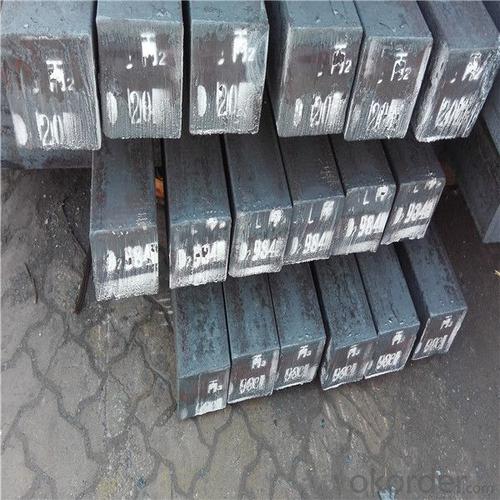
Carbon steel billet price for sale from china
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 25437 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
Steel billet
Rectangular billet continuous casting billet and mainly general carbon steel, low carbon low silicon cold-rolled material, high quality carbon structural steel, high strength low alloy steel, special steel, etc.
The billet is mainly divided into two kinds from the shape:
Slab: cross section width and height of the ratio of the larger, mainly used for rolling plate.
Qaulity:own factory, stable quality
Tolerance: Strictly according to the G/B and JIS standard
Delivery time: within 45 days after receiving the L/C or advanced T/T payment.
Price term: FOB/CIF/ CFR according to clients requirements
Gade:
Standard | C(%) | Mn(%) | S(%) | P(%) | Si(%) |
Q195 | ≤0.12 | ≤0.50 | ≤0.040 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.30 |
Q235 | ≤0.20 | ≤1.40 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.35 |
Q275 | ≤0.22 | ≤1.50 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.35 |
20MnSi | 0.17-0.25 | 1.2-1.6 | ≤ 0.050 | ≤ 0.050 | 0.40-0.80 |
3SP | 0.14-0.22 | 0.40-0.85 | ≤ 0.050 | ≤ 0.040 | 0.05-0.15 |
5SP | 0.28-0.37 | 0.50-1.00 | ≤ 0.050 | ≤ 0.040 | 0.15-0.30 |
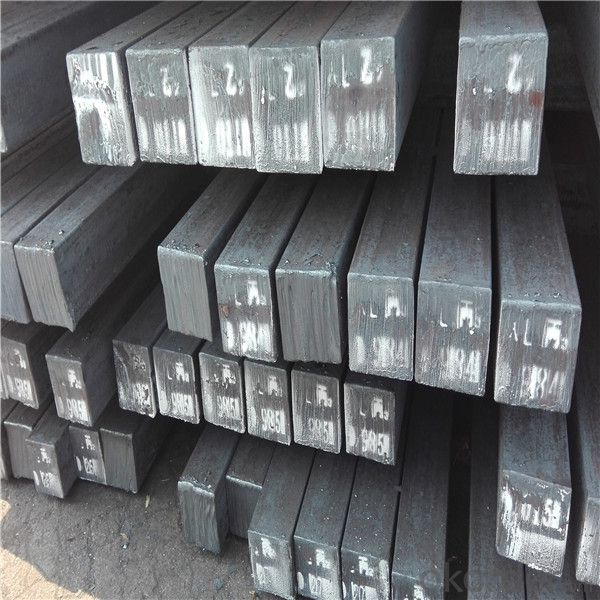
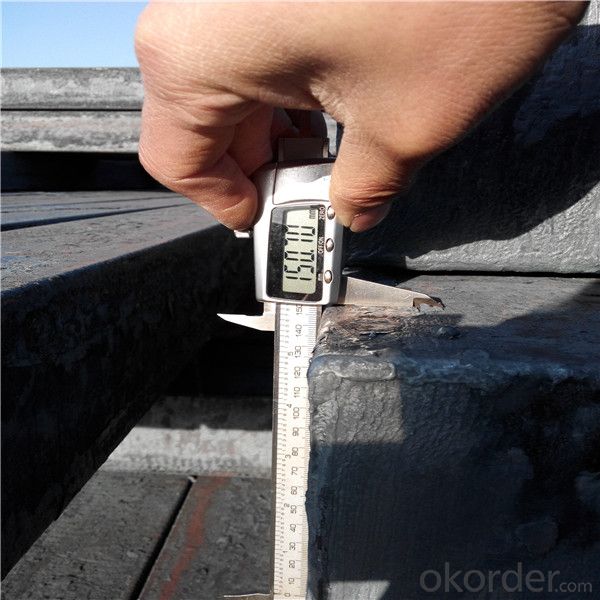
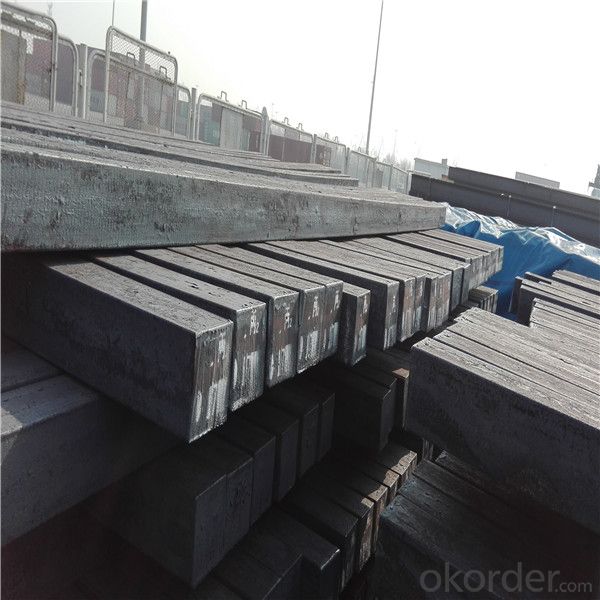
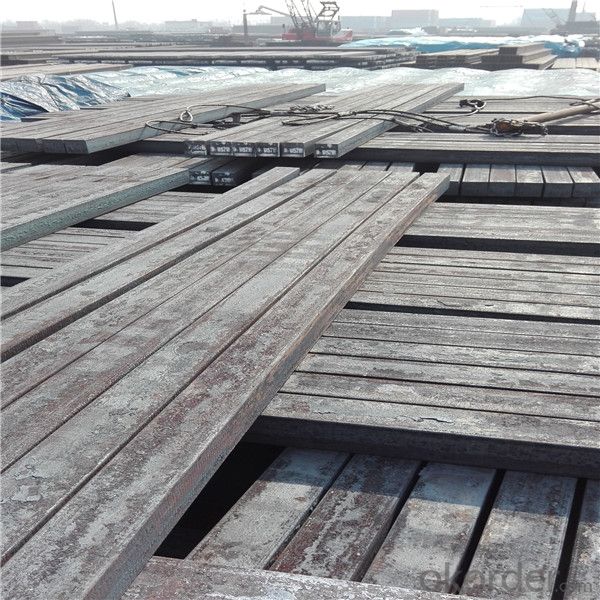




Our service :
We have a plant and professional team to provide our best service, from the start of production until the
loading into the vessel, we have a complete quality follow up procedure, to assure our products arrives to the customer with satisfaction. Welcome new and old customers
to contact us for future business relationships! We will give you a surpise price.
Packing :
Within 30 days
1.Standard export package
2.In bundles with steel strips
3.As the requirements of the customers
FAQ:
Q: What is payment terms?
A: FOB 30% T/T IN ADVANCE AS DEPOSIT AND 70% T/T BEFORE SHIPMENT
CIF and CFR 30% T/T IN ADVANCE AS DEPOSIT AND 70% T/T AS THE COPY OF B/L OR L/C AT SIGHT
Q:How to guarantee the quality of the products?
A:We have established the international advanced quality management system,every link from raw material
to final product we have strict quality test;We resolutely put an end to unqualified products flowing into the market.
At the same time, we will provide necessary follow-up service assurance.
Q:How long can we receive the product after purchase?
A :In the purchase of product within three working days, We will arrange the factory delivery as soon as possible.
The pecific time of receiving is related to the state and position of customers.
- Q: What are the different quality standards for steel billets?
- There are several quality standards for steel billets, including ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), ISO (International Organization for Standardization), and EN (European Norm) standards. These standards define various parameters such as chemical composition, mechanical properties, and dimensional tolerances that steel billets must meet in order to ensure their quality and suitability for different applications.
- Q: How do steel billets differ from steel ingots?
- Steel billets and steel ingots differ in terms of their shape and size. Steel billets are typically long and narrow, resembling a thick bar or rod, while steel ingots are larger and have a rectangular or square shape. Additionally, steel billets are usually smaller in size compared to steel ingots. Moreover, steel billets are often produced through continuous casting, while steel ingots are typically made through the traditional method of pouring molten steel into molds.
- Q: What are the potential applications of steel billets in the agricultural aftermarket?
- Steel billets have a wide range of potential applications in the agricultural aftermarket. One of the key uses of steel billets in this industry is for the manufacturing of agricultural machinery and equipment. Steel billets are commonly used to fabricate components such as plows, cultivators, seeders, and harvesting equipment. The agricultural industry requires durable and robust machinery that can withstand the harsh conditions of farming operations. Steel billets provide the necessary strength and toughness to withstand the demanding tasks involved in agriculture, such as tilling the soil or harvesting crops. The high-strength properties of steel billets make them ideal for withstanding heavy loads and rough terrain. Additionally, steel billets can be used for constructing storage and handling structures in the agricultural sector. Steel buildings and structures are highly resistant to weathering, pests, and fire, making them suitable for storing grain, livestock, and other agricultural products. Steel billets can be used to fabricate the main framework of these structures, ensuring their durability and longevity. Another potential application of steel billets in the agricultural aftermarket is for the production of fencing and livestock handling equipment. Steel fencing is commonly used in agricultural settings to secure boundaries, contain livestock, and protect crops from animals. Steel billets can be shaped and welded to create strong and reliable fencing materials that can withstand the test of time. Furthermore, steel billets can be utilized in the manufacturing of irrigation systems and water management equipment. Agricultural operations often require efficient irrigation systems to ensure proper water distribution to crops. Steel billets can be used to fabricate pipes, valves, and other components that are critical for irrigation systems, providing a durable and long-lasting solution. In summary, steel billets have numerous potential applications in the agricultural aftermarket. From manufacturing machinery and equipment to constructing storage structures, fencing, and irrigation systems, steel billets offer the strength, durability, and reliability required in the demanding agricultural industry.
- Q: Can steel billets be used in the production of agricultural equipment?
- Yes, steel billets can be used in the production of agricultural equipment. Steel billets are semi-finished products that are typically cast in a continuous casting process. They can be further processed into various shapes and sizes to manufacture agricultural equipment such as plows, cultivators, harrows, seeders, and other farm machinery. The use of steel billets in agricultural equipment offers several advantages. Steel is known for its strength, durability, and resistance to wear and tear, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications in the agricultural industry. Additionally, steel can withstand harsh environmental conditions, ensuring that the equipment remains reliable and functional even in challenging farming environments. Moreover, steel can be easily molded and fabricated into different forms, allowing for the customization of agricultural equipment to meet specific requirements. Overall, the use of steel billets in the production of agricultural equipment contributes to the efficiency, productivity, and longevity of farming operations.
- Q: Can steel billets be painted or coated for decorative purposes?
- Yes, steel billets can be painted or coated for decorative purposes. The surface of steel billets can be prepared and treated to ensure proper adhesion of paint or coating, allowing for customization and enhancing their appearance for decorative applications.
- Q: How are steel billets prepared for further processing?
- Steel billets are prepared for further processing through a series of steps, which include heating the steel to a specific temperature, followed by hot rolling to shape it into desired forms.
- Q: Can steel billets be used for structural applications?
- Yes, steel billets can be used for structural applications. Steel billets are semi-finished products commonly used in the manufacturing of various structural components such as beams, columns, and rods. These billets can be further processed through rolling or forging to create the desired shapes and sizes required for structural applications. The high strength and durability of steel make it a popular choice for constructing buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure projects.
- Q: I want to buy a fishing pole, I don't know how to distinguish it. Know what, please reply, thank you, [em10]!
- The tonality of a fishing rod is actually modulated by a different modulus of carbon cloth.Some fishing overall with the 30T following carbon cloth, just use a very small amount of 40T or 46T carbon cloth, called high carbon rod, is actually confuse the public practice of fishing by weighing, hand identification, high carbon rod with real light, hard, two rods in a play, a ratio is obvious.
- Q: Can steel billets be used for making kitchen utensils?
- Yes, steel billets can be used for making kitchen utensils. Steel billets are raw materials that can be shaped and formed into various products, including kitchen utensils. The steel used for kitchen utensils needs to be of high quality, with properties such as corrosion resistance, durability, and heat resistance. Steel billets can be melted, cast, and then forged into desired shapes and sizes for making kitchen utensils like knives, spoons, forks, cookware, and more. The steel used in kitchen utensils is often treated and finished to enhance its performance and appearance. Overall, steel billets serve as a starting point in the manufacturing process of kitchen utensils, providing the necessary raw material for creating durable and functional tools for cooking and food preparation.
- Q: How do steel billets contribute to the overall vibration resistance of a structure?
- Steel billets, due to their specific characteristics, significantly contribute to the overall vibration resistance of a structure. First and foremost, steel is a very dense and rigid material, which means that it possesses a high natural frequency. This high natural frequency allows steel billets to absorb and dissipate the energy generated by external vibrations more effectively than other materials. Moreover, steel billets have excellent damping properties. Damping refers to the ability of a material to reduce the amplitude of vibrations over time. Steel billets, being highly dense and rigid, are able to absorb and dissipate vibrations quickly, preventing them from propagating throughout the structure. This helps in reducing the overall vibration levels and, subsequently, increasing the overall vibration resistance of the structure. Furthermore, steel billets possess high tensile strength and stiffness, which allow them to resist deformation under dynamic loads. This means that when subjected to vibration forces, steel billets are able to maintain their shape and structural integrity, minimizing the risk of failure or damage. The high tensile strength of steel also enables it to withstand the impact of external forces without undergoing significant deformation or permanent damage. In addition, steel billets can be designed and manufactured to specific dimensions and shapes, allowing for precise integration into various structural components. This ensures that the steel billets are optimally positioned within the structure, enhancing their vibration resistance capabilities. Overall, steel billets contribute to the overall vibration resistance of a structure by effectively absorbing and dissipating vibrations, resisting deformation, and maintaining their structural integrity. Through these properties, steel billets help to minimize the impact of external vibrations and ensure the longevity and stability of the structure.
Send your message to us
Carbon steel billet price for sale from china
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 25437 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords