Steel Rail, Hot Rolled, GB, DIN, AREMA, JIS, BS, UIC for Sale
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description of Steel Rail, Hot Rolled, GB, DIN, AREMA, JIS, BS, UIC for Sale:
Sizes: 38kg, 43kg, 45kg, 50kg, 60kg.
Production Standard: GB2585-81, DIN, AREMA, JIS, BS, UIC, etc.
Material: 50MN, U71MN, 900A, 110A, etc.
Length: 6m-25m according to the requriements of the clients
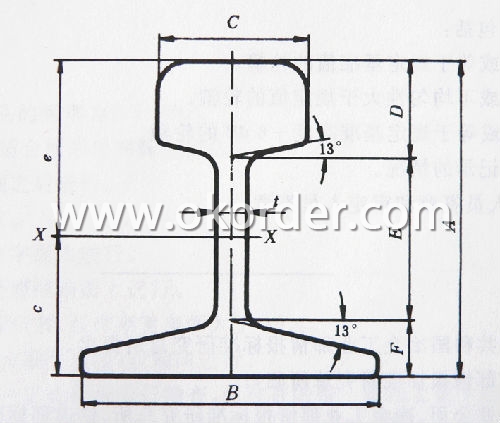
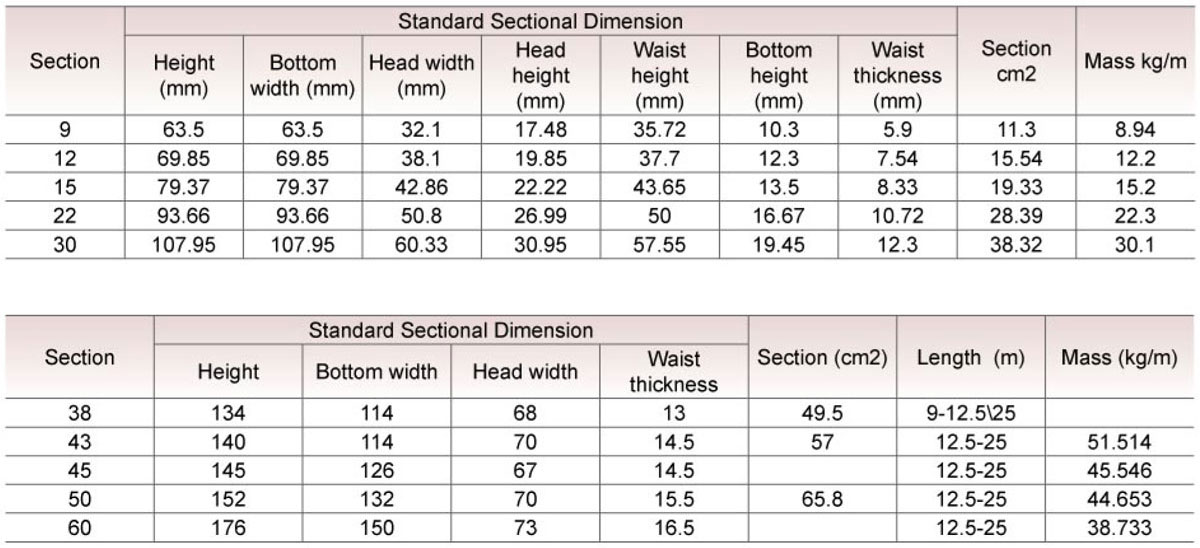
Usages of Steel Rail, Hot Rolled, GB, DIN, AREMA, JIS, BS, UIC for Sale:
Light rail is mainly used in forest region, mines, factories and construction sites laid of the place such as temporary transport line and light motorcycles with line. Be widely used for railway, subway, transportation track, express, curve way, tunnel way and so on.
Packaging & Delivery of Steel Rail, Hot Rolled, GB, DIN, AREMA, JIS, BS, UIC for Sale:
1. Packing: it is nude packed in bundles by steel wire rod
2. Bundle weight: not more than 3.5MT for bulk vessel; less than 3 MT for container load
3. Marks:
Color marking: There will be color marking on both end of the bundle for the cargo delivered by bulk vessel. That makes it easily to distinguish at the destination port.
Tag mark: there will be tag mark tied up on the bundles. The information usually including supplier logo and name, product name, made in China, shipping marks and other information request by the customer.
If loading by container the marking is not needed, but we will prepare it as customer request.
4. Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the maximum quantity can be loaded is around 40MTs by each truck. If the order quantity cannot reach the full truck loaded, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.
5. Delivered by container or bulk vessel
6. Delivery Time: All the Hot Rolled Steel Rail will be transpoted at the port of Tianjin, China within 30 days after receiving the advance payment by T/T or the orginal L/C at sight.
Inspection of Steel Rail, Hot Rolled, GB, DIN, AREMA, JIS, BS, UIC for Sale:
We will send the MTC of the factory to the clients dirrectly which contain the anlisis of the heat, chemiqul composition, phisical characteristicas, etc.
And our inspectors will arrive at the factory to meke the inspection of the size, length, weight and quantity before the transportation from the factory.
FAQ:
Q1: Why buy Materials & Equipment from OKorder.com?
A1: All products offered by OKorder.com are carefully selected from China's most reliable manufacturing enterprises. Through its ISO certifications, OKorder.com adheres to the highest standards and a commitment to supply chain safety and customer satisfaction.
Q2: What makes stainless steel stainless?
A2: Stainless steel must contain at least 10.5 % chromium. It is this element that reacts with the oxygen in the air to form a complex chrome-oxide surface layer that is invisible but strong enough to prevent further oxygen from "staining" (rusting) the surface. Higher levels of chromium and the addition of other alloying elements such as nickel and molybdenum enhance this surface layer and improve the corrosion resistance of the stainless material.
Q3: Can stainless steel rust?
A3: Stainless does not "rust" as you think of regular steel rusting with a red oxide on the surface that flakes off. If you see red rust it is probably due to some iron particles that have contaminated the surface of the stainless steel and it is these iron particles that are rusting. Look at the source of the rusting and see if you can remove it from the surface.
Images:


- Q: How are steel rails connected?
- Steel rails are connected through a process called rail welding, where the ends of two rails are heated and fused together to create a seamless joint. This ensures a smooth and continuous track for trains to travel on.
- Q: How are steel rails protected against excessive vibrations?
- Several methods are utilized to protect steel rails against excessive vibrations. Resilient fastenings or rail pads are one of the primary approaches employed. These materials are placed between the rail and the fastening system to absorb and dissipate vibrations generated by passing trains. By acting as a cushion, resilient fastenings reduce the impact and vibrations transmitted to the rail. Another technique involves the use of ballast, a layer of crushed stones beneath the railway tracks. This ballast functions as a shock absorber, absorbing vibrations and evenly distributing the load of passing trains. Its presence aids in stabilizing the rails and minimizing excessive vibrations. In order to prevent excessive vibrations, regular maintenance and inspection of the rails are crucial. Any defects, such as cracks or damaged sections, are promptly identified and repaired. By ensuring the rails are well-maintained, the risk of vibrations is minimized. Furthermore, the design of the rail system itself plays a vital role in mitigating excessive vibrations. The alignment, curvature, and elevation of the tracks are carefully planned to reduce the occurrence and impact of vibrations. Employing proper track design techniques, such as providing transition curves, also helps in minimizing the vibrations caused by train movements. Ultimately, a combination of resilient fastenings, ballast, regular maintenance, and thoughtful rail system design work together to safeguard steel rails against excessive vibrations, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of railways.
- Q: Can steel rails be used in urban transit systems?
- Yes, steel rails can be used in urban transit systems. They are commonly used in various types of railways, including urban rail systems such as subways and light rail systems. Steel rails provide durability, stability, and smoothness for trains, making them suitable for efficient and reliable urban transportation.
- Q: How do steel rails handle changes in track alignment?
- Steel rails are designed to handle changes in track alignment by being flexible and durable. They can withstand the forces caused by changes in the track's direction, curves, and twists without breaking or deforming. This flexibility allows the rails to smoothly transition from one alignment to another, ensuring the stability and safety of the train tracks.
- Q: What are the safety measures for working on elevated steel rail tracks?
- Some safety measures for working on elevated steel rail tracks include wearing proper personal protective equipment (PPE) such as hard hats, safety glasses, and high-visibility clothing. Workers should also be trained on fall protection and have access to appropriate fall protection systems such as harnesses and guardrails. Regular inspections of the track and equipment should be conducted to ensure they are in good working condition. Additionally, workers should receive proper training on safe work practices, including proper lifting techniques and the use of tools and equipment.
- Q: Can steel rails be used in high-capacity railways?
- Yes, steel rails can be used in high-capacity railways. In fact, steel rails are the most commonly used material for railway tracks worldwide due to their durability, strength, and cost-effectiveness. Steel rails have the ability to withstand heavy loads and intense pressure, making them suitable for high-capacity railways where trains carry large volumes of passengers or freight. Additionally, steel rails are highly resistant to wear and tear, which ensures a longer lifespan and reduces maintenance and replacement costs. The flexibility and versatility of steel rails also allow for smooth and efficient train operations, enabling high-capacity railways to efficiently transport large numbers of people or goods over long distances.
- Q: Can steel rails be used in railway systems with multiple tracks?
- Yes, steel rails can be used in railway systems with multiple tracks. Steel rails are commonly used in railway systems worldwide and can be easily adapted to accommodate multiple tracks. They provide the necessary strength, durability, and stability required for efficient train operations on both single and multiple tracks.
- Q: Can steel rails be reused if a track is decommissioned?
- Yes, steel rails can be reused if a track is decommissioned. The rails can be carefully removed, inspected for any damage or wear, and if found to be in good condition, they can be repurposed for use in other tracks or projects. Recycling and reusing steel rails is a sustainable practice that helps minimize waste and conserves resources.
- Q: Why are some city railways called light rail? What is heavy rail?
- At present, the passenger flow of Shanghai's largest public transport facilities, Rail Transit Pearl Line: date of traffic was 729 thousand people, namely the peak stage of one-way traffic of 20 thousand and 400 passengers per hour; forward (to 2020) the daily traffic of 914 thousand passengers per hour, is the peak stage of one-way traffic of 51 thousand and 500 passengers. The train formation is 6, the train running time is 5.5 minutes, and the forward time is 2.1 minutes. Therefore, the Pearl Line of rail traffic should not be called "light rail" strictly, but should belong to Metro system.
- Q: How are steel rails protected from warping?
- Steel rails are protected from warping through a process called thermite welding, where the rails are heated and then fused together using a mixture of aluminum powder and iron oxide. This welding process ensures that the rails remain straight and resistant to warping, even under heavy loads and extreme weather conditions.
Send your message to us
Steel Rail, Hot Rolled, GB, DIN, AREMA, JIS, BS, UIC for Sale
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























