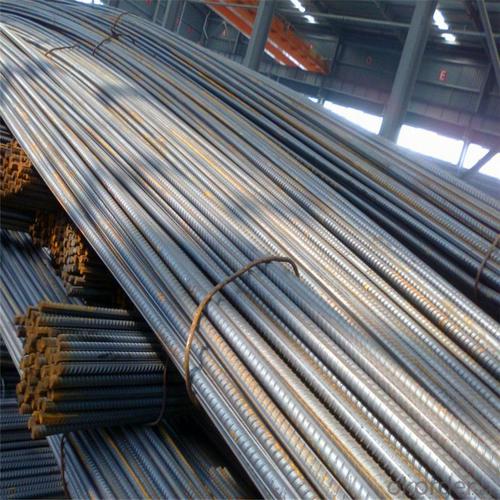
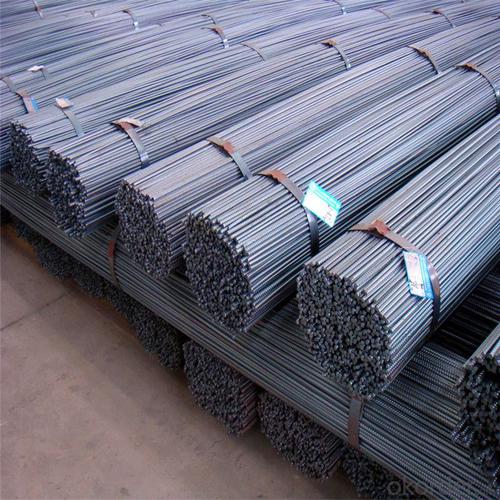
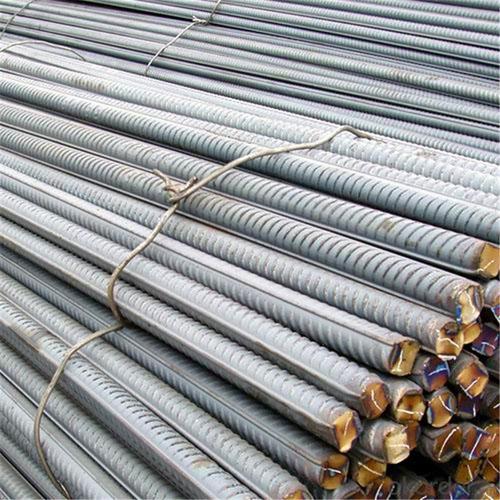
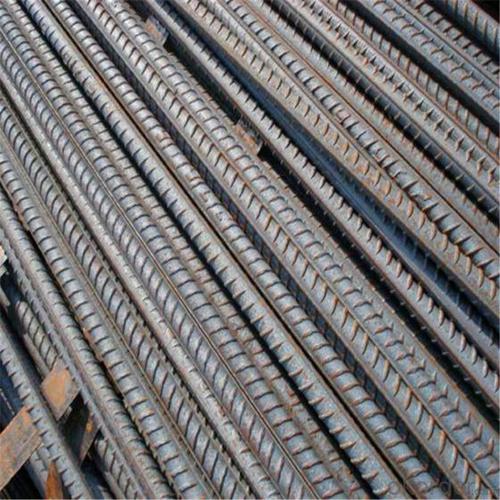
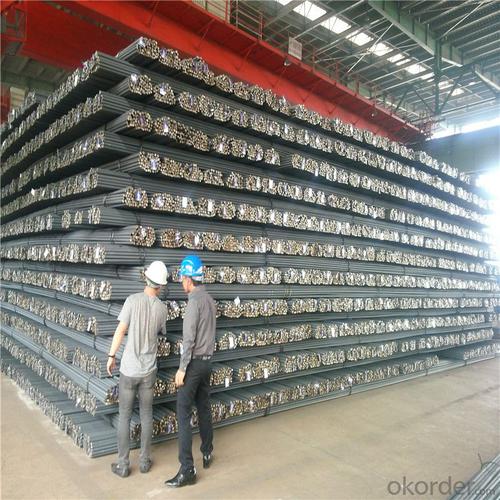
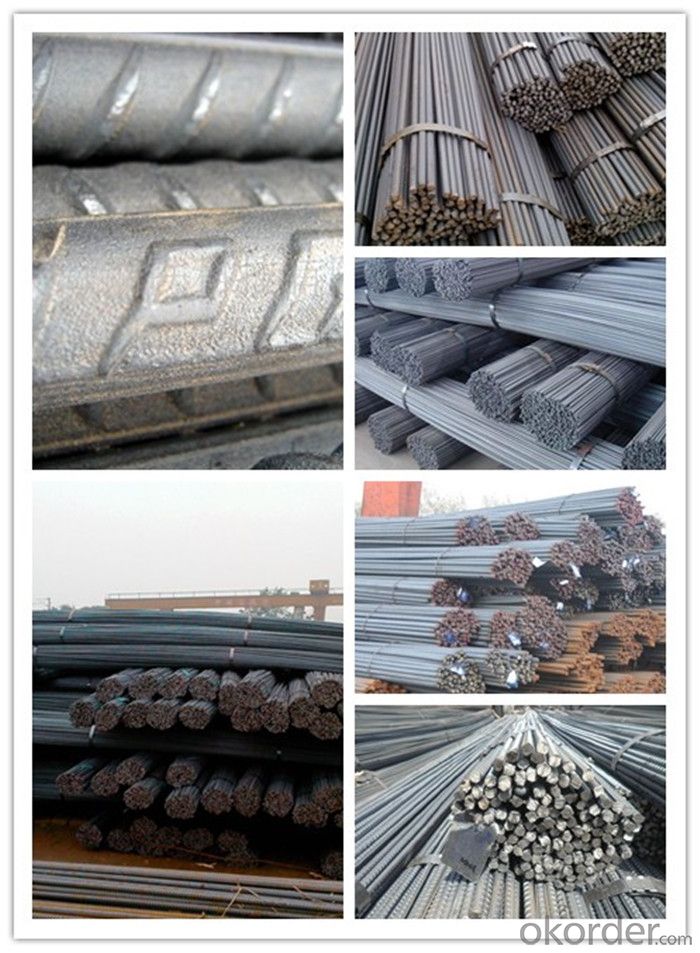
Wire Coiled Deformed Bars of Building Metal
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 500000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
Wire Coiled Deformed Bars of Building Metal
Description of Wire Coiled Deformed Bars
1, Diameter: 5.5mm-10mm Wire Coiled Deformed Bars
10m- 40mm Wire Coiled Deformed Bars
2, Length: 6m, 9m, 12m or customized
3, Standard: GB, ASTM, AISI, SAE, DIN, JIS, EN
OEM technology - send detailed technical parameters for accurate quotation.
2, Produce Process: smelt iron - EAF smelt billet - ESR smelt billet -
hot rolled or forged to get the steel round bar and plate
3, Heat Treatment: annealing, normalizing, tempering, quenching
4, Surface Treatment: Black
5, Quality Assurance: We accept third party inspection for all orders.
You can ask testing organizations such as SGS, BV, etc. to test our products before shipping.
Chemical Composition of Wire Coiled Deformed Bars
Grade | Technical data of the original chemical composition(%) | |||||
Reinforcing steel bar HRB335 | C | Mn | Si | S | P | B |
≤0.25 | ≤1.60 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | >0.0008 | |
Physics Capability | ||||||
Yield Strength(N/cm2) | Tensile Strength(N/cm2) | Elongation(%) | ||||
≥ 335 | ≥490 | ≥16 | ||||
Reinforcing steel bar HRB400 | C | Mn | Si | S | P | B |
≤0.25 | ≤0.16 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | 0.04-0.12 | |
Physics Capability | ||||||
Yield Strength(N/cm2) | Tensile Strength(N/cm2) | Elongation(%) | ||||
≥ 400 | ≥ 570 | ≥ 14 | ||||
Products Show of Wire Coiled Deformed Bars
Company Information
CNBM International Corporation is the most important trading platform of CNBM group.
Whith its advantages, CNBM International are mainly concentrate on Cement, Glass, Iron and Steel, Ceramics industries and devotes herself for supplying high qulity series of refractories as well as technical consultancies and logistics solutions.
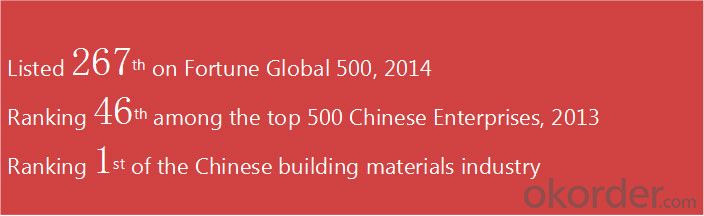
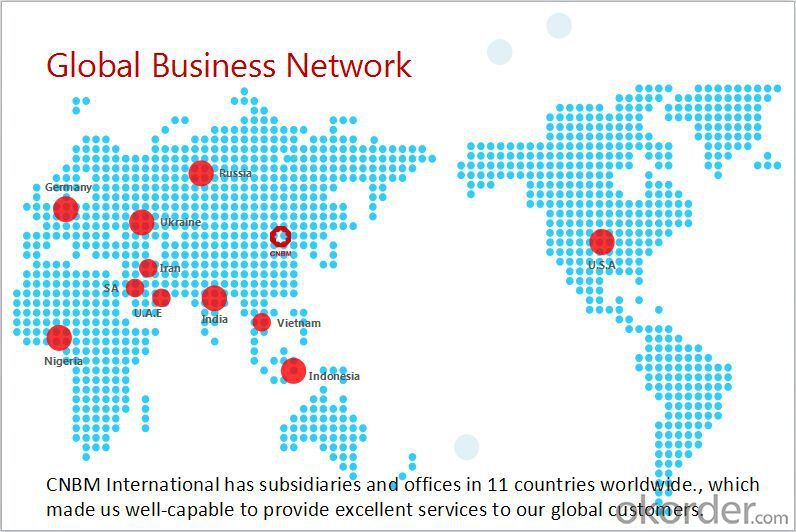
F A Q
1, Your advantages?
professional products inquiry, products knowledge train (for agents), smooth goods delivery, excellent customer solution proposale
2, Test & Certificate?
SGS test is available, customer inspection before shipping is welcome, third party inspection is no problem
3, Factory or Trading Company?
CNBM is a trading company but we have so many protocol factories and CNBM works as a trading department of these factories. Also CNBM is the holding company of many factories.
4, Payment Terms?
30% TT as deposit and 70% before delivery.
Irrevocable L/C at sight.
5, Trading Terms?
EXW, FOB, CIF, FFR, CNF
6, After-sale Service?
CNBM provides the services and support you need for every step of our cooperation. We're the business partner you can trust.
For any problem, please kindly contact us at any your convenient time.
We'll reply you in our first priority within 24 hours.
- Q: Can special steel be cast?
- Yes, special steel can be cast.
- Q: What are the emerging trends in the special steel industry?
- Some of the emerging trends in the special steel industry include the growing demand for lightweight and high-strength steel in the automotive and aerospace sectors, the increasing adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies such as additive manufacturing, and the focus on sustainability and eco-friendly practices in steel production. Additionally, there is a rising emphasis on research and development to develop innovative alloys and steel grades that offer superior performance and durability for various applications.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to the energy aftermarket industry?
- Special steel contributes to the energy aftermarket industry by providing high-quality and durable materials that are essential for the manufacturing of various energy-related components. It is used in the production of turbines, generators, pipelines, and other critical equipment, ensuring optimal performance and longevity in energy production and distribution. The special properties of this steel, such as corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance, and strength, make it an ideal choice for demanding applications in the energy sector. Its availability and usage in the industry contribute to enhanced efficiency, reliability, and overall sustainability in the energy aftermarket.
- Q: What are the different mechanical properties of special steel?
- Special steels have a variety of mechanical properties that make them unique and suitable for specific applications. Some of the key mechanical properties of special steel include high strength, excellent toughness, good wear resistance, and superior corrosion resistance. High strength is one of the most important properties of special steel. It allows the material to withstand heavy loads and stress without deformation or failure. This property makes special steel suitable for applications where structural integrity and durability are critical, such as in the construction of buildings, bridges, and machinery. Another significant mechanical property of special steel is its toughness. Toughness refers to the ability of a material to absorb energy and resist fracture under impact or sudden loads. Special steels with high toughness are essential for applications that involve dynamic and high-impact forces, such as in the manufacturing of tools, gears, and machinery components. Wear resistance is another important mechanical property of special steel. It refers to the ability of a material to resist damage and deterioration due to friction, abrasion, or erosion. Special steel with good wear resistance is commonly used in applications where it will be subjected to harsh conditions or repetitive mechanical actions, such as in the production of cutting tools, dies, and molds. Superior corrosion resistance is a valuable mechanical property of special steel, especially in environments where exposure to moisture, chemicals, or extreme temperatures is likely. Special steels with high corrosion resistance can withstand the deteriorating effects of oxidation, rust, and chemical reactions, making them suitable for applications in industries such as marine, chemical, and oil and gas. In summary, special steels possess a range of mechanical properties that set them apart from conventional steels. High strength, excellent toughness, good wear resistance, and superior corrosion resistance are some of the key mechanical properties that make special steel a preferred choice for various industrial applications.
- Q: What are the properties of corrosion-resistant stainless steel?
- Corrosion-resistant stainless steel possesses several key properties that make it highly resistant to corrosion. These properties include a high chromium content, which forms a protective oxide layer on the surface of the steel, preventing corrosion. Additionally, stainless steel is often alloyed with other elements such as nickel and molybdenum, which further enhance its corrosion resistance. The steel is also highly durable, with excellent strength and toughness, making it suitable for a wide range of applications in various industries. Overall, corrosion-resistant stainless steel offers exceptional resistance to corrosion, ensuring its longevity and reliability in harsh environments.
- Q: Can special steel be used in the construction equipment manufacturing industry?
- Yes, special steel can be used in the construction equipment manufacturing industry. Special steel is known for its exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to wear and tear, making it suitable for constructing heavy-duty machinery and equipment used in the construction industry. It offers superior performance in challenging and demanding applications, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the manufactured equipment. Additionally, special steel can be tailored to meet specific requirements and improve the functionality and efficiency of construction equipment.
- Q: Can special steel be used in the production of gearboxes?
- Yes, special steel can be used in the production of gearboxes. Special steel, such as alloy steel or heat-treated steel, is often preferred for gear manufacturing due to its high strength, durability, and resistance to wear and fatigue. These properties make special steel well-suited for transmitting power and withstanding the demands of heavy-duty applications, making it an ideal material choice for gearboxes.
- Q: How does special steel comply with international standards?
- Special steel is a type of steel that is specifically designed and manufactured to possess exceptional properties and performance characteristics. When it comes to complying with international standards, special steel undergoes a rigorous process to ensure its quality and adherence to the established norms. Firstly, special steel production adheres to international standards through the selection of raw materials. The composition and quality of the raw materials used in the manufacturing process are carefully controlled and tested to meet the specifications outlined by international standards organizations. This ensures that the special steel produced is of the desired quality and possesses the required mechanical properties. Secondly, special steel manufacturers follow standardized production processes. These processes are designed in accordance with international guidelines and standards to guarantee consistency and traceability. Through the use of advanced technologies and quality control measures, special steel manufacturers can monitor and control every stage of production, from melting and casting to rolling and heat treatment. This ensures that the final product meets the required standards in terms of chemical composition, mechanical properties, and dimensional tolerances. Furthermore, special steel undergoes stringent testing and inspection procedures to validate its compliance with international standards. This includes various destructive and non-destructive testing methods such as ultrasonic testing, hardness testing, and microstructure analysis. These tests are conducted by certified laboratories and independent third-party agencies to ensure unbiased and accurate results. In addition, special steel manufacturers often have their production processes and quality management systems audited and certified by recognized bodies, such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization), to demonstrate their commitment to compliance with international standards. It is also worth mentioning that special steel manufacturers actively participate in international standardization committees, such as ASTM International and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). By engaging in these committees, they can contribute to the development and revision of international standards, ensuring that their products remain up to date and in line with the latest industry requirements. In conclusion, special steel complies with international standards through careful selection of raw materials, adherence to standardized production processes, rigorous testing and inspection procedures, and active participation in international standardization committees. By following these measures, special steel manufacturers demonstrate their commitment to producing high-quality products that meet the stringent requirements of international standards.
- Q: What are the different methods for quenching special steel?
- There are several methods for quenching special steel, including oil quenching, water quenching, air quenching, and polymer quenching. These methods involve rapidly cooling the steel to achieve desirable hardness and strength properties. Oil quenching involves submerging the steel in oil, which provides a slower and more controlled cooling process. Water quenching, on the other hand, involves immersing the steel in water for a faster and more aggressive cooling rate. Air quenching refers to simply exposing the steel to air, allowing it to cool naturally. Lastly, polymer quenching involves using a specialized polymer solution as the quenching medium, which offers a combination of controlled cooling and reduced distortion. The choice of quenching method depends on the specific steel composition and desired properties.
- Q: What are the different methods for tempering special steel?
- There are several methods for tempering special steel, each with its own advantages and considerations. Some of the common methods used for tempering special steel include: 1. Air Tempering: This method involves heating the steel to a specific temperature and then allowing it to cool in still air. Air tempering is often used for low alloy steels and results in a uniform hardness throughout the steel. 2. Oil Tempering: In this method, the steel is heated to a specific temperature and then quenched in oil to cool it rapidly. Oil tempering is commonly used for tool steels as it provides a good balance between hardness and toughness. 3. Water Tempering: Similar to oil tempering, water tempering involves quenching the steel in water after heating it to a specific temperature. This method provides a higher rate of cooling and results in a harder steel, but it may also lead to increased brittleness. 4. Salt Bath Tempering: In this method, the steel is immersed in a molten salt bath at a specific temperature. The salt bath provides a more controlled and uniform heat transfer, resulting in a consistent hardness throughout the steel. 5. Cryogenic Tempering: Cryogenic tempering involves cooling the steel to extremely low temperatures, often below -100°C (-148°F), using liquid nitrogen or helium. This method helps to further reduce residual stresses and increase the wear resistance of the steel. It is important to note that the specific method chosen for tempering special steel depends on various factors, including the type of steel, desired hardness, intended application, and the desired balance between hardness and toughness. It is crucial to follow proper heat treatment guidelines and consult with experts to ensure the best results for a specific steel alloy.
Send your message to us
Wire Coiled Deformed Bars of Building Metal
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 500000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords


































