuses or burn your car down.
- Q: my amplifier s power cable is not long enough to reach battery . so is there any problem if i take another piece of power cable and then attach them ?
- It's safe enough, as long as you make a good splice, and insulate it well. For automotive use, I like insulated, crimp-on splices. If this is a really high-power setup, and the power cable run is that long, you may be better off replacing it with heavier-gauge wire.
- Q: If you submerss the metal end of any kind of power cable like an extension cord in water will it work again?
- It will if dried out over night. Placing it in direct sunlight will dry it faster. A hand held hair blower/dryer will work the best. Never use a wet cord for anything! This could lead to electric shock and/or death!
- Q: hey guys, i recently bought a new desktop computer however when i unpacked it and put it all together i discovered that i had not received a power cable for the tower. i discovered an old one in the mess that is my bottom drawer and was wandering does it matter what power cable is used for the tower? or are there different power cables for different PSU's?
- As long as it fits, it should work.
- Q: I'm trying to install my radeon x800 xl graphics card into my dell inspiron 531 desktop. After inserting the card in the pci-e slot, and connecting the monitor cord to the card, I thought everything would work fine. I booted the computer and I got the error quot;You have not connected the power cable to your video cardquot;What do I need to do? This is an older video card, and I may have lost this supposed power cable. I'm lost with this and my computer won't even boot now. Any help is much appreciated. I'm willing to buy this power cord if i need to.
- In okorder /... EDIT The adapter would connect to any two unused 4 pin molex connectors coming from the power supply, it doesn't connect to the motherboard.
- Q: I bought a microphone that requires a phantom power source and I want to connect the mic to my computer using a XLR to USB cable. Will the USB/XLR cable also power my mic or do I need to buy an additional power source?
- But there are many more interfaces and you should pick the one that best suites your needs. Personally I use the M-Audio FireWire 410 which has a lot of other connectors besides 2x XLR like SPDIF and MIDI. cheers.
- Q: I am installing a sound system in my car straight from scratch. I have built the subwoofer enclosure but now I have run into a problem. The existing amplifier power cable is too short to reach my amp. I was wondering if any other cable could be used as a substitute to extend it just a few more inches or do I need to buy a whole new amp kit? Thanks
- Splices are not wise when high current is passed. It's a perfect spot for overheating. However, using a distrobution block as a splice would work fine. It won't look pretty but you can cut up a set of jumper cables as long as they're the same guage. Of course the more strands in stranded wire, the better.
Send your message to us
Flame retardant house wiring electrical control cable
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 1000000meters m/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords