Steel I-Beams
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25Mt m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000Mt m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specifications of Steel I-Beams
1. Invoicing on theoretical weight or actual weight as customer request
2. Length: 5.8m, 6m, 9m, 12m as following table
3. Sizes of Steel I-Beams: 80mm-270mm
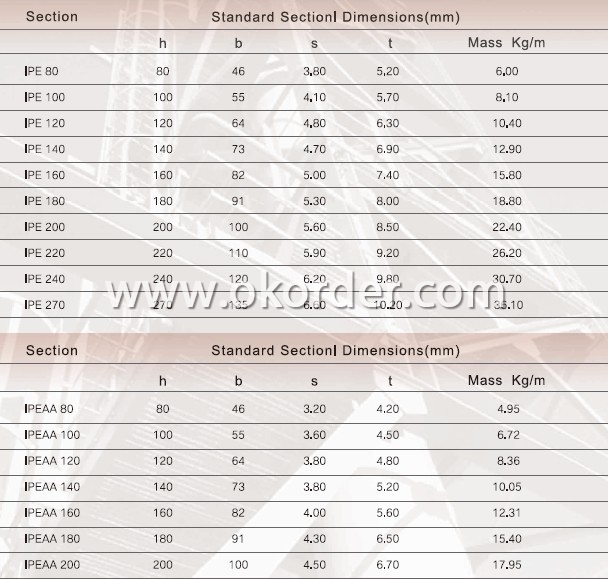
Dimensional Specifications of Steel I-Beams: EN10025, ASTM, GB Standard, JIS, etc.
Material Specifications of Steel I-Beams: EN10025, S235JR, GB Q235B or Equivalent
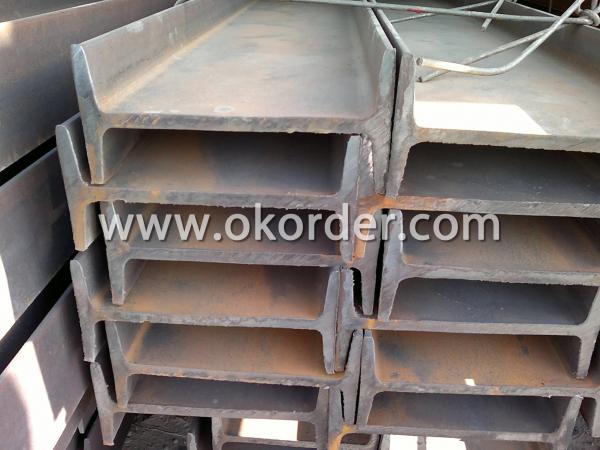

Applications of Steel I-Beams
Commercial building structure
Pre-engineered buildings
Machinery support structures
Prefabricated structure
Medium scale bridges
Package & Delivery of Steel I-Beams
1. Package: All the products are packed in bundles and tied by steel wire rod then put into containers or in bulk cargo. Each bundle of I-Beam will be hung with the markings of CNBM or as the requriements of the customer. Each bundle contains about 50 pieces.
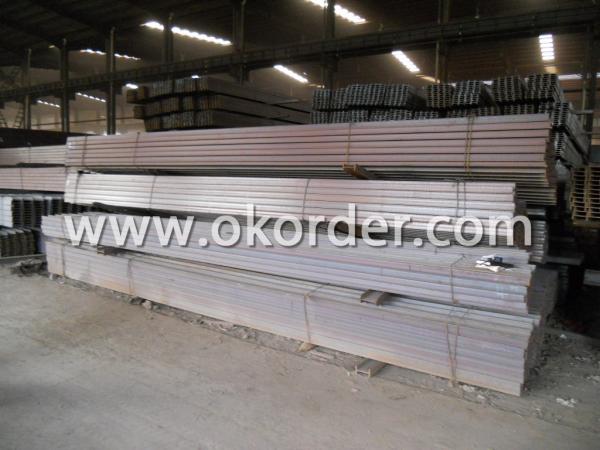

2.Tag mark: there will be tag mark tied up on the bundles. The information usually including supplier logo and name, product name, made in China, shipping marks and other information request by the customer.
If loading by container the marking is not needed, but we will prepare it as customer request.
3. Delivery: The Steel I-Beams will be delivered to the loading port in 45 days after receiving your advance payment or the original L/C at sight.
4. Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the maximum quantity can be loaded is around 40MTs by each truck. If the order quantity cannot reach the full truck loaded, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.


- Q: Are steel I-beams suitable for agricultural or industrial buildings?
- Indeed, agricultural and industrial buildings can rely upon steel I-beams as a suitable option. Renowned for their robustness and resilience, steel I-beams prove themselves as an excellent choice for bearing substantial burdens and enduring severe weather. Their versatility extends to various agricultural and industrial uses, encompassing the support of roofs, walls, and floors, as well as providing structural reinforcement for equipment and machinery. Moreover, steel I-beams exhibit resistance against pests, fire, and decay, rendering them a durable and economically sound selection for agricultural and industrial constructions.
- Q: How do you calculate the torsional deflection of a steel I-beam?
- To calculate the torsional deflection of a steel I-beam, you need to consider the beam's cross-sectional properties, such as its moment of inertia, torsional constant, and length. By applying the torsion equation, which relates the applied torque, the polar moment of inertia, and the length of the beam, you can determine the torsional deflection at a given point along the beam.
- Q: Can steel I-beams be used in hotels or hospitality buildings?
- Yes, steel I-beams can be used in hotels or hospitality buildings. Steel I-beams are commonly used in the construction industry due to their strength, durability, and ability to support heavy loads. They provide structural support and can be used in various applications, including framing, columns, and beams, making them suitable for hotels or hospitality buildings where large open spaces and high load-bearing capacities are often required.
- Q: What are the advantages of using steel I-beams in construction?
- There are several advantages of using steel I-beams in construction. Firstly, steel I-beams offer superior strength and durability, allowing for the construction of large and tall structures with minimal material usage. Secondly, steel I-beams have a high load-bearing capacity, enabling them to support heavy loads and resist bending or warping. Additionally, steel I-beams are versatile and can be easily fabricated into various shapes and sizes to suit different architectural designs. Lastly, steel I-beams are fire-resistant, making them a safe choice for construction projects.
- Q: How are steel I-beams installed on a construction site?
- Steel I-beams are installed on a construction site by first preparing the foundation or support structure. The beams are then lifted into place using cranes or other heavy machinery. They are carefully aligned and secured in position using bolts, welding, or a combination of both. Additional supports may be added as needed to ensure stability and structural integrity.
- Q: How do you calculate the bending capacity of a steel I-beam?
- To determine the bending capacity of a steel I-beam, various factors must be taken into account, such as the steel's material properties, the I-beam's shape and dimensions, and the load applied. Below is a stepwise procedure for calculating the bending capacity: 1. Establish the material properties: Acquire the yield strength and modulus of elasticity for the steel being used. These values are typically found in material specification documents or handbooks. 2. Identify the I-beam's shape and dimensions: Measure the flange width, flange thickness, web depth, and web thickness of the I-beam. These measurements determine the section modulus (Z) and moment of inertia (I) of the I-beam. 3. Calculate the section modulus (Z): The section modulus measures a beam's resistance to bending and can be determined using the formula: Z = (b * h^2) / 6, where b represents the flange width and h is the web depth. 4. Calculate the moment of inertia (I): The moment of inertia indicates a beam's resistance to bending about its neutral axis. For an I-beam, the formula for calculating the moment of inertia is: I = (b * h^3) / 12 + A * (d - h/2)^2, where A represents the flange area and d is the total depth of the I-beam. 5. Determine the applied load: Determine the type and magnitude of the load that will be imposed on the I-beam. This could be a uniformly distributed load (e.g., floor load) or a concentrated load (e.g., point load). 6. Calculate the bending stress: The bending stress, also known as flexural stress, can be calculated using the formula: σ = M / (Z * y), where M represents the bending moment, Z is the section modulus, and y is the distance from the neutral axis to the extreme fiber. 7. Determine the maximum bending moment: Depending on the applied load type, the maximum bending moment can be calculated using appropriate equations. For instance, in the case of a uniformly distributed load, the maximum bending moment can be calculated as M = (w * L^2) / 8, where w represents the load per unit length and L is the span length. 8. Calculate the bending capacity: Finally, compare the calculated bending stress (σ) to the steel's yield strength. If the bending stress is lower than the yield strength, the steel I-beam possesses adequate bending capacity. However, if the bending stress exceeds the yield strength, the beam may undergo plastic deformation or fail. It is essential to note that this procedure provides an estimate of the bending capacity and should be utilized as an initial design tool. For precise and accurate calculations, it is advisable to consult a structural engineer or refer to design codes and standards specific to your region.
- Q: Can steel I-beams be used for architectural canopies or awnings?
- Architectural canopies or awnings can indeed utilize steel I-beams. Renowned for their strength and durability, steel I-beams are a popular choice for structural purposes. Employed in canopies or awnings, they furnish a dependable framework capable of withstanding diverse weather conditions and supporting the weight of the materials employed. Moreover, steel I-beams can be tailored to suit desired designs and dimensions, permitting a versatile and visually pleasing architectural element. However, it is crucial to consider factors like load requirements, local building codes, and the necessity for additional weatherproofing and finishing options when utilizing steel I-beams for canopies or awnings. Consulting a structural engineer or architect is highly recommended to guarantee the appropriate design and installation of steel I-beams for architectural canopies or awnings.
- Q: Can steel I-beams be used in data center or technology facility construction?
- Yes, steel I-beams can be used in data center or technology facility construction. Steel I-beams are commonly utilized in the construction of commercial and industrial buildings, including data centers and technology facilities. These beams offer several advantages, such as high strength-to-weight ratio, durability, and ease of installation. They provide structural support and load-bearing capacity required for heavy equipment and infrastructure in data centers. Additionally, steel I-beams can be easily customized to meet specific project requirements, making them a suitable choice for constructing data centers and technology facilities.
- Q: Are steel I-beams resistant to pests and insects?
- Pests and insects do not pose a threat to steel I-beams, unlike wood that can be easily destroyed by termites, ants, and other pests. Steel, being an inorganic material, does not serve as a food source for these creatures. As a result, steel I-beams exhibit exceptional resistance to infestation and damage caused by pests and insects. Consequently, steel structures are frequently employed in construction to minimize the possibility of pest-related problems that could undermine the stability of a building.
- Q: What are the fire protection measures required for steel I-beams in certain applications?
- Fire protection measures required for steel I-beams in certain applications typically include the application of fire-resistant coatings or the use of fire-rated enclosures to prevent structural failure and maintain the integrity of the beams during a fire. Additionally, fireproofing materials such as gypsum-based boards or intumescent paints can be used to insulate the steel beams and delay their exposure to high temperatures. The specific fire protection measures depend on the building codes and regulations, as well as the fire rating requirements for the particular application.
1. Manufacturer Overview
| Location | Tangshan, China |
| Year Established | 2009 |
| Annual Output Value | Above US$ 230 Million |
| Main Markets | Mid East; Southeast Asia; Korea |
| Company Certifications | ISO 9001:2008; |
2. Manufacturer Certificates
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period |
3. Manufacturer Capability
| a) Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | Tianjin; |
| Export Percentage | 81% - 90% |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | 21-50 People |
| Language Spoken: | English; Chinese; |
| b) Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | Above 500,000 square meters |
| No. of Production Lines | 1 |
| Contract Manufacturing | OEM Service Offered; |
| Product Price Range | Average |
Send your message to us
Steel I-Beams
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25Mt m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000Mt m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords


























