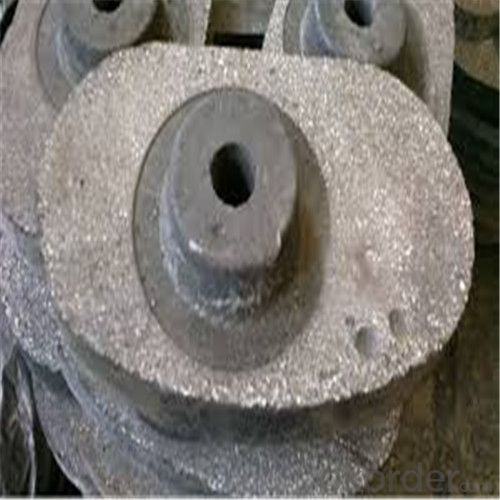
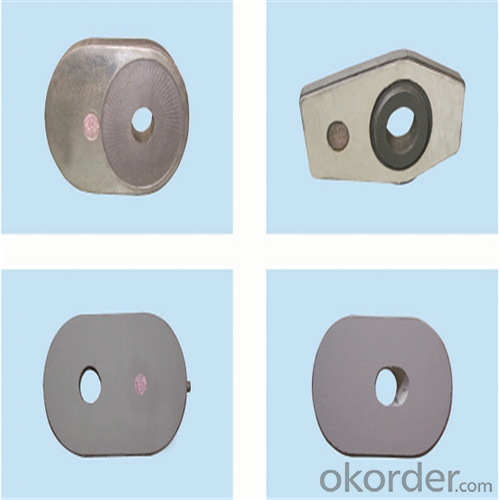
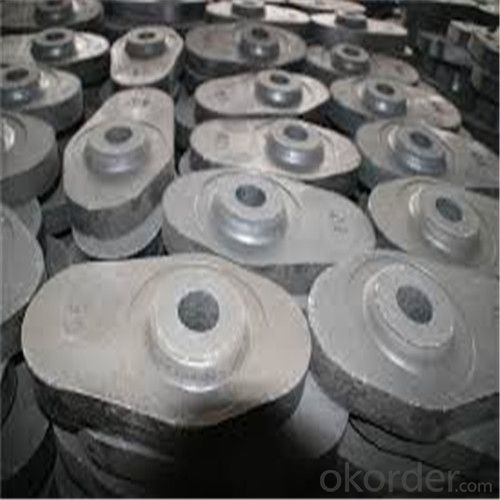
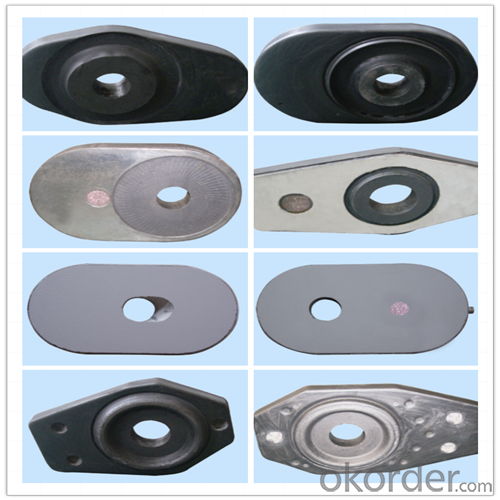
Monolithic Refractories High Temperature Ladle Sliding Gate for Iron and Steel Industry 2024
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for High Performance Refractory Ladle Slide Gate
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Shape: | Plate | Material: | Alumina Block |
| SiO2 Content (%): | N/A | Al2O3 Content (%): | 80-90% | MgO Content (%): | N/A |
| CaO Content (%): | N/A | Refractoriness (Degree): | 1770°< Refractoriness< 2000° | CrO Content (%): | N/A |
| SiC Content (%): | N/A | Model Number: | CS80 | Brand Name: | |
| Product name: | High performance refractory ladle slide gate | Model No.: | cs80 | Brand name: | CMAX |
| Quality: | Al-C or Al-Zr-C | Service life: | 4-6 heats | Apparent porosity: | 7% Max |
| Bulk density:: | 3.1 MIN | C.C.S: | 120MPA | MOQ: | 100 pcs for trial |
| Delivery time: | 60 working days upon receipt of deposit |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Inner carton packing, outer wooden case suitable for long term sea shipping |
| Delivery Detail: | three months working days upon receipt of deposit |
Specifications
Surface flatness less than 0.05mm
High mechanical strength
Erosion resistance
Oxidation resistance
Thermal shock stability
General Chemical Analysis for refractory ladle slide gate :
slide gate plate widely including Alumina carbon and Alumina Zirconia Carbon slide gate plate, MgO and MgO-spinel slide gate plate,nonoxides bonding slide gate plateand unburned slide gate plate.
Alumina -Zirconia-Carbon material
| Al-Zr-C Material | |||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) |
| 85 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
Composite type: Al-Zr-C for working line, outer Al-C material
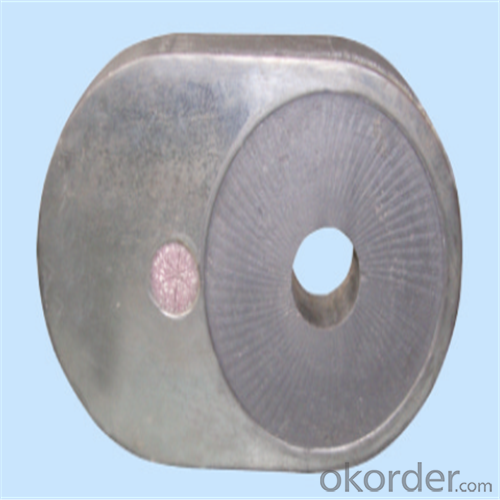
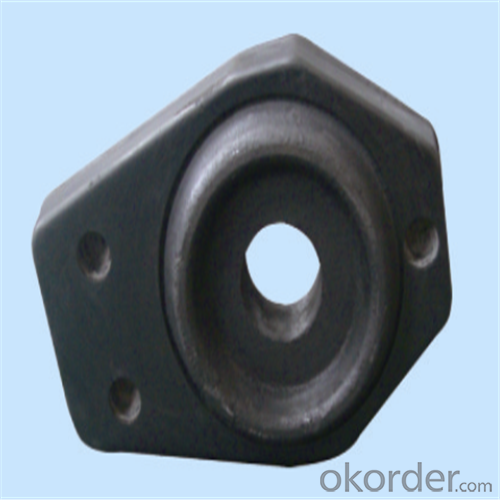
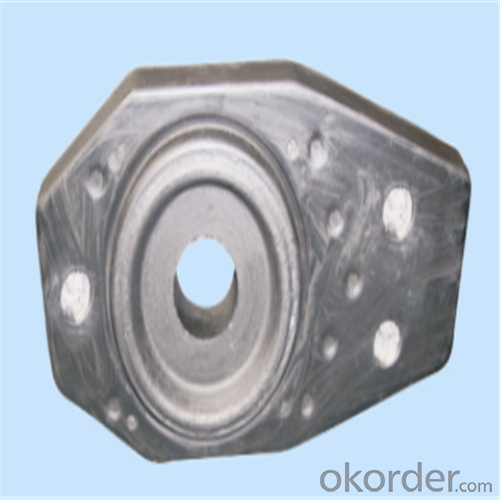



| Al-Zr-C & Al-C Material | ||||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S | |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) | |
| Inner side (Working face) | 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| Outside | 90 | 3 | 0 | 9 | 3 | |
Using the raw materials of tabular alumina, zirconia-corundum, carbon and other high-grade additives, after sintering to obtain characteristics of oxidation resistance, scour strength, erosion resistance, thermal shock resistance, shape stable and long service life, made our products the preferred materials for the large and medium-sized steel ladle, refining ladle, series of alloy steel ladle, and tundish. Our high performance sintering sliding gates include alumina carbon , Al2O3-ZrO2-C, etc, can meet the needs of different steel grade.
Other Products

About us


Sample is on your request.
Welcome to visit our factory~
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand the chemical attacks in copper smelting applications?
- Monolithic refractories have the ability to withstand chemical attacks in copper smelting applications due to their unique properties and composition. These refractories are specifically designed to resist the harsh and corrosive environment found in copper smelting processes. Firstly, monolithic refractories are made from high-quality materials such as alumina, silica, and magnesia, which have high melting points and are chemically stable. These materials are carefully selected to ensure they can withstand the corrosive effects of copper smelting, such as the presence of sulfur compounds and acidic gases. The refractory's composition also includes various additives and bonding agents that enhance its resistance to chemical attacks. Additionally, monolithic refractories have excellent thermal shock resistance, meaning they can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or spalling. In copper smelting applications, the extreme temperatures involved can cause thermal stress on the refractory lining. The refractories' ability to withstand these temperature fluctuations is crucial in preventing the formation of cracks and ensuring their long-term performance. Furthermore, monolithic refractories have a dense and compact structure, which provides an effective barrier against the penetration of molten copper and other corrosive substances. This dense structure prevents the chemical attacks from penetrating the refractory lining, thus ensuring its durability and longevity. Moreover, monolithic refractories offer superior erosion resistance, which is essential in copper smelting applications where high-velocity gases and molten metal flows can cause erosion of the refractory lining. The refractory's erosion resistance prevents the degradation of the lining and maintains its structural integrity. Overall, monolithic refractories are specially designed to withstand the chemical attacks encountered in copper smelting applications. By utilizing high-quality materials, incorporating additives, and possessing excellent thermal shock resistance, density, and erosion resistance, these refractories provide a reliable and durable lining that can withstand the harsh conditions of copper smelting processes.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand high temperatures and thermal cycling?
- Monolithic refractories, with their unique composition and structural characteristics, are designed to endure high temperatures and thermal cycling. To begin with, these refractories are composed of high-quality raw materials like alumina, silica, and magnesia. These materials possess exceptional thermal properties, including high melting points and low thermal conductivity. Consequently, they can maintain their strength and integrity even in extreme temperatures. Additionally, monolithic refractories are engineered to have a dense and compact microstructure. This dense structure prevents the infiltration of heat and gases, minimizing thermal shock and crack formation. Moreover, the compact microstructure enhances the refractory's thermal conductivity, allowing it to efficiently distribute and dissipate heat. Furthermore, special additives and bonding agents are often incorporated into monolithic refractories to enhance their resistance to thermal cycling. These additives improve the refractory's thermal expansion properties, enabling it to expand and contract without cracking or spalling during rapid temperature changes. Some bonding agents also provide flexibility to the refractory, allowing it to withstand thermal stresses without compromising its structural integrity. In addition to these inherent characteristics, proper installation techniques are crucial for the refractory's ability to withstand high temperatures and thermal cycling. Careful application and curing ensure uniformity and minimize the development of internal stresses. Adequate curing and heat treatment processes create a strong and durable bond between the refractory and the substrate, enhancing its resistance to thermal shock and cyclic thermal loading. In summary, the composition, microstructure, and installation techniques of monolithic refractories work together to enable them to withstand high temperatures and thermal cycling. These factors result in excellent thermal conductivity, resistance to thermal shock, and the ability to expand and contract without compromising the refractory's structural integrity.
- Q: How are monolithic refractories inspected and tested for quality assurance?
- Monolithic refractories are inspected and tested for quality assurance through a series of rigorous processes to ensure their reliability and performance. These inspections and tests are crucial in maintaining consistent quality standards and identifying any potential defects or weaknesses in the refractory material. Firstly, visual inspections are conducted to check for any visible defects such as cracks, spalling, or signs of poor manufacturing. This step helps identify any obvious issues that may affect the refractory's performance. Next, physical properties such as density, porosity, and thermal conductivity are measured using specialized equipment. These measurements are compared against predetermined standards to ensure the refractory material meets the required specifications. Density and porosity are important indicators of the refractory's strength and resistance to heat and chemicals, while thermal conductivity determines its ability to transfer heat efficiently. In addition, mechanical tests are performed to assess the refractory's strength and resistance to mechanical stress. This involves subjecting the material to compressive, tensile, and flexural forces to evaluate its structural integrity and durability. To ensure the refractory's performance in high-temperature environments, thermal tests are conducted. These tests involve exposing the refractory to extreme temperatures and monitoring its behavior. Thermal expansion and shrinkage, resistance to thermal shock, and thermal cycling are some of the parameters evaluated during these tests. Chemical analysis is another important aspect of quality assurance for monolithic refractories. Samples of the refractory material are analyzed to determine their chemical composition and assess their resistance to various corrosive environments. This analysis helps ensure that the refractory is suitable for the specific applications it will be used in. Lastly, field tests may be conducted at actual operating sites to evaluate the refractory's performance under real-world conditions. These tests involve monitoring the refractory's behavior in terms of wear and tear, thermal insulation, and resistance to chemical attack. The results obtained from field tests are crucial in validating the refractory's performance and making any necessary adjustments to the manufacturing process. Overall, monolithic refractories undergo a comprehensive inspection and testing process, encompassing visual inspections, physical and mechanical tests, thermal analysis, chemical analysis, and field tests. This systematic approach ensures that the refractories meet the required quality standards, providing reliability and longevity in the demanding environments they are designed for.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories improve the lining of converters and refining vessels?
- Monolithic refractories enhance the lining of converters and refining vessels by providing superior thermal insulation, chemical resistance, and structural integrity. They eliminate the need for bricklaying, offering a seamless lining with reduced joints, thereby minimizing heat loss and ensuring efficient heat transfer. Additionally, monolithic refractories are highly resistant to the corrosive effects of molten metals and slag, prolonging the lifespan of the lining. Their flexibility enables easy installation and repair, resulting in reduced downtime and improved overall performance of converters and refining vessels.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories improve the efficiency of ladle and tundish preheating stations?
- Crucial for enhancing the efficiency of ladle and tundish preheating stations, monolithic refractories are specifically designed to withstand high temperatures and thermal shocks, making them an ideal choice for preheating applications. One significant way in which monolithic refractories enhance efficiency is by offering excellent heat insulation. With low thermal conductivity, these refractories minimize heat loss from the preheating station to the surroundings. Consequently, the ladle or tundish preheating station retains more heat, resulting in faster and more efficient vessel heating. Furthermore, monolithic refractories possess outstanding heat retention properties. Once heated, these refractories can gradually store and release heat over time. This characteristic ensures a consistent and controlled heating process in the ladle or tundish preheating station. By maintaining a stable temperature, the refractories guarantee uniform vessel heating and prevent thermal shocks that could cause cracking or other damage. Moreover, monolithic refractories exhibit excellent resistance to chemical reactions and erosion caused by molten metals and slag. Ladles and tundishes frequently encounter corrosive environments, and the use of monolithic refractories protects against degradation and extends the lifespan of the preheating station. This durability reduces the need for frequent maintenance and replacement, resulting in cost savings and improved overall efficiency. To summarize, monolithic refractories enhance the efficiency of ladle and tundish preheating stations by providing exceptional heat insulation, heat retention, and resistance to chemical reactions. These properties lead to faster and more uniform heating, reduced heat loss, and increased preheating station durability. Ultimately, these advantages contribute to improved productivity and cost-effectiveness in the steelmaking process.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories impact the overall productivity of iron and steel operations?
- Monolithic refractories have a significant impact on the overall productivity of iron and steel operations. These refractories are used to line the furnaces, ladles, and other high-temperature equipment, providing insulation and protection against extreme heat, chemical reactions, and mechanical wear. By ensuring the integrity and durability of these critical components, monolithic refractories enhance the efficiency and longevity of iron and steel production processes. They minimize downtime caused by frequent repairs or replacements, improve thermal management, and optimize energy consumption. Ultimately, the use of monolithic refractories leads to increased productivity, reduced costs, and improved quality control in iron and steel operations.
- Q: What are the advantages of using insulating castables in the iron and steel industry?
- There are several advantages of using insulating castables in the iron and steel industry. Firstly, insulating castables provide excellent thermal insulation. They have low thermal conductivity, which helps to minimize heat loss from the furnaces and other equipment. This is particularly important in the iron and steel industry, where high temperatures are required for various processes. The insulation provided by castables helps to maintain a stable temperature within the furnace, resulting in improved energy efficiency and reduced fuel consumption. Secondly, insulating castables have high strength and excellent resistance to thermal shock. This is crucial in the iron and steel industry, where extreme temperature changes are common. The castables can withstand rapid heating and cooling cycles without cracking or compromising their structural integrity. This ensures the longevity and durability of the refractory lining, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and repairs. Furthermore, insulating castables are lightweight and easy to install. Their low density makes them easier to handle and transport, resulting in reduced labor costs and shorter installation times. This is particularly advantageous in large-scale iron and steel plants, where time and cost efficiency are critical. Moreover, insulating castables offer good corrosion resistance. The harsh environment in the iron and steel industry, with the presence of molten metal, slag, and various chemicals, can cause corrosion and erosion of refractory materials. Insulating castables are designed to withstand these corrosive conditions, ensuring the longevity of the lining and minimizing the risk of downtime and production disruptions. Lastly, insulating castables are versatile and can be customized to meet specific requirements. They are available in various compositions and densities, allowing for tailored solutions to different applications within the iron and steel industry. This versatility ensures optimal performance and efficiency in various furnace and equipment designs. In conclusion, the advantages of using insulating castables in the iron and steel industry include excellent thermal insulation, high strength, resistance to thermal shock, lightweight installation, corrosion resistance, and versatility. These benefits contribute to improved energy efficiency, reduced maintenance costs, increased durability, and enhanced overall productivity in the industry.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the reduction of heat loss in iron and steel furnaces?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in reducing heat loss in iron and steel furnaces by providing excellent insulation and maintaining a high level of thermal efficiency. These materials are designed to withstand extreme temperatures and are applied as a single, seamless lining, eliminating joints and gaps that could allow heat to escape. By creating a barrier between the hot furnace and the surrounding environment, monolithic refractories effectively minimize heat loss, ensuring optimal energy utilization and cost savings in the iron and steel industry.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories prevent heat loss through convection?
- Monolithic refractories effectively prevent heat loss through convection due to their unique composition and structure. Unlike traditional refractory bricks, which often have gaps and are porous, monolithic refractories are made of a single, seamless structure. This eliminates any possible pathways for hot gases or air to circulate and carry away heat by convection. Furthermore, monolithic refractories have a high thermal conductivity and are often dense, making them excellent conductors of heat. This allows them to rapidly absorb and distribute heat, minimizing the temperature difference between the hot surface and the surrounding environment. By reducing the temperature gradient, monolithic refractories decrease the driving force for convection, resulting in reduced heat loss through this mechanism. Moreover, monolithic refractories can be applied as a continuous lining, conforming to the shape of the equipment or furnace being protected. This seamless application eliminates joints or gaps where hot gases or air could escape and carry away heat. The uniform and uninterrupted lining further decreases the potential for convection heat loss. In summary, monolithic refractories are specifically designed to create a barrier that hinders the movement of hot gases or air, effectively minimizing heat loss through convection. Their dense composition, high thermal conductivity, and seamless application all contribute to their effectiveness in preventing heat loss through this mechanism.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories enhance the performance of ladle and tundish covers?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in enhancing the performance of ladle and tundish covers in several ways. Firstly, monolithic refractories offer excellent thermal insulation properties. Ladles and tundishes are exposed to extremely high temperatures during the steelmaking process. By using monolithic refractories, the covers can effectively trap and retain heat, preventing excessive heat loss. This insulation capability not only helps to maintain the desired temperature of the molten steel but also reduces the energy consumption required for heating. Secondly, monolithic refractories provide superior resistance to thermal shock. When ladles and tundishes are filled with molten steel, there is a rapid and drastic temperature change in the refractory lining. This thermal shock can cause cracking and spalling of the lining, compromising its integrity. However, monolithic refractories possess high thermal shock resistance, allowing them to withstand these sudden temperature fluctuations without significant damage. This ensures the longevity and durability of the ladle and tundish covers. Furthermore, monolithic refractories exhibit excellent corrosion resistance. The molten steel and other aggressive chemicals present in the ladles and tundishes can erode the refractory lining over time. However, monolithic refractories are specifically designed to withstand these corrosive environments, protecting the covers from chemical attack and erosion. This resistance to corrosion enhances the lifespan of the ladle and tundish covers, reducing the need for frequent replacements and associated downtime. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer good mechanical strength and stability. The ladles and tundishes undergo various mechanical stresses, including the weight of the molten steel, thermal expansions, and vibrations. The use of monolithic refractories provides the necessary strength and stability to withstand these mechanical forces, preventing structural failures and maintaining the integrity of the covers. In summary, monolithic refractories enhance the performance of ladle and tundish covers by providing excellent thermal insulation, resistance to thermal shock and corrosion, and sufficient mechanical strength. These properties ensure efficient steelmaking processes, reduce maintenance costs, and prolong the lifespan of ladles and tundishes.
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories High Temperature Ladle Sliding Gate for Iron and Steel Industry 2024
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords