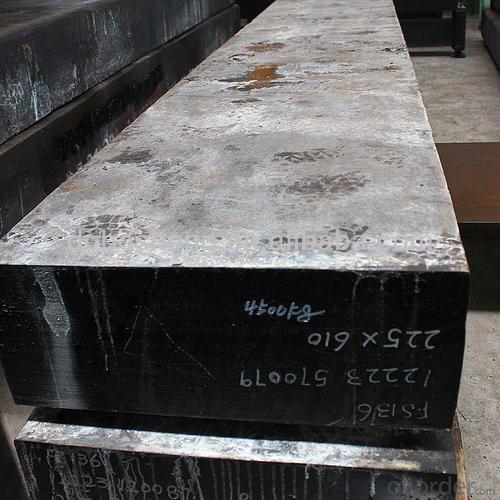
Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 145mm
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 145mm
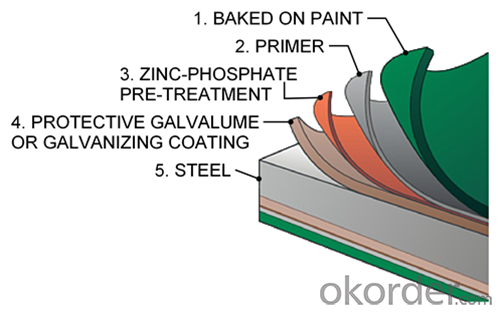
Description of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 145mm
Prepainted Rolled steel Coil is a kind of coated steel coil/sheet. With the cold rolled steel of different strength and thickness as substrate, it is produced through applying Al-Zn coat on both faces by hot dip process. In its coating, Al accounts for about 55%, Si 1.6%, while the remaining is Zn. Aluminum zinc coils enjoys both the physical protective feature and durability of Al and the electrochemical protective property of Zn. And its surface has bright silver color and regular embossed-like figure, which are highly decorative. RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing

Main Feature of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 145mm
1.Corrosion resistance: It mainly depends on the zinc protection. When the zinc being worn,
2. Heat resistance: steel sheet has excellent heat resistance, can withstand high temperatures over 300 centigrade, and is similar with aluminized steel high temperature oxidation resistance. It often used in chimney pipes, ovens, fluorescent lighting device and the device cover.
3. Heat reflective: Galvanized steel plate heat-reflective high rate is twice as galvanized steel, often used to make insulation materials. RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing
Applications of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 145mm
1. Construction and building: roofing; ventilating duct; handrail; partition panel;etc.
2. Electric appliance: refrigerator; washing machine; refrigerator; DVD;etc.
3.Transportation: oil tank; gas tank;road sign; etc.
4.Agriculture constructions :barn; etc.RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing
5.Others:vending machine; game machine; auto parts spare parts etc.

Specifications of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 145mm
Product | Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 145mm |
Material Grade | SGCC / SGCH / DX51D+AZ, etc |
Thickness | 0.5-3.0mm |
Width | 700-1500mm |
Tolerance | Thickness: +/-0.02mm , Width:+/-2mm |
Zinc-coating | AZ30-150g/m2 |
Technique | Raw material: Hot rolled steel coil --> Cold rolled_>hot dipped galvalume |
Surface | Dried, Chromated, Unoiled,RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing |
Spangle | Regular spangle , small spangle, zero spangle |
ID | 508MM 610MM |
Coil weight | 25MT max |
Export package | Cardboard inner sleeves, Waterproof paper, galvanized steel covered and steel strip packed |
FAQ of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 145mm
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1. What is the minimum order quantity ?
Our MOQ is 100 mt for each size each specification. Usually we can offer discount if can buy large QTY once. RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing
2. How long can we receive the product after ordering?
Our general delivery time is 30 days after confirmation, but so some special orders, we have offer special delivery time
3. How to guarantee the quality of the products?
We have established the international advanced quality management system ,every link from raw material to final product we have strict quality test;We resolutely put an end to unqualified products flowing into the market. At the same time, we will provide necessary follow-up service assurance.
4. What is the payment?
We accept T/T, L/C
- Q: How are steel billets classified based on their chemical composition?
- Steel billets are classified based on their chemical composition primarily into three categories: carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel. Carbon steel contains mainly iron and carbon, with trace amounts of other elements. Alloy steel is a combination of iron with other elements, such as manganese, chromium, nickel, or molybdenum, to enhance its mechanical properties. Stainless steel, on the other hand, contains iron along with a minimum of 10.5% chromium, which provides excellent corrosion resistance.
- Q: What are the different methods of steel billet inspection?
- There are several different methods of steel billet inspection that are commonly used in the manufacturing industry. These methods are employed to ensure the quality and integrity of the steel billets before they are further processed into various end products. Some of the most common methods of steel billet inspection include: 1. Visual Inspection: This is the simplest and most basic method of inspection, where trained inspectors visually examine the billets for any surface defects, such as cracks, pits, or any other irregularities. This method is typically used as an initial screening process before more advanced inspection techniques are employed. 2. Ultrasonic Testing: Ultrasonic testing utilizes high-frequency sound waves to detect any internal defects or inconsistencies within the steel billets. This method involves the use of a transducer that emits sound waves into the billet, and the reflected waves are analyzed to identify any flaws or abnormalities. Ultrasonic testing is effective in detecting internal defects like voids, inclusions, or cracks. 3. Magnetic Particle Inspection: This method is particularly useful for detecting surface and near-surface defects in steel billets. It involves applying a magnetic field to the billet and then applying iron particles to the surface. The particles will cluster around any magnetic leakage caused by surface cracks or defects, making them easily visible to the inspector. 4. Eddy Current Testing: Eddy current testing is a non-destructive method used to detect surface and near-surface defects in conductive materials, including steel billets. It involves passing an alternating current through a coil, creating an electromagnetic field. Any changes in the electromagnetic field caused by defects in the billet's surface are detected and analyzed, allowing for the identification of flaws. 5. X-ray Inspection: X-ray inspection is a widely used method for inspecting steel billets. It involves passing X-rays through the billet and capturing the resulting image on a film or digital detector. This method is highly effective in detecting both internal and external defects, such as cracks, voids, inclusions, or segregation. These are just a few of the commonly employed methods of steel billet inspection. Each method has its advantages and limitations, and the choice of inspection technique depends on factors such as the type of defect being targeted, the size and shape of the billets, and the specific requirements of the end product. By utilizing a combination of these inspection methods, manufacturers can ensure the quality and reliability of the steel billets they produce.
- Q: What are the different production methods for steel billets?
- There are several different production methods for steel billets, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. 1. Casting: One of the most common methods is the casting process, where molten steel is poured into a mold and allowed to solidify. This method can be further divided into continuous casting and ingot casting. Continuous casting involves the continuous pouring of molten steel into a water-cooled mold, which results in a continuous solidification process. Ingot casting, on the other hand, involves pouring molten steel into individual molds to create ingots that are then used as raw material for further processing. 2. Direct Reduction: Another method is the direct reduction process, which involves the reduction of iron ore in the presence of a reducing agent such as natural gas or coal. This process produces direct reduced iron (DRI), which can then be used to produce steel billets through subsequent melting and casting processes. 3. Electric Arc Furnace (EAF): The EAF method involves melting scrap steel in an electric arc furnace. This process is commonly used in recycling steel as it allows for the use of various scrap sources, including old cars, appliances, and industrial waste. The molten steel is then cast into billets or other desired shapes. 4. Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF): The BOF method is a traditional steelmaking process that involves the conversion of molten iron from a blast furnace into steel through the injection of oxygen. This process is used for large-scale production of steel billets and offers high efficiency and flexibility in terms of raw material usage. 5. Powder Metallurgy: Powder metallurgy is an alternative method that involves compacting and sintering metal powders to create solid objects. In the case of steel billets, metal powders are compressed into the desired shape and then heated to a high temperature to achieve solidification. Each of these production methods has its own advantages and is suited for different applications and production scales. The choice of method depends on various factors including the desired properties of the steel, cost considerations, environmental impact, and availability of raw materials.
- Q: Are steel billets used in the manufacturing of tools?
- Yes, steel billets are commonly used in the manufacturing of tools. Steel billets serve as the starting material for various tool manufacturing processes, including forging, extrusion, and machining. These billets are typically heated and shaped into the desired tool form, which is then further processed and refined to create high-quality tools with excellent strength, durability, and performance.
- Q: What are the specifications for stainless steel billets used in the marine industry?
- Stainless steel billets used in the marine industry must adhere to specific specifications to ensure optimal performance and durability in harsh marine environments. These specifications typically include the following: 1. Material Composition: Stainless steel billets for marine applications are usually made from austenitic stainless steel grades such as 304, 316, or 316L. These grades offer excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and good weldability. 2. Corrosion Resistance: The stainless steel billets must have high resistance to corrosion caused by saltwater, moisture, and other aggressive marine elements. They should exhibit excellent resistance to pitting, crevice corrosion, and chloride-induced stress corrosion cracking. 3. Mechanical Properties: The billets should possess sufficient tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation to withstand the demanding conditions encountered in the marine industry. These properties ensure that the stainless steel can handle the heavy loads, vibrations, and impacts experienced at sea. 4. Heat Treatment: Proper heat treatment processes, such as annealing, may be required to enhance the stainless steel's mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. Heat treatment can also eliminate residual stresses and improve the material's toughness. 5. Surface Finish: The surface of the billets should be free from defects, such as cracks, pits, and inclusions, which could compromise the structural integrity or promote corrosion. A smooth, polished surface is often desired to minimize friction and facilitate easier cleaning. 6. Dimensional Tolerance: Stainless steel billets used in the marine industry must adhere to specific dimensional tolerances to ensure compatibility with other marine components and facilitate ease of manufacturing and assembly. 7. Certification: Billets for the marine industry may need to meet various certification standards, such as ASTM, ISO, or specific industry standards like the American Bureau of Shipping (ABS) or Det Norske Veritas Germanischer Lloyd (DNV-GL) certifications. These certifications ensure that the stainless steel meets the required quality and safety standards. Overall, the specifications for stainless steel billets used in the marine industry focus on corrosion resistance, mechanical properties, heat treatment, surface finish, dimensional tolerances, and adherence to relevant certifications. These specifications ensure that the stainless steel billets can withstand the harsh marine environment, prolonging the lifespan of marine structures and components.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the production of mining machinery?
- Steel billets are used in the production of mining machinery as they serve as the raw material for forging and shaping various components such as gears, shafts, frames, and structural elements. These billets are heated and then formed into desired shapes through processes like rolling, machining, and welding. The high strength and durability of steel make it ideal for withstanding the harsh conditions and heavy loads associated with mining operations, ensuring the reliability and performance of mining machinery.
- Q: What are the different types of steel billet rolling defects?
- During the rolling process, various defects can arise in steel billets, which can have adverse effects on the final product's quality and integrity. The most commonly encountered types of steel billet rolling defects are as follows: 1. Surface cracks: These are minute cracks that manifest on the billet's surface. They can result from inadequate cooling or excessive rolling pressure. Surface cracks jeopardize the steel's strength and durability. 2. Center cracks: Inner core cracks occur when temperature control during the rolling process is incorrect. Center cracks can lead to structural weaknesses and reduced steel performance. 3. Scalloping: Scalloping refers to the formation of shallow depressions or grooves on the billet's surface. It usually arises due to uneven or improper rolling pressure distribution. Scalloping negatively impacts the steel's appearance and surface quality. 4. Lamination: Lamination defects involve the separation of layers within the billet. They can be caused by the presence of impurities or inclusions in the steel, as well as inadequate heating or rolling conditions. Lamination defects weaken the steel and increase the risk of failure. 5. Wavy edges: Wavy edges occur when the billet's edges become uneven or distorted during rolling. This can be the result of improper alignment or uneven pressure distribution. Wavy edges affect the steel's dimensional accuracy and overall quality. 6. Surface defects: Surface defects encompass scratches, pits, or other imperfections on the billet's surface. They may occur due to insufficient cleaning or handling procedures, as well as improper rolling conditions. Surface defects impact the steel's appearance and surface quality. In conclusion, these steel billet rolling defects hold significant implications for the final product's quality, performance, and safety. Manufacturers must closely monitor the rolling process and implement appropriate quality control measures to minimize the occurrence of these defects.
- Q: What are the common shipping methods for steel billets?
- Steel billets can be shipped using different methods, including container shipping, bulk shipping, and rail transportation. Container shipping is commonly used when transporting smaller quantities of billets. Billets are loaded into standard shipping containers, usually 20 or 40 feet long, and then transported by cargo vessels. This method is convenient and ensures the safety of the billets during transit. Bulk shipping, on the other hand, is preferred for larger quantities of steel billets. In this method, billets are loaded directly onto cargo vessels without using containers. This allows for cost-effective transportation of large volumes of billets. Specialized bulk carriers are designed to handle heavy cargo and ensure secure delivery. For domestic or regional transportation, rail transportation is a popular option. Steel billets are loaded onto specialized railcars that can carry heavy loads, and they are transported through rail networks. This method offers efficient and reliable transportation, especially for shorter distances. Ultimately, the choice of shipping method for steel billets depends on factors such as quantity, destination, cost, and logistical capabilities. Each method has its own advantages and considerations, so it is important to select the most suitable option based on the specific requirements of the shipment.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the production of power generation equipment?
- Steel billets are used in the production of power generation equipment due to their strength, durability, and versatility. Power generation equipment, such as turbines and generators, require sturdy and reliable components to withstand the harsh operating conditions and provide uninterrupted power supply. Steel billets, which are small, semi-finished steel products, serve as the raw material for manufacturing various parts of power generation equipment. They are typically melted down and cast into specific shapes to create components such as turbine blades, shafts, casings, and rotors. The use of steel billets in power generation equipment ensures high structural integrity, as steel is known for its excellent mechanical properties. It possesses high tensile strength, allowing it to withstand the extreme rotational forces and pressures experienced within turbines and generators. Additionally, steel exhibits good resistance to corrosion and high temperatures, making it ideal for use in power generation equipment that operates in harsh environments. Furthermore, steel billets can be easily machined and welded, allowing for precise manufacturing and assembly of complex parts. This flexibility in shaping and joining steel billets enables the production of customized components tailored to the specific requirements of power generation equipment. In summary, steel billets play a crucial role in the production of power generation equipment by providing a strong, durable, and versatile material for creating various components. Their use ensures the reliability and longevity of power generation equipment, allowing for efficient and uninterrupted power generation.
- Q: How do steel billets contribute to the overall safety of a structure?
- Steel billets play a significant role in contributing to the overall safety of a structure in several ways. Firstly, steel billets serve as the raw material for manufacturing steel bars, beams, columns, and other structural components. These components are widely used in construction due to their high strength and durability. By using steel billets as the starting material, the resulting steel products exhibit excellent load-bearing capacity, which enhances the structural integrity of the building. Moreover, steel billets undergo a rigorous manufacturing process that includes various quality control checks. These checks ensure that the billets possess consistent and reliable mechanical properties, such as high tensile strength and impact resistance. As a result, when these billets are used in the construction of a structure, they contribute to its overall safety by providing a reliable and robust framework that can withstand external forces, such as wind, earthquakes, or heavy loads. Additionally, steel billets are often produced using advanced metallurgical techniques, such as controlled cooling or heat treatment, to achieve specific properties required for structural applications. These processes help in improving the microstructure of the steel, reducing internal defects, and enhancing its resistance to corrosion, fatigue, and other forms of degradation. This, in turn, increases the lifespan of the structure and minimizes the risk of structural failure, thus ensuring the safety of the occupants. Furthermore, steel billets can be manufactured with precise dimensions and tolerances, allowing for accurate and efficient construction. This precision in fabrication ensures that structural components fit together seamlessly, reducing the likelihood of gaps, misalignments, or weak points that could compromise the safety of the structure. Lastly, steel billets are highly recyclable, making them an environmentally friendly choice for construction. By opting for steel billets, the construction industry can reduce its carbon footprint and contribute to sustainable development. This focus on sustainability aligns with the overall safety of a structure, as a sustainable approach ensures the long-term stability and resilience of the built environment. In conclusion, steel billets contribute to the overall safety of a structure by providing high-strength, durable, and reliable materials for construction. Their consistent mechanical properties, resistance to external forces, improved microstructure, and precise fabrication ensure a strong and secure framework. Moreover, their recyclability promotes sustainability, further enhancing the long-term safety and integrity of the structure.
Send your message to us
Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 145mm
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords































