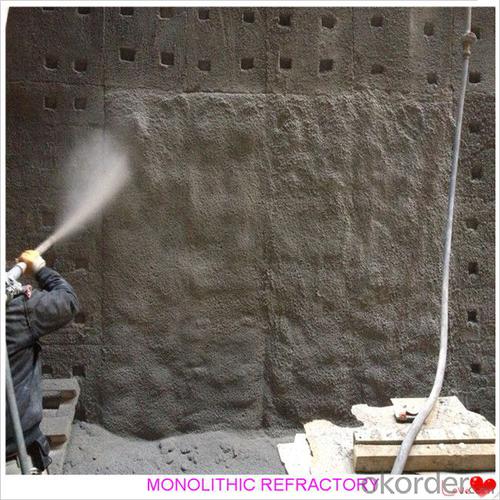
Monolithic Refractories Portland Cement 42.5 Castable A Std for Iron and Steel Industry
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 3000000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Portland Cement 42.5 Castable A STD For Fireplace and Industrial Furnace
Product Description:
Portland cement 42.5 castable is manufactured according to international standards. The product is famous for its excellent abrasion resistance and low thermal conductivity. Further, these can be provided in different specifications as required by the clients. The Portland cement 42.5 castables are used high purity raw materials and additives as the main material, and made of under superfine powder adding technology.
Product Advantages:
The material has excellent structural stability and air tightness, and has high physical and chemical properties, also has a fine working ability.They should be used with the same material products.
Product Applications:
For feature of Portland cement 42.5 castable, they have excellent abrasion resistance, thermal shock resistance, high-temperature resistance, anti-corrode and have high intensity.
Designed for refractory lining of blast furnace iron and slag runners, skimmers and soon
They can be used in troughs of small and mid size BFs and in all positions of the troughs where fast tapping is required.
Product Specifications:

FAQ:
1. How you can control your quality?
For each production processing, we have complete QC system for the chemical composition
and Physical properties. After production, all the goods will be tested, and the quality certificate
will be shipped along with goods.
2. What's your delivery time?
It usually needs about 20days- 45 days after receiving the deposit.
3. Do you provide free samples?
Yes, we can provide a free sample for testing, If we have sample in stock,
The quantity based on the material type, The buyer should bear all the shipping costs.
4. What's your payment terms?
We can accept 30% deposit, 70% balance before shipment for ordrs over $ 2000.
5. Can we visit your Company?
Yes, certainly. You are very welcome to China and we will be honored to have a customer and friend.
Product Picture:




- Q: What are the common failure mechanisms of monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry?
- Common failure mechanisms observed in monolithic refractories within the iron and steel industry include: 1. Thermal spalling: Monolithic refractories endure extreme temperature variations during the iron and steel production process. These rapid changes in temperature can cause the refractory material to expand and contract, resulting in thermal stress and eventual spalling. This failure mechanism is particularly prevalent in areas where the refractory is exposed to elevated temperatures, such as the hot face of a furnace. 2. Chemical attack: The iron and steel production process involves the utilization of various chemicals and molten metal, which can react with the refractory material over time. Chemical attack can lead to the deterioration of the refractory, resulting in cracks, erosion, and eventual failure. Slag, alkalis, sulfur, and other impurities present in the production environment are commonly responsible for this type of damage. 3. Abrasion: The movement of materials, such as iron ore, coke, and fluxes, can cause abrasion on the refractory lining. This mechanical wear and tear weaken the refractory material, eventually leading to failure. Areas experiencing high material flow rates or turbulence, such as tapholes or launder systems, are particularly prone to abrasion. 4. Corrosion: Monolithic refractories can be susceptible to corrosion caused by gases, liquids, and solids found in the iron and steel production environment. Corrosion occurs due to the presence of oxygen, water vapor, and various chemical compounds, such as carbon monoxide and sulfur compounds. It results in the formation of corrosive products, such as oxides or sulfides, which degrade the refractory material over time. 5. Mechanical stress: Monolithic refractories may undergo mechanical stress due to factors like thermal expansion and contraction, vibration, or mechanical impact. Excessive mechanical stress can lead to the development of cracks or fractures in the refractory lining, compromising its integrity and resulting in failure. To mitigate these failure mechanisms, it is crucial to select appropriate refractory materials, conduct regular inspections, and perform necessary maintenance. Furthermore, designing refractory linings that consider specific operational conditions and employing appropriate installation techniques can enhance their performance and lifespan within the iron and steel industry.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories prevent heat loss through convection?
- Monolithic refractories prevent heat loss through convection by their unique composition and structure. Unlike traditional refractory bricks, which are often porous and have gaps between them, monolithic refractories are made of a single, seamless structure. This eliminates any potential pathways for hot gases or air to circulate and carry away the heat through convection. Additionally, monolithic refractories are often dense and have a high thermal conductivity, which means they are excellent conductors of heat. This property allows them to quickly absorb and distribute the heat, minimizing the temperature difference between the hot surface and the surrounding environment. By reducing the temperature gradient, monolithic refractories minimize the driving force for convection, thereby reducing heat loss through this mechanism. Furthermore, monolithic refractories can be applied as a continuous lining, conforming to the shape of the equipment or furnace being protected. This seamless application eliminates joints or gaps where hot gases or air could escape and carry away heat. This uniform, uninterrupted lining further reduces the potential for convection heat loss. Overall, monolithic refractories are designed to create a barrier that prevents the movement of hot gases or air, thereby minimizing heat loss through convection. Their dense composition, high thermal conductivity, and seamless application all contribute to their effectiveness in preventing heat loss through this mechanism.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories perform in reheating furnace applications?
- Due to their exceptional thermal stability, strength, and resistance to thermal shock, monolithic refractories are highly effective in reheating furnace applications. These refractories are specifically designed to withstand the harsh operating conditions commonly found in reheating furnaces, including high temperatures and rapid temperature changes. One major advantage of using monolithic refractories in reheating furnace applications is their ability to provide a seamless lining. Unlike traditional brick refractories that require extensive installation and joints, monolithic refractories can be easily applied as a single, homogeneous layer. This eliminates the risk of thermal stress and cracking at joints, ensuring a more reliable and durable lining. Furthermore, monolithic refractories offer excellent thermal insulation properties, which help conserve energy and reduce heat loss in the reheating furnace. This not only improves overall furnace efficiency but also reduces operational costs. In addition to their insulation properties, monolithic refractories exhibit high mechanical strength, allowing them to withstand the mechanical stress and abrasion caused by the movement of the furnace charge. They also have good resistance to chemical attack from gases, slags, and molten metals commonly encountered in reheating furnace operations. Another advantage of monolithic refractories is their ease of repair and patching, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous furnace operation. They can be easily shaped and molded to fit various furnace geometries, making them highly versatile and adaptable to different reheating furnace designs. In summary, monolithic refractories offer exceptional performance in reheating furnace applications by providing superior thermal stability, strength, and resistance to thermal shock. Their seamless lining, thermal insulation properties, and resistance to mechanical and chemical stress make them an ideal choice for ensuring reliable and efficient furnace operation.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand thermal shock and mechanical stress?
- Monolithic refractories are engineered to withstand high temperatures and harsh working conditions, making them ideal for applications that involve thermal shock and mechanical stress. Firstly, monolithic refractories are designed with a high thermal conductivity, which allows them to quickly absorb and distribute heat. This property helps to minimize thermal gradients within the material, reducing the risk of thermal shock. When exposed to sudden temperature changes, the refractory material expands and contracts uniformly, preventing cracks and fractures from forming. Secondly, these refractories have excellent thermal shock resistance due to their low thermal expansion coefficient. This means that they have a minimal tendency to expand or contract when subjected to temperature fluctuations. As a result, they can withstand rapid changes in temperature without experiencing significant structural damage. Furthermore, monolithic refractories possess high mechanical strength, enabling them to withstand various types of mechanical stress. They are formulated with carefully selected raw materials and additives that enhance their load-bearing capacity and resistance to mechanical forces. This enables them to withstand the weight of the surrounding materials, as well as any external forces or vibrations that may be present in the application environment. Moreover, monolithic refractories have good structural integrity and stability, thanks to their dense and compact microstructure. These materials are typically formed by a combination of fine powders, binders, and additives, which are mixed and shaped to create a solid, cohesive structure. This structure provides resistance against mechanical stress, preventing the refractories from crumbling or disintegrating under pressure. In summary, monolithic refractories withstand thermal shock and mechanical stress through their high thermal conductivity, low thermal expansion coefficient, robust mechanical strength, and structural integrity. These properties make them reliable and durable materials for applications requiring resistance to extreme temperatures and challenging operating conditions.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories improve the performance and efficiency of iron and steel production?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in improving the performance and efficiency of iron and steel production. These specialized materials are designed to withstand extreme temperatures, chemical reactions, and mechanical stresses, making them ideal for use in high-temperature industrial processes. One of the key ways in which monolithic refractories enhance performance is by providing a protective lining in furnaces, kilns, and other equipment used in iron and steel production. Due to their superior heat resistance, they protect the underlying structure from the intense heat and prevent any detrimental effects on the equipment. This results in reduced downtime, longer service life, and ultimately, increased overall efficiency. Monolithic refractories also ensure better thermal efficiency in the production process. By minimizing heat losses, these materials help to maintain a stable and uniform temperature distribution, thereby improving the energy efficiency of the system. This is particularly important in iron and steel production, where precise temperature control is crucial for achieving the desired metallurgical properties of the final product. Furthermore, monolithic refractories offer excellent resistance to chemical corrosion, erosion, and slag attacks. They act as a barrier between the molten metal and the refractory lining, preventing undesirable reactions and material degradation. This helps to maintain the integrity of the furnace lining, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements. Consequently, it leads to increased productivity and cost savings in the long run. Another advantage of monolithic refractories is their ability to be easily shaped, repaired, or replaced. Unlike traditional brick refractories, which require extensive labor and time-consuming installation, monolithic refractories can be applied in a more flexible and efficient manner. Their flexible nature allows for easy repair of damaged areas, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous production. In summary, the use of monolithic refractories significantly enhances the performance and efficiency of iron and steel production. These materials provide a protective lining, improve thermal efficiency, resist chemical corrosion, and offer easy installation and repair options. By optimizing the production process, monolithic refractories contribute to higher productivity, reduced downtime, and increased cost-effectiveness in the iron and steel industry.
- Q: What are the specific requirements of monolithic refractories for steel ladle purging applications?
- Monolithic refractories used for steel ladle purging applications need to possess specific characteristics. These include high resistance to thermal shock and spalling, excellent erosion and corrosion resistance, low porosity, and high strength at high temperatures. Additionally, they should have good thermal conductivity and be capable of withstanding aggressive steel compositions and temperatures. Overall, the specific requirements for monolithic refractories in steel ladle purging applications are aimed at ensuring durability, longevity, and optimal performance in the harsh conditions of the steelmaking process.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand high temperatures in iron and steel processing?
- Monolithic refractories are able to withstand high temperatures in iron and steel processing due to their unique composition and properties. These refractories are primarily made of a single, continuous material, making them highly resistant to thermal shock and mechanical stress. Additionally, they have a high melting point and excellent heat insulation properties, allowing them to maintain their integrity even in extreme heat conditions. The refractories also possess good chemical stability, preventing reactions with molten metals and other corrosive substances often encountered in iron and steel processing facilities. Overall, the combination of these features enables monolithic refractories to endure the intense temperatures and harsh conditions involved in iron and steel processing.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories enhance the performance of ladle and tundish purging systems?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in enhancing the performance of ladle and tundish purging systems in several ways. Firstly, monolithic refractories offer excellent thermal insulation properties. Ladle and tundish purging systems require high temperatures to effectively remove impurities and gases from molten metal. The use of monolithic refractories helps to minimize heat loss and maintain the desired temperature within the system. This ensures that the purging process is carried out efficiently and effectively. Secondly, monolithic refractories provide superior erosion and corrosion resistance. During the purging process, the molten metal and purging gases can be highly corrosive and abrasive. Monolithic refractories are designed to withstand such harsh conditions, preventing erosion and corrosion of the lining. This prolongs the lifespan of the ladle and tundish purging systems, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements. Furthermore, monolithic refractories offer excellent strength and stability. Ladle and tundish purging systems experience significant mechanical stresses due to the movement of molten metal and purging gases. The use of monolithic refractories ensures the structural integrity of the lining, preventing any deformation or failure under these conditions. This allows for smooth and uninterrupted purging operations, improving the overall performance of the system. In addition, monolithic refractories provide ease of installation and maintenance. Unlike traditional brick and mortar refractories, monolithic refractories can be easily applied as a single, homogeneous layer. This simplifies the installation process and reduces the time and effort required for maintenance. Any necessary repairs or replacements can be carried out more efficiently, minimizing downtime and maximizing the productivity of the ladle and tundish purging systems. Overall, monolithic refractories enhance the performance of ladle and tundish purging systems by providing excellent thermal insulation, erosion and corrosion resistance, strength and stability, as well as ease of installation and maintenance. These properties contribute to the efficient and effective removal of impurities and gases from molten metal, ensuring high-quality output and optimizing the overall productivity of the purging process.
- Q: What are the recommended installation techniques for monolithic refractories?
- The recommended installation techniques for monolithic refractories typically involve proper surface preparation, mixing of refractory materials, and precise application. It is crucial to clean and remove any loose debris from the substrate before installation. The refractory materials should be mixed thoroughly with the appropriate water content to achieve the desired consistency. It is recommended to use vibration or tamping techniques during application to remove air pockets and ensure proper compaction. Careful curing and drying processes should be followed to prevent thermal shock and achieve optimal performance.
- Q: What are the specific requirements of monolithic refractories for ladle transfer applications?
- Monolithic refractories used in ladle transfer applications have specific requirements to ensure their effectiveness and durability. These requirements are essential for maintaining the integrity of the ladle lining and preventing any issues during the transfer process. Firstly, monolithic refractories for ladle transfer applications must have excellent thermal shock resistance. Ladles are subjected to extreme temperature changes during the transfer process, and the refractories must be able to withstand rapid heating and cooling without cracking or spalling. This property helps to prevent any damage to the lining and maintains the structural integrity of the ladle. Secondly, ladle transfer applications require monolithic refractories with high resistance to chemical attack. Ladles often come into contact with various molten metals and slag, which can have corrosive properties. The refractories must be able to withstand these corrosive environments and maintain their physical and chemical properties over time. Another important requirement is good mechanical strength. Ladles can experience significant mechanical stress during the transfer process, including impacts and vibrations. Therefore, the monolithic refractories need to have sufficient strength to resist these mechanical forces and prevent any cracking or failure in the lining. Furthermore, ladle transfer applications often involve the use of fluxes and additives, which can have different physical properties. The refractories used must have compatibility with these fluxes and additives to ensure proper performance and avoid any adverse reactions that could affect the ladle's lining. Lastly, monolithic refractories for ladle transfer applications should have low porosity. Low porosity helps to minimize the penetration of molten metal and slag into the refractory lining, reducing the risk of erosion and extending the service life of the refractories. In summary, the specific requirements of monolithic refractories for ladle transfer applications include excellent thermal shock resistance, high resistance to chemical attack, good mechanical strength, compatibility with fluxes and additives, and low porosity. By meeting these requirements, the refractories can effectively withstand the harsh conditions of ladle transfer and ensure the longevity and performance of the ladle lining.
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories Portland Cement 42.5 Castable A Std for Iron and Steel Industry
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 3000000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords