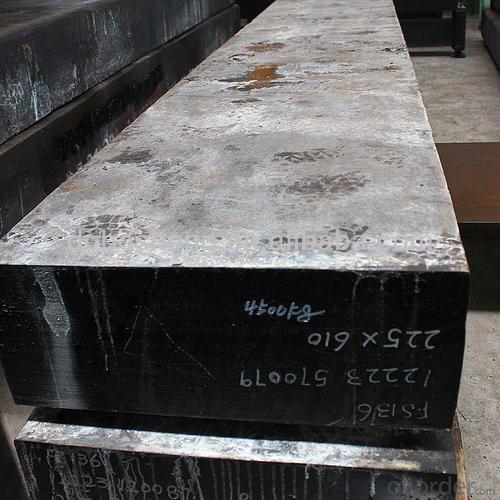
Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 140mm
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 140mm
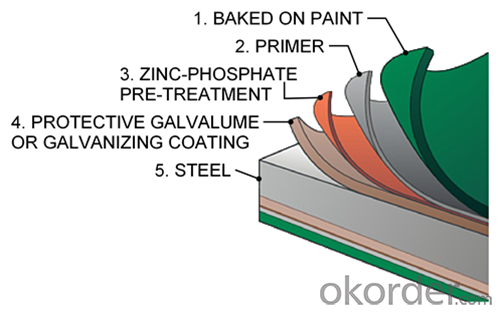
Description of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 140mm
Prepainted Rolled steel Coil is a kind of coated steel coil/sheet. With the cold rolled steel of different strength and thickness as substrate, it is produced through applying Al-Zn coat on both faces by hot dip process. In its coating, Al accounts for about 55%, Si 1.6%, while the remaining is Zn. Aluminum zinc coils enjoys both the physical protective feature and durability of Al and the electrochemical protective property of Zn. And its surface has bright silver color and regular embossed-like figure, which are highly decorative. RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing

Main Feature of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 140mm
1.Corrosion resistance: It mainly depends on the zinc protection. When the zinc being worn,
2. Heat resistance: steel sheet has excellent heat resistance, can withstand high temperatures over 300 centigrade, and is similar with aluminized steel high temperature oxidation resistance. It often used in chimney pipes, ovens, fluorescent lighting device and the device cover.
3. Heat reflective: Galvanized steel plate heat-reflective high rate is twice as galvanized steel, often used to make insulation materials. RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing
Applications of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 140mm
1. Construction and building: roofing; ventilating duct; handrail; partition panel;etc.
2. Electric appliance: refrigerator; washing machine; refrigerator; DVD;etc.
3.Transportation: oil tank; gas tank;road sign; etc.
4.Agriculture constructions :barn; etc.RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing
5.Others:vending machine; game machine; auto parts spare parts etc.

Specifications of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 140mm
Product | Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 140mm |
Material Grade | SGCC / SGCH / DX51D+AZ, etc |
Thickness | 0.5-3.0mm |
Width | 700-1500mm |
Tolerance | Thickness: +/-0.02mm , Width:+/-2mm |
Zinc-coating | AZ30-150g/m2 |
Technique | Raw material: Hot rolled steel coil --> Cold rolled_>hot dipped galvalume |
Surface | Dried, Chromated, Unoiled,RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing |
Spangle | Regular spangle , small spangle, zero spangle |
ID | 508MM 610MM |
Coil weight | 25MT max |
Export package | Cardboard inner sleeves, Waterproof paper, galvanized steel covered and steel strip packed |
FAQ of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 140mm
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1. What is the minimum order quantity ?
Our MOQ is 100 mt for each size each specification. Usually we can offer discount if can buy large QTY once. RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing
2. How long can we receive the product after ordering?
Our general delivery time is 30 days after confirmation, but so some special orders, we have offer special delivery time
3. How to guarantee the quality of the products?
We have established the international advanced quality management system ,every link from raw material to final product we have strict quality test;We resolutely put an end to unqualified products flowing into the market. At the same time, we will provide necessary follow-up service assurance.
4. What is the payment?
We accept T/T, L/C
- Q: How has the demand for steel billets changed over time?
- The demand for steel billets has experienced fluctuations over time, influenced by various factors. Historically, there has been a steady growth in the demand for steel billets due to the increasing industrialization and urbanization worldwide. As construction and infrastructure projects expanded, the demand for steel billets, which serve as the raw material for various steel products, also increased. However, the demand for steel billets has not been immune to economic cycles. During periods of economic downturns, such as the global financial crisis in 2008, the demand for steel billets declined as construction and manufacturing activities slowed down. This led to a surplus of steel billets in the market, resulting in decreased prices and reduced demand from steel mills. In recent years, the demand for steel billets has been influenced by global trends and geopolitical factors. The increasing focus on sustainable development and environmental concerns has led to a growing demand for green construction materials, including steel produced from recycled sources. This has prompted steel manufacturers to adapt their production processes to meet these demands and ensure the availability of environmentally friendly steel billets. Moreover, geopolitical factors such as trade disputes and tariffs have also impacted the demand for steel billets. The imposition of tariffs on steel imports by certain countries has led to a decrease in demand for imported steel billets, while simultaneously increasing demand for domestically produced steel billets. Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on the demand for steel billets. Lockdowns, travel restrictions, and disrupted supply chains caused a decline in construction activities and manufacturing output, leading to a decrease in demand for steel billets. However, as economies recover and governments implement stimulus measures to boost infrastructure projects, the demand for steel billets is expected to gradually rebound. In summary, the demand for steel billets has experienced fluctuations over time, influenced by economic cycles, global trends towards sustainability, geopolitical factors, and the COVID-19 pandemic. The long-term growth in demand for steel billets remains closely tied to construction and infrastructure development, making it vital for steel manufacturers to adapt to changing demands and market conditions.
- Q: What are the different shapes available for steel billets?
- There are several different shapes available for steel billets, including square, round, rectangular, and hexagonal shapes.
- Q: What is carbon accumulation?
- Generally refers to the polycarbonate, PC, is a kind of thermoplastic plastics, good transparency, good mechanical properties, surface hardness, common uses such as CD, plastic glasses, a fence, protective window, public places, vacuum cleaners, coffee machine, juicer barrel, refrigerator shelf, pure such as the bucket.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of castings?
- Steel billets play a crucial role as a primary material for creating castings. Castings, which are solid metal objects, are produced by pouring molten metal into a mold and allowing it to cool and solidify. The initial step in this process involves heating steel billets until they become molten. Subsequently, the molten steel is poured into a mold, typically made of sand or metal, which is specifically designed to have the desired shape and dimensions of the final casting. The molten steel is then left to cool and solidify within the mold. During this cooling process, the steel adopts the shape of the mold, ultimately forming the desired casting. This cooling phase is of utmost importance as it determines crucial mechanical properties, including strength and hardness, of the end product. Once the steel has solidified, the mold is removed, and the casting undergoes cleaning and finishing stages. This may involve removing any excess material, such as gates or risers, which were used to facilitate the pouring of the molten metal. Additionally, the casting may undergo further processes like machining or heat treatment to achieve the desired final specifications. To summarize, steel billets are utilized in the manufacturing of castings by melting them and pouring the molten steel into a mold to achieve the desired shape. The subsequent cooling and solidification of the molten steel within the mold lead to the formation of a solid casting, which can then undergo additional processing and finishing as needed.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the production of mining conveyors?
- The production of mining conveyors heavily relies on steel billets, which are essential for creating sturdy and durable components. Mining conveyors are responsible for transporting bulk materials like coal, ore, and gravel across long distances. To withstand the harsh conditions of a mining environment, these conveyors require robustness and durability. Conveyor rollers, crucial for the conveyor system's functionality, are manufactured using steel billets as the raw material. These rollers provide support and guidance to the conveyor belt. Initially, the steel billets undergo a heating process, which enhances their malleability, making shaping easier. Once heated, they are rolled into desired shapes to form the conveyor rollers. By incorporating steel billets into the production of mining conveyors, the resulting rollers possess excellent strength and resistance to wear and tear. The steel's properties, including toughness and hardness, make it highly suitable for enduring heavy loads and abrasive materials. Moreover, steel billets offer customization options to cater to specific requirements. Each mining operation may have unique needs in terms of conveyor dimensions, load capacities, and environmental conditions. With the use of steel billets, manufacturers can produce conveyor rollers of various sizes and specifications, ensuring a tailored fit for each mining operation. In conclusion, steel billets play a vital role in the production of mining conveyors as they serve as the primary material for manufacturing conveyor rollers. These rollers are indispensable for supporting and guiding the conveyor belt, enabling efficient and reliable transportation of bulk materials in the mining industry. By utilizing steel billets, the resulting conveyor rollers are strong, durable, and capable of withstanding the harsh conditions prevalent in the mining sector.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of bridges?
- Steel billets are crucial for bridge manufacturing as they act as the starting point for creating different structural elements. Usually rectangular or square, these billets are heated and rolled in mills to form various sections like beams, columns, and girders. After being rolled into the desired shape, the steel billets go through further processing to enhance their strength and durability. This involves heat treatment and quenching processes to improve mechanical properties such as hardness and toughness. Additionally, surface treatments are applied to protect against corrosion, ensuring the bridge's longevity. The shaped and treated steel sections derived from these billets are then assembled and welded together to create the bridge's framework. These structural elements provide the necessary load-bearing capacity and stability to support the bridge's weight, as well as withstand external forces like traffic loads, wind, and seismic activity. Moreover, steel billets are vital for constructing bridge piers and abutments, which offer support and anchorage. These components are often reinforced with steel bars or rebar, produced from billets, to increase their strength and ability to withstand vertical and horizontal forces. In conclusion, steel billets are essential raw materials for manufacturing bridges. Through rolling, shaping, heat treatment, and surface treatment processes, these billets are transformed into beams, columns, and other sections that form the bridge's framework. The resulting steel components provide the necessary strength, durability, and load-bearing capacity for the construction of safe and reliable bridges.
- Q: How do steel billets differ from steel bars?
- Steel billets and steel bars are both forms of semi-finished steel products, but they differ in terms of their size, shape, and production process. Steel billets are typically square or rectangular in shape and have a larger cross-sectional area compared to steel bars. They are produced through a casting process, where liquid steel is poured into molds and then allowed to solidify. On the other hand, steel bars are long, cylindrical shapes that are formed by rolling billets through a series of rolling mills. The rolling process increases the length and reduces the cross-sectional area of the steel, resulting in a more uniform shape and size.
- Q: Are steel billets used in the manufacturing of industrial machinery?
- Yes, steel billets are commonly used in the manufacturing of industrial machinery. They serve as a primary raw material for various components and parts, providing strength, durability, and versatility required in heavy-duty applications.
- Q: What are the different types of cutting methods used for steel billets?
- There are several different types of cutting methods used for steel billets, including sawing, shearing, flame cutting, and water jet cutting.
- Q: What are the different methods of steel billet surface plating?
- There are several different methods of steel billet surface plating, each with its own advantages and applications. Some of the most common methods include: 1. Electroplating: This is a widely used method where an electric current is used to deposit a layer of metal onto the surface of the steel billet. The billet is submerged in a solution containing metal ions, and when the current is applied, the metal ions are attracted to the steel surface, forming a thin coating. 2. Hot-dip galvanizing: In this method, the steel billet is dipped into a bath of molten zinc. The high temperature causes the zinc to bond with the steel, forming a protective layer. This process is commonly used for steel structures that will be exposed to harsh environments or corrosive elements. 3. Powder coating: This technique involves applying a dry powder to the surface of the steel billet, which is then heated to form a protective layer. Powder coating offers excellent durability, resistance to corrosion, and a wide range of color options. 4. Physical vapor deposition (PVD): PVD is a method where a thin film of metal is deposited onto the surface of the steel billet through a physical process such as evaporation or sputtering. This technique is commonly used for decorative purposes and to enhance the hardness and wear resistance of the steel surface. 5. Chemical conversion coating: This process involves treating the steel billet with a chemical solution that forms a protective layer on the surface. Common conversion coatings include phosphate and chromate coatings, which provide corrosion resistance and improve paint adhesion. 6. Thermal spraying: In this method, a heated material, typically a metal or ceramic powder, is sprayed onto the steel billet surface using a high-velocity gas or flame. The sprayed material forms a coating, providing enhanced protection against wear, corrosion, and high temperatures. Each of these methods has its own benefits and is suitable for different applications. The choice of plating method depends on factors such as the desired level of protection, cost, aesthetics, and specific requirements of the steel billet's end use.
Send your message to us
Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 140mm
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords
































