Light Rail
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao Port, China
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25Tons m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specifications of Light Rail
Production Standard: GB 11264-89, DIN, AREMA, JIS, BS, UIC, etc.
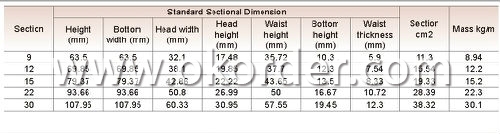
Sizes: 9kg, 12kg, 15kg, 22kg, 30kg
Length: 6m-25m according to the requriements of the clients
Material: Q235B, 55Q, 900A, etc.
Alloy No | Grade | Element(%) | ||||
C
| Mn | S
| P
| Si
| ||
Q235 |
B
|
0.12—0.20 |
0.3—0.7 |
≤0.045 |
≤0.045
|
≤0.3
|
Invoicing on theoretical weight or actual weight as customer request
Payment terms: 30% advance payment by T/T, 70% payment against the copy of the B/L; 100% L/C at sight, etc.
Usages of Light Rail
Light rail is mainly used in forest region, mines, factories and construction sites laid of the place such as temporary transport line and light motorcycles with line. Be widely used for railway, subway, transportation track, express, curve way, tunnel way and so on.
Packaging & Delivery of Light Rail
1. Packing: it is nude packed in bundles by steel wire rod
2. Bundle weight: not more than 3.5MT for bulk vessel; less than 3 MT for container load
3. Marks:
Color marking: There will be color marking on both end of the bundle for the cargo delivered by bulk vessel. That makes it easily to distinguish at the destination port.

Tag mark: there will be tag mark tied up on the bundles. The information usually including supplier logo and name, product name, made in China, shipping marks and other information request by the customer.
If loading by container the marking is not needed, but we will prepare it as customer request.

4. Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the maximum quantity can be loaded is around 40MTs by each truck. If the order quantity cannot reach the full truck loaded, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.

5. Delivered by container or bulk vessel

6. Delivery Time: All the Hot Rolled Steel Rail will be transpoted at the port of Tianjin, China within 30 days after receiving the advance payment by T/T or the orginal L/C at sight.
Inspection of Light Rail
We will send the MTC of the factory to the clients dirrectly which contain the anlisis of the heat, chemiqul composition, phisical characteristicas, etc.
And our inspectors will arrive at the factory to meke the inspection of the size, length, weight and quantity before the transportation from the factory.


- Q: How are steel rails aligned during installation?
- Steel rails are aligned during installation using precision measurement tools and techniques such as laser alignment systems, track gauges, and string lines. These tools help to ensure that the rails are correctly positioned and aligned with the required specifications, including the proper alignment, levelness, and gauge (distance between the rails). This precise alignment is crucial for the safe and efficient functioning of railway tracks.
- Q: What are the standard lengths of steel rails?
- The specific application and country determine the varying standard lengths of steel rails. Nonetheless, in numerous countries, the customary length for railway track steel rails is generally 12 meters or 39.37 feet. This length is commonly utilized due to the convenient transportation, installation, and maintenance it offers. Moreover, shorter steel rail lengths, like 6 meters or 20 feet, may be employed for particular purposes or industries. It is important to mention that specialized applications or specific railway systems may have divergences in rail lengths.
- Q: Name the basic structure and function of the rail
- Rail is the main component of railway track. Its function is to guide the wheel of the rolling stock, to bear the great pressure of the wheel and to deliver it to the sleeper. The rail must provide a continuous, smooth, and least resistant rolling surface for the wheel. In electrified railway or automatic block section, rail can also be used as track circuit.
- Q: What are the requirements for steel rail storage and handling?
- The requirements for steel rail storage and handling include proper storage conditions, such as a dry and well-ventilated area to prevent corrosion. Handling should be done with appropriate lifting equipment to avoid damage or distortion to the rails. Additionally, rails should be stored in a way that prevents any bending or twisting, and they should be kept away from moisture, chemicals, and extreme temperatures.
- Q: How do steel rails handle changes in track alignment due to temperature variations?
- Steel rails have the ability to handle changes in track alignment caused by temperature variations due to their high strength and flexibility. As the temperature rises, steel expands, allowing the rails to elongate and adjust accordingly without significant deformation or damage. Similarly, when the temperature drops, steel contracts, minimizing the risk of buckling or misalignment. Additionally, proper maintenance practices such as regular inspections and adjustments help ensure that steel rails maintain their structural integrity and alignment, even in extreme temperature conditions.
- Q: What are the common materials used for rail sleepers with steel rails?
- The common materials used for rail sleepers with steel rails are wood, concrete, and composite materials.
- Q: How are steel rails protected against chemical spills or leaks?
- Steel rails are protected against chemical spills or leaks through the application of protective coatings or liners. These coatings act as a barrier, preventing the chemicals from directly contacting the steel and causing corrosion. Additionally, regular inspections and maintenance procedures are carried out to promptly identify and address any potential spills or leaks to minimize their impact on the steel rails.
- Q: How do steel rails handle uneven track settlements?
- Steel rails are designed to handle uneven track settlements by flexing and adjusting to the changes in the track alignment. The flexibility of steel allows it to absorb the impact and distribute the load evenly, minimizing the effects of settlement on the train's stability and smoothness of the ride. Additionally, regular maintenance and monitoring of the tracks help identify and rectify any settlement issues promptly, ensuring safe and efficient rail operations.
- Q: What are the different types of rail maintenance vehicles used with steel rails?
- There are several different types of rail maintenance vehicles used with steel rails. These vehicles are designed to perform various tasks that are necessary for the upkeep and maintenance of railway tracks. Here are some of the most common types: 1. Ballast Regulator: This vehicle is used to distribute and shape the ballast, which is the crushed stone or gravel that supports the railway tracks. It helps to maintain the proper alignment and stability of the tracks. 2. Tamping Machine: Tamping machines are used to pack the ballast underneath the sleepers, ensuring a stable and even track bed. These vehicles use hydraulic or pneumatic systems to apply pressure on the ballast, effectively compacting it. 3. Rail Grinder: Rail grinders are used to remove any irregularities or defects on the surface of the tracks. These vehicles consist of grinding stones or rotating discs that smooth out the rail surface, improving ride quality and reducing noise. 4. Rail Welding Machine: Rail welding machines are used to join two sections of rail together. These machines use electric or thermite welding techniques to create a strong and seamless connection between the rails. 5. Track Geometry Measurement Vehicle: These vehicles are equipped with specialized sensors and measuring equipment to assess the condition of the tracks. They collect data on parameters such as track alignment, gauge, and elevation, which helps identify any issues that need to be addressed. 6. Rail Inspection Vehicle: Rail inspection vehicles are used to visually inspect the tracks for any signs of damage or wear. These vehicles are equipped with cameras and sensors to detect defects such as cracks, corrosion, or loose fastenings. 7. Rail Cleaning Vehicle: These vehicles are used to remove debris, vegetation, and other foreign objects from the tracks. They help maintain a clean and obstruction-free railway environment, which is essential for safe and efficient train operations. These are just a few examples of the different types of rail maintenance vehicles used with steel rails. Each vehicle plays a vital role in ensuring the safety, reliability, and longevity of railway tracks, contributing to smooth and uninterrupted train services.
- Q: What is the cost of manufacturing steel rails?
- The cost of manufacturing steel rails can vary depending on factors such as the size, length, and quality of the rails, as well as market conditions and production efficiency. It is best to consult with steel manufacturers or suppliers for specific pricing information.
1. Manufacturer Overview
| Location | Shandong, China |
| Year Established | 1993 |
| Annual Output Value | Above US$ 20 Million |
| Main Markets | Exported to Thailand, India, Brazil, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Japan, Vietnam and many other countries and regions |
| Company Certifications |
2. Manufacturer Certificates
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period |
3. Manufacturer Capability
| a) Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | Qingdao; Rizhao |
| Export Percentage | 41% - 50% |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | 21-30 People |
| Language Spoken: | English; Chinese |
| b) Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | Above 10,000 square meters |
| No. of Production Lines | 2 |
| Contract Manufacturing | OEM Service Offered |
| Product Price Range | Average |
Send your message to us
Light Rail
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao Port, China
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25Tons m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords