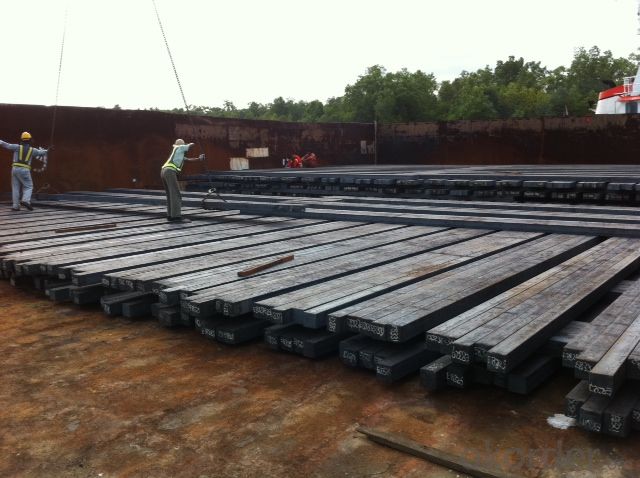
Prime square alloy steel billet 145mm Q235
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Prime square alloy steel billet 145mm Q235
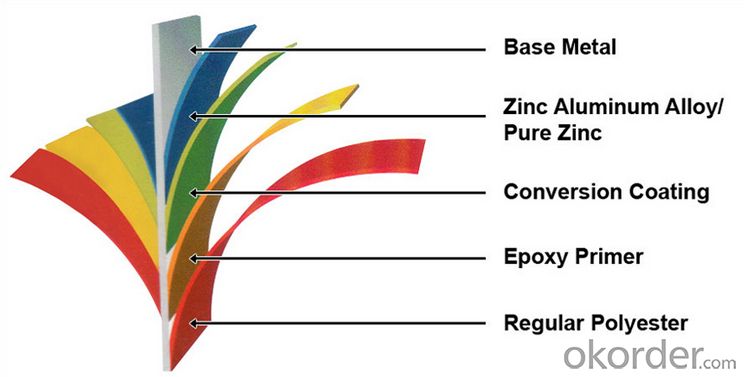
Description of Prime square alloy steel billet 145mm Q235
1) Excellent corrosion resistance: The zinc layer provides a good protection of Pre-painted Galvanizeed Steel Sheet.
2) High heat resistance: The reflective surface of the material aids in efficiently reflecting the sunlight away and in turn reducing the amount of heat transmitted. The thermal reflectivity converts into energy savings.
3) Aesthetics: Pre-Painted Galvanized steel sheet is available in plethora of patterns and multiple sizes as per the requirements that given by our customers.
4) Versatility: can be used in the various areas.

Main Feature of Prime square alloy steel billet 145mm Q235
Manufacture Progress:HRC-CRC-GALVANIZED-COLOR COATED
Application : Construction, electrical, transportation, steel plant, composite board plant, steel tile factory
Payment & Shipping Terms:T/T ,L/C, and FOB CHINA
Minimum Order Quantity: 25Tons
Packge Type: Moisture-proof paper inner,Steel outside,Bundle by steel rope.
Package in Container : Wood as a foot pad, wire rope reinforcement,PPGI steel coil tied together by steel rope.
Applications of Prime square alloy steel billet 145mm Q235
1) Excellent corrosion resistance: The zinc layer provides a good protection of Pre-painted Galvanizeed Steel Sheet.
2) High heat resistance: The reflective surface of the material aids in efficiently reflecting the sunlight away and in turn reducing the amount of heat transmitted. The thermal reflectivity converts into energy savings.
3) Aesthetics: Pre-Painted Galvanized steel sheet is available in plethora of patterns and multiple sizes as per the requirements that given by our customers.
4) Versatility: can be used in the various areas.

Specifications of Prime square alloy steel billet 145mm Q235
Product | Billet |
Material Grade | SGCC / SGCH / DX51D+AZ, etc |
Thickness | 0.6-3.0mm |
Width | 500-1500mm |
Tolerance | Thickness: +/-0.02mm , Width:+/-2mm |
Zinc-coating | Z30-150g/m2 |
Technique | Raw material: Hot rolled steel coil --> Cold rolled_>hot dipped galvalume |
Surface | Dried, Chromated, Unoiled |
Spangle | Regular spangle , small spangle, zero spangle |
ID | 508MM 610MM |
Coil weight | 1-25MT |
Export package | Cardboard inner sleeves, Waterproof paper, galvanized steel covered and steel strip packed |
FAQ of Prime square alloy steel billet 145mm Q235
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1. How Can I Visit There?
Our company is located in Tianjin City, China, near Beijing. You can fly to Tianjin Airport Directly. All our clients, from home or aboard, are warmly welcome to visit us!
2. How Can I Get Some Sample?
We are honored to offer you sample.
3. Why choose CNBM?
we always fix steel produce in container well to make it safe arrive at destination port
we always provide best and professional forward service for our buyer
we always apply 14days free detention for our buyers container in destination
we provide one set After-sales service for our buyer
we provide China inland steel market price report
we help our buyer become number one in local market .
- Q: What are the potential applications of steel billets in the textile aftermarket?
- Steel billets have limited potential applications in the textile aftermarket due to their heavy and rigid nature. However, they can be used as weights for fabric stretching or as support structures for heavy machinery in textile factories.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the production of automotive components?
- Automotive components heavily rely on steel billets as a crucial raw material. During the manufacturing process, these billets are heated and then either forged or rolled to form different shapes and sizes, ultimately creating the desired automotive parts. These billets serve as the foundation for producing crucial components such as engine blocks, crankshafts, connecting rods, axles, and suspension parts. Steel's high strength and durability make it the perfect material for these vital components, ensuring the safety and performance of automobiles. Once heated, the steel billets undergo various shaping processes, including hot forging or hot rolling. Hot forging involves applying pressure to the heated billet using a die to achieve the desired shape. This process not only finalizes the component's shape but also enhances its mechanical properties by aligning the steel's grain structure. On the other hand, hot rolling involves passing the heated billet through a series of rolling mills to gradually reduce its thickness and shape it into a specific profile. This method is commonly used for manufacturing long automotive components such as axles or suspension parts. Following the shaping process, the automotive components undergo additional manufacturing steps such as heat treatment, machining, and surface finishing to enhance their strength, precision, and aesthetic appeal. Steel billets offer numerous advantages in automotive component production. Their exceptional mechanical properties, including high strength, toughness, and wear resistance, make them ideal for withstanding the demanding conditions and loads experienced by automotive parts. Moreover, steel's malleability and formability enable manufacturers to create intricate and complex designs, ensuring optimal functionality and performance. In conclusion, steel billets play a crucial role in automotive component production by serving as the raw material that is shaped and formed into various critical parts. Steel's strength, durability, and versatility make it an essential material for ensuring the safety, reliability, and performance of automobiles.
- Q: How do steel billets contribute to the oil and gas industry?
- The oil and gas industry heavily relies on steel billets, which play a crucial role in numerous applications. These semi-finished metal products serve as vital raw materials for manufacturing pipes, valves, fittings, and other equipment necessary for extracting, transporting, and refining oil and gas. The primary application of steel billets in this industry involves producing seamless pipes. These pipes are essential for securely and reliably transporting oil and gas over long distances. Steel billets are heated and rolled to form seamless pipes that offer exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to high-pressure environments. Offshore drilling, subsea pipelines, and other critical activities in the oil and gas sector rely on these pipes. Additionally, steel billets are utilized in manufacturing valves and fittings that are essential for oil and gas infrastructure. Valves play a vital role in controlling the flow of oil and gas during production and transportation processes. Steel billets are shaped into valve bodies, which are then machined precisely to ensure proper functionality and reliability. Similarly, fittings such as couplings, elbows, and tees, are made from steel billets to create a secure and leakage-free system that connects different sections of pipelines and equipment. Moreover, steel billets are a primary material for constructing storage tanks and pressure vessels in the oil and gas industry. These tanks are used to store crude oil, natural gas, and various petroleum products. Steel billets are transformed into plates, which are then welded together to form these large-scale storage containers. The inherent strength and corrosion resistance of steel make it an ideal material for ensuring the safe containment of valuable resources. In conclusion, steel billets are indispensable in the oil and gas industry as they are transformed into various components required for extraction, transportation, and refining processes. From seamless pipes for long-distance transportation to valves, fittings, and storage tanks, steel billets provide the necessary strength, durability, and reliability demanded by this challenging industry.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of industrial compressors?
- Steel billets are an integral part of the manufacturing process for industrial compressors. These billets, which are essentially semi-finished steel products in the form of a rectangular solid, serve as the starting material for creating various components of the compressor. Firstly, steel billets are heated to high temperatures and then passed through a series of rolling mills to be shaped into specific forms such as bars, rods, or sheets. These processed steel billets are then used to fabricate critical components of the compressor, including the crankshaft, connecting rods, cylinder blocks, and piston rings. The crankshaft, a central component responsible for converting the reciprocating motion of the piston into rotational motion, is typically forged from a steel billet. The billet is subjected to controlled heating, shaping, and machining processes to achieve the desired shape and strength required for the crankshaft to withstand the high pressures and forces within the compressor. Similarly, connecting rods, which connect the piston to the crankshaft, are also manufactured from steel billets. These billets are machined to precise dimensions and undergo various heat treatment processes to ensure optimal strength and durability. Cylinder blocks, the main structural frame of the compressor, are often casted from steel billets. The billets are melted and poured into molds to form the desired shape. Once solidified, the cylinder block undergoes further machining to create the cylinder bores, mounting surfaces, and other necessary features. Additionally, steel billets are used to produce piston rings, which are crucial for maintaining proper compression and preventing leakage. The billets are machined and then subjected to heat treatment processes to enhance wear resistance and ensure a proper fit within the cylinder. Overall, steel billets are essential in the manufacturing of industrial compressors as they provide the raw material for creating key components. The ability to shape and process steel billets allows for the production of strong, durable, and high-performance compressors that can meet the demanding requirements of various industries.
- Q: How are steel billets inspected before they are used in production?
- Steel billets are inspected thoroughly before they are used in production to ensure their quality and adherence to the required specifications. The inspection process typically involves several key steps. Firstly, visual inspection is conducted to examine the surface of the billets for any surface defects such as cracks, seams, or deformities. Any irregularities can indicate potential weaknesses or problems in the billet that may affect its performance during production. Secondly, dimensional inspection is performed to verify the billet's size, length, width, and other critical dimensions. This is crucial to ensure that the billets meet the precise requirements of the production process and can be seamlessly integrated into the manufacturing operations. Thirdly, ultrasonic testing is often employed to detect any internal defects or discontinuities within the billets. Ultrasonic waves are passed through the billet, and any reflections or echoes are analyzed to identify any flaws such as voids, inclusions, or cracks that may compromise the structural integrity of the billets. Additionally, magnetic particle inspection may be carried out to identify surface or near-surface defects that may not be visible to the naked eye. This technique involves applying magnetic particles to the surface of the billet and detecting any magnetic leakage caused by defects through the use of magnetic fields. Furthermore, chemical analysis is frequently performed to ensure that the steel billets have the desired chemical composition. This involves taking samples from the billets and subjecting them to various tests to determine the percentages of different elements present. This analysis guarantees that the billets possess the necessary chemical properties for the intended application. Overall, steel billets undergo a comprehensive inspection process that encompasses visual examination, dimensional verification, ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle inspection, and chemical analysis. This multi-faceted approach ensures that the billets meet the required quality standards and are suitable for use in production, thus minimizing the risk of any performance issues or failures during manufacturing processes.
- Q: What are the different grades of steel billets?
- There are several different grades of steel billets, each with its own specific properties and applications. Some of the commonly used grades include: 1. Mild Steel Billets: These are low carbon steel billets that are often used in general construction and engineering applications. They have a relatively low tensile strength and are easily weldable and formable. 2. Carbon Steel Billets: These contain a higher carbon content than mild steel billets, giving them increased strength and hardness. They are commonly used in the manufacturing of automotive parts, machinery, and tools. 3. Alloy Steel Billets: These are steel billets that have been alloyed with other elements such as chromium, nickel, or molybdenum to improve specific properties. Alloy steel billets offer enhanced strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for applications in the aerospace, defense, and oil and gas industries. 4. Stainless Steel Billets: These billets contain high levels of chromium and nickel, which provide excellent corrosion resistance and durability. Stainless steel billets are commonly used in the production of kitchen appliances, cutlery, and medical equipment. 5. High-Speed Steel Billets: These billets are alloyed with tungsten, molybdenum, or vanadium to create a steel with exceptional hardness and heat resistance. High-speed steel billets are primarily used in the production of cutting tools such as drill bits and saw blades. It is important to note that the specific grades of steel billets can vary depending on the manufacturing standards and region. These grades are classified based on their chemical composition, mechanical properties, and intended applications, ensuring that the right steel billet is selected for the desired end use.
- Q: What are the different types of steel billet surface defects?
- There are several types of steel billet surface defects, including cracks, scale, surface laps, scratches, and pitting.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of construction scaffolding?
- Steel billets are used in the manufacturing of construction scaffolding as they serve as the primary raw material. These billets are first heated and then passed through a series of processes such as rolling, cutting, and shaping to form the necessary components of scaffolding, including tubes, frames, and joints. The high strength and durability of steel make it an ideal choice for scaffolding, ensuring the safety and stability required for construction workers.
- Q: How do steel billets contribute to the manufacturing of industrial machinery?
- Steel billets play a crucial role in the manufacturing of industrial machinery. These billets are essentially semi-finished steel products that are formed into a specific shape and size. They serve as the raw material for producing various components and parts used in industrial machinery. Firstly, steel billets provide the necessary strength and durability required for industrial machinery. The high tensile strength and toughness of steel make it ideal for withstanding heavy loads, vibrations, and extreme conditions that machinery often encounters. By using steel billets, manufacturers can ensure that the machinery they produce is capable of withstanding these demanding conditions, thereby increasing its reliability and longevity. Secondly, steel billets can be easily molded and shaped into different forms, allowing for the production of complex and intricate components. Industrial machinery often requires precision-engineered parts that are tailored to specific functions and applications. Steel billets can be cast or forged into these intricate shapes, ensuring that the machinery operates with optimal efficiency and accuracy. Additionally, steel billets offer excellent machinability, meaning they can be easily cut, drilled, and shaped using various machining techniques. This makes it possible to create intricate details and tolerances required for the precise functioning of industrial machinery. The ability to machine steel billets with precision allows manufacturers to produce components that fit together seamlessly, minimizing any potential performance issues. Moreover, steel billets provide a cost-effective solution for manufacturing industrial machinery. Steel is readily available and has a relatively low cost compared to other materials. Its superior strength-to-weight ratio also allows manufacturers to design machinery that is lighter in weight without compromising its structural integrity. This not only reduces manufacturing costs but also makes the machinery more portable and easier to transport. Furthermore, steel billets offer excellent corrosion resistance, which is crucial for industrial machinery that operates in harsh environments. The protective oxide layer that forms on the surface of steel billets helps prevent rust and corrosion, ensuring that the machinery remains in optimal working condition even in challenging conditions. In conclusion, steel billets are essential in the manufacturing of industrial machinery due to their strength, durability, machinability, cost-effectiveness, and corrosion resistance. These properties enable manufacturers to produce reliable, precise, and long-lasting machinery that can withstand demanding industrial applications.
- Q: What are the potential safety risks associated with handling steel billets?
- Handling steel billets can pose several potential safety risks. First and foremost, the weight of steel billets can be substantial, and improper lifting or carrying techniques can lead to musculoskeletal injuries such as strains and sprains. It is important to use proper lifting equipment and techniques to minimize the risk of these injuries. Another potential safety risk is the sharp edges and corners of steel billets. If not handled carefully, these edges can cause lacerations or puncture wounds. Wearing appropriate personal protective equipment, such as cut-resistant gloves, can help mitigate this risk. Steel billets may also be hot when they are being handled, especially if they have recently been processed or manufactured. Contact with hot billets can result in burns or thermal injuries. It is crucial to use heat-resistant gloves or other protective measures when handling hot steel billets. Additionally, steel billets are often transported using heavy machinery such as cranes or forklifts. Operating these machines without proper training or supervision can lead to accidents, including collisions, falling objects, or overturning of equipment. Adequate training, following safety protocols, and maintaining clear communication are essential to minimize these risks. Finally, steel billets may contain various chemical coatings or residues, which can be hazardous if ingested, inhaled, or come into contact with the skin. It is important to be aware of any potential hazardous substances present on the billets and take appropriate precautions, such as wearing protective clothing, gloves, and respiratory equipment if necessary. Overall, the potential safety risks associated with handling steel billets include musculoskeletal injuries, lacerations or puncture wounds, burns or thermal injuries, accidents involving heavy machinery, and exposure to hazardous substances. Following proper safety procedures, using appropriate protective equipment, and receiving comprehensive training can help mitigate these risks and ensure a safe working environment.
Send your message to us
Prime square alloy steel billet 145mm Q235
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords
































