YZP2(IPW54) Special frequency-changing three-phase asynchronous motor for tower crane
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
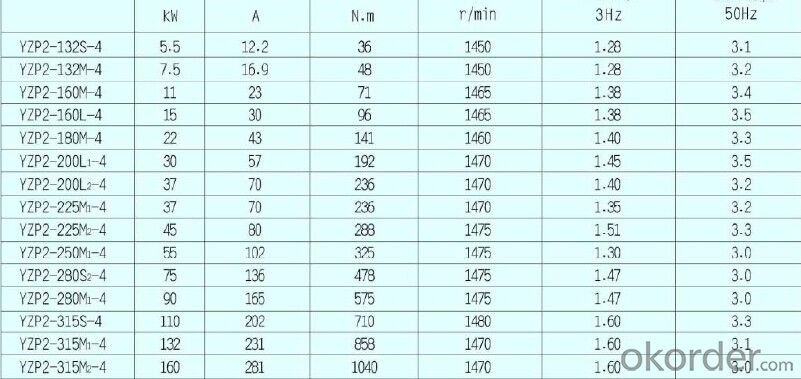
Power:
5.5-hundreds KW
Overview
YZPE2 variable-frequency three-phase asynchronous motor for lifting and metallurgy purposes is developed according to the characteristics of the
available tower crane, based on almost 10 years of experience in R&D of primary hoisting motor brake for the tower crane and metallurgy variable-frequency
motor. Lt is mainly used as a lifting mechanism of the tower crane, and also a trolley mechanism of heavy-duty crane
Features
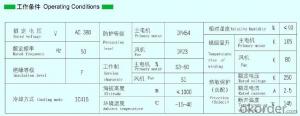
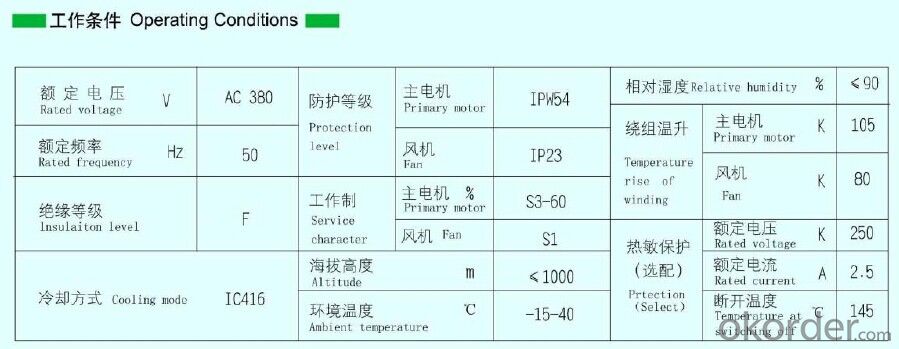
A variable一frequency special motor is equipped, available with a wide range offrequency conversion, small starting current and big starting torque;
A thermal protection component is buried into the winding, and can be wired into motor temperature control& protection system, making the motor
operation more secure and reliable;
Strengthened inter-turn insulation is adopted in the stator winding, so the insulation reliability is higher;
Equipped with axial一flow fan or centrifugal fan, with good cooling effect and lower motor temperature rise;
Special bearing is adopted for variable一frequency motor, so it's more suitable for variable一frequency operating environment;
The rotating shaft is subject to alloy steel heat treatment, showing better mechanical strength;
The brake (fitted with special manual release device) is a de-energized brake type (national utility model patent, Patent No. ZL201120188124.9), with big
braking torque and short response time
Users’Options:
A rotary encoder can be set at the end ofthe motor as per the user demands, so a speed closed-loop control system isformed to make adjustment more reliable and accurate. The encoder model isconfirmed by the users when signing the contract
- Q: I just asked a question about generating electricity from an AC motor and someone told me to quot;energize the windingsquot;. Can someone tell me what that is?
- you might be able to put some AC voltage at the correct phase into the capacitor start winding of the motor. If it is not a capacitor start motor, it might not have a winding that can be energized to operate as a generator. It will be tricky to produce the AC voltage at the correct phase and may not be practical since it might need to be in-phase with the speed of the motor. My guess is you will not be able to energize the capacitor start windings of an AC motor with DC and get anything useful. It might make a nice experiment for a science fair project, however if you do do an experiment driving with such a motor, be careful, the voltages can be lethal. a much better way to get electrical power from commonly available parts is to spin an automobile alternator that you got from a junkyard
- Q: is it possible to reduce rpm of AC motor with the help of rheostat?
- A rheostat will only limit current which limits torque. To control speed requires an inverter. A rather expensive device compared to an SCR controlled DC motor but it is worth it in some applications
- Q: I am planing to send some equipment overseas but I am not sure if there is going to be a problem or not. Here in the u.s., our cycle is 60hz, and where I am going it is 50hz. Please help.
- Check to see if the motor is rated at 50 hz. It may be that it works perfectly fine (with lower output of course) at 50 hz.
- Q: Does the DC motor work the same as the AC motor?
- DC motor has fast response, large starting torque and rotational speed from zero to the rated speed with rated torque available performance, but the advantages of DC motor is a DC motor because of its disadvantages, to generate performance under rated load torque is constant, the armature magnetic field and the rotor flux to maintain constant 90 degrees, this by brush and commutator. Carbon brush and commutator motor rotates in sparks, so in addition to cause toner component damage, use is restricted.
- Q: I am looking for a device that would allow me to control how fast a AC motor spins. I am using a 110v AC motor that came off a air compressor. Can anyone help?
- A light dimmer might work with a shaded pole motor driving a fan.
- Q: I listen to AM sports talk radio in my job trailer at work and notice that whenever anyone uses an AC motor on site, (Circular saw, corded drills, theading machines) , anything with coils and brushes, I get horrible static through the radio. Is there a filter to eliminate this noise?
- You might try a differrent kind of radio. Like one of those that are made by tool manufacturers for job sites. They have a lot of shielding around the tuning circuits to reduce the amount of EMI from power tools that gets picked up by the tuning circuits. You can't use a filter to reduce the noise. You need better RF shielding.
- Q: 4.5 amp 120 VAC 60hz MOTOR SPEED CONTROL SWITCH? help!?
- Most AC motors are not suitable for simple speed controls. Generally, you should contact a motor manufacturer's tech support to see which (if any) speed controls are suitable for a particular motor. Split phase motors are unlikely to start at a low speed setting and will burn out.
- Q: if i change voltage will the rpm of motor will be affected
- if it is dc motor speed is proportional to voltage. for induction motor without load it will not depend on voltage much but only frequency
- Q: How is the speed controlled on an electrical DC (or AC) motor? I'm sure I've heard that a motor will almost instantly reach full speed and this would be a problem in electric cars or even remote control ones, so I was wondering what components have to be used to solve this problem to allow the speed to gradually increase or to be adjusted in the case of an electric vehicle?
- The output speed of the motor depends on the amount of current passing through it. What you are thinking of is the torque of an electric motor, unlike a reciprocating engine an electric motor produces max. torque however fast the motor is turning. To control speed you would use some kind of variable resistor which would allow you to alter the current passing through it. Hope this helped :)
- Q: my AC unit at home is not working. I called two companies and they are giving me different quotes and fixing different things? Apparently the motor is not working, but one wants to replace quot;fan motorquot; and quot;blower wheelquot; and he quoted me $1450; another company said he needs to replace the quot;blower motorquot; and the bill for that would be $800. Both of them said the fan/motor aren't working and the unit does sound wrong when it's running.... but why are they recommending changing different things? The first company already charged me $200 for changing the capacitor, and that worked for a few days, but now i'm being told that it's the fan that's not working.... help please.....
- Where do you live those prices sound like Beverly Hills, are your neighbors Tom Cruise and Brad Pitt on the other side. Tops pay $350-400 for a new blower, you can buy them on OKorder for $150 and its literally just 3 screws and a clip and you just saved a ton.
Send your message to us
YZP2(IPW54) Special frequency-changing three-phase asynchronous motor for tower crane
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches