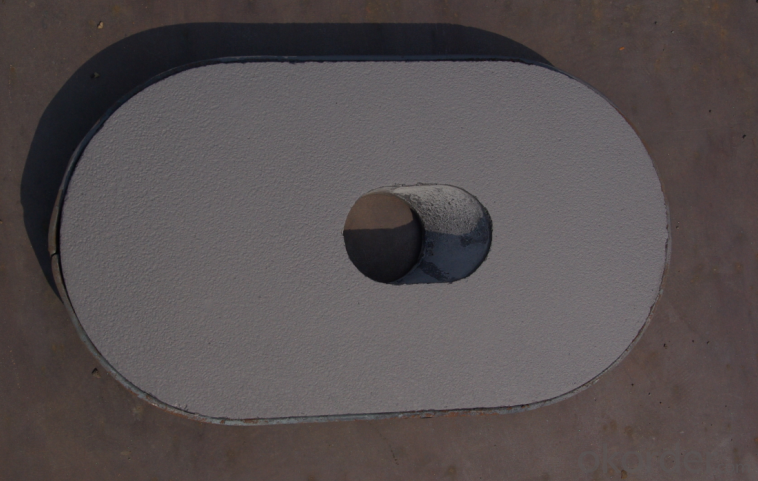
Monolithic Refractories Zirconia Slide Gate Nozzle for Iron and Steel Industry
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Zirconia Slide Gate Nozzle for Steel Industry
Slide gate plate widely used in large ladle, middle ladle and small ladle to fit for high quality steel casting.
Slide gate plate widely including Alumina carbon and Alumina Zirconia Carbon slide gate plate, MgO and MgO-spinel slide gate plate,nonoxides bonding slide gate plateand unburned slide gate plate.
Burnt Slide gate
Item B60,B50,C40type | Al-C Slide Gate | Al-Zr-C Slide Gate | ||||||
AlC-70 | AlC -75 | AlC -80 | AlC-85 | AlC -86 | AlZrC -70 | AlZrC-75 | AlZrC -77 | |
Al2O3,% | 70 | 75 | 80 | 85 | 86 | 70 | 75 | 77 |
C+SiC,% | 7 | 7 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
ZrO2,% | - | - | - | - | - | 6 | 6 | 2.5 |
A.P.,% max | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 7 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
B.D.,g/cm3 | 2.8 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 3.0 | 2.95 | 3.00 | 3.05 | 2.90 |
C.C.S., MPa min | 65 | 70 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 110 | 115 | 100 |
Unburned compound AlC Slide gate
Item B60,B50,C40type | Al-C Slide Gate | ||||
AlC-70A | AlC-75A | AlC-80A | AlC-85A | AlC-86A | |
Al2O3,% | 70 | 75 | 80 | 85 | 86 |
C,% | 7 | 7 | 5 | 5 | 4 |
A.P.,% max | 10 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 7 |
B.D. g/cm3 min | 2.8 | 2.9 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 2.95 |
C.C.S., MPa min | 65 | 70 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
zirconium core :
Item | ZN- 65 | ZN- 70 | ZN- 75 | ZN- 80 | ZN- 85 | ZN- 90 | ZN- 93A | ZN- 93B | ZN- 93C | ZN- 93D | ZN- 95A | ZN- 95B | ZN- 96 |
ZrO2(%) | ≥65 | ≥70 | ≥75 | ≥80 | ≥85 | ≥90 | ≥93 | ≥93 | ≥93 | ≥93 | ≥95 | ≥95 | ≥96 |
Bulk density (g/cm3) | ≥3.8 | ≥3.8 | ≥3.9 | ≥4.0 | ≥4.1 | ≥4.3 | ≥5.1 | ≥4.9 | ≥4.7 | ≥4.4 | ≥4.6 | ≥5.2 | ≥5.2 |
Apparent Porosity(%) | ≤23 | ≤22 | ≤22 | ≤20 | ≤20 | ≤20 | ≤13 | ≤15 | ≤18 | ≤20 | ≤20 | ≤9 | ≤5.6 |
Thermal shock resistance (cycles)(1100℃,water cooling) | >5 | >5 | >5 | >5 | >5 | >5 | >5 | >5 | >5 | >5 | >5 | >8 | >10 |


FAQ
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
①How about your company?
A world class manufacturer & supplier of castings forging in carbon steel and alloy steel,is one of the large-scale professional investment casting production bases in China,consisting of both casting foundry forging and machining factory. Annually more than 8000 tons Precision casting and forging parts are exported to markets in Europe,America and Japan. OEM casting and forging service available according to customer’s requirements.
②How to guarantee the quality of the products?
We have established the international advanced quality management system,every link from raw material to final product we have strict quality test;We resolutely put an end to unqualified products flowing into the market. At the same time, we will provide necessary follow-up service assurance.
- Q: What are the advantages of using insulating castables in the iron and steel industry?
- The advantages of using insulating castables in the iron and steel industry are numerous. Firstly, insulating castables have excellent thermal insulation properties, which help to reduce heat loss during the manufacturing process. This leads to increased energy efficiency and cost savings for the industry. Additionally, insulating castables have a low thermal conductivity, meaning they can withstand high temperatures without transferring excessive heat. This is crucial in the iron and steel industry, where temperatures can reach extremely high levels. By using insulating castables, the industry can ensure the longevity and durability of its equipment and structures. Furthermore, insulating castables have good resistance to thermal shock, meaning they can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or breaking. This is particularly beneficial in the iron and steel industry, where the heating and cooling processes are frequent and intense. Lastly, insulating castables have a low density, making them lightweight and easier to handle and install. This not only saves time and effort during installation but also reduces the structural load on equipment and structures. Overall, the use of insulating castables in the iron and steel industry offers advantages such as improved energy efficiency, enhanced durability, resistance to thermal shock, and ease of installation.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the reduction of heat loss in iron and steel furnaces?
- Reducing heat loss in iron and steel furnaces is a crucial role played by monolithic refractories. These refractories are specifically designed to create a seamless lining throughout the furnace, eliminating any joints or seams that could result in thermal leaks. Monolithic refractories effectively contribute to heat loss reduction in two ways. Firstly, they possess excellent thermal insulation properties that restrict the transfer of heat from the furnace to its surroundings. With their low thermal conductivity, they effectively maintain the high temperatures required for efficient iron and steel production within the furnace, while minimizing heat loss to the surrounding environment. Secondly, monolithic refractories act as a protective barrier, preventing the escape of hot gases and molten metal. This barrier ensures the integrity of the furnace lining, preventing any gaps or cracks that could allow heat to escape. By creating a tight and continuous lining, monolithic refractories significantly reduce heat loss by keeping the heat contained within the furnace. Furthermore, monolithic refractories exhibit a high resistance to thermal shock and erosion, which are common challenges faced in iron and steel furnaces. These refractories can withstand rapid temperature changes, preventing sudden cracks or failures that could result in heat loss. Additionally, they are resistant to the corrosive effects of molten metal and hot gases, guaranteeing the longevity of the lining and preserving its insulating properties over time. To summarize, monolithic refractories contribute to the reduction of heat loss in iron and steel furnaces through their exceptional thermal insulation properties, ability to provide a continuous lining, resistance to thermal shock and erosion, and protection against corrosive substances. By minimizing heat loss, these refractories optimize energy efficiency and productivity in the furnace, leading to cost savings and improved overall performance in the iron and steel industry.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand thermal shock and mechanical stress?
- Monolithic refractories are designed to withstand thermal shock and mechanical stress due to their unique composition and installation process. These refractories are made from a single, continuous material, eliminating any joints or seams that could weaken the structure. Additionally, they have a high thermal conductivity which allows them to efficiently distribute and dissipate heat, minimizing thermal gradients that can cause cracking. Furthermore, the installation technique involves forming the refractory in situ, ensuring a tight fit and reducing the likelihood of mechanical failure. Overall, the combination of their composition, thermal conductivity, and installation method enables monolithic refractories to withstand thermal shock and mechanical stress effectively.
- Q: What are the advantages of using plastic refractories in the iron and steel industry?
- There are several advantages of using plastic refractories in the iron and steel industry. Firstly, plastic refractories offer excellent thermal insulation properties. They have low thermal conductivity, which means they can effectively retain heat and prevent excessive heat loss during the manufacturing process. This is crucial in the iron and steel industry as maintaining high temperatures is essential for the proper functioning of furnaces and other equipment. Secondly, plastic refractories have superior resistance to chemical attack and corrosion. They can withstand exposure to various chemicals, including molten metals and slag, without deteriorating or losing their structural integrity. This is especially important in the iron and steel industry, where materials come into contact with highly corrosive substances on a regular basis. Another advantage of plastic refractories is their ease of installation and repair. Unlike other refractory materials, plastic refractories can be easily shaped and molded into the desired form, allowing for precise fitting and quick installation. Additionally, they can be easily repaired or patched in case of damage or wear, which reduces downtime and maintenance costs. Furthermore, plastic refractories exhibit good mechanical strength and abrasion resistance. This enables them to withstand the physical stresses and mechanical forces present in the iron and steel industry, such as vibrations, impacts, and mechanical loading. Their high resistance to wear and tear ensures longevity and reduces the need for frequent replacements. Lastly, plastic refractories have a high thermal shock resistance. They can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or spalling. This is beneficial in the iron and steel industry, where materials are subjected to extreme temperature differentials, such as during the heating and cooling cycles of furnaces. In conclusion, the advantages of using plastic refractories in the iron and steel industry include excellent thermal insulation, resistance to chemical attack, ease of installation and repair, good mechanical strength, abrasion resistance, and high thermal shock resistance. These properties make plastic refractories an ideal choice for various applications in this industry, ensuring efficient and reliable operations.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories enhance the performance of ladle and tundish purging systems?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in enhancing the performance of ladle and tundish purging systems in several ways. Firstly, monolithic refractories offer excellent thermal insulation properties. Ladle and tundish purging systems require high temperatures to effectively remove impurities and gases from molten metal. The use of monolithic refractories helps to minimize heat loss and maintain the desired temperature within the system. This ensures that the purging process is carried out efficiently and effectively. Secondly, monolithic refractories provide superior erosion and corrosion resistance. During the purging process, the molten metal and purging gases can be highly corrosive and abrasive. Monolithic refractories are designed to withstand such harsh conditions, preventing erosion and corrosion of the lining. This prolongs the lifespan of the ladle and tundish purging systems, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements. Furthermore, monolithic refractories offer excellent strength and stability. Ladle and tundish purging systems experience significant mechanical stresses due to the movement of molten metal and purging gases. The use of monolithic refractories ensures the structural integrity of the lining, preventing any deformation or failure under these conditions. This allows for smooth and uninterrupted purging operations, improving the overall performance of the system. In addition, monolithic refractories provide ease of installation and maintenance. Unlike traditional brick and mortar refractories, monolithic refractories can be easily applied as a single, homogeneous layer. This simplifies the installation process and reduces the time and effort required for maintenance. Any necessary repairs or replacements can be carried out more efficiently, minimizing downtime and maximizing the productivity of the ladle and tundish purging systems. Overall, monolithic refractories enhance the performance of ladle and tundish purging systems by providing excellent thermal insulation, erosion and corrosion resistance, strength and stability, as well as ease of installation and maintenance. These properties contribute to the efficient and effective removal of impurities and gases from molten metal, ensuring high-quality output and optimizing the overall productivity of the purging process.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand chemical attack from molten metals and slag?
- Monolithic refractories are highly resistant to chemical attack from molten metals and slag due to their unique composition and structure. These refractories are typically made from a single, solid piece with no joints or seams, which minimizes the opportunity for chemical penetration. One of the key factors that enables monolithic refractories to withstand chemical attack is their high melting point. These materials are designed to have a melting point significantly higher than the temperature of the molten metal or slag they are exposed to. This prevents the refractory from melting or deforming when in contact with the hot molten substances. In addition to their high melting point, monolithic refractories are formulated with materials that have excellent chemical resistance. They are often composed of a combination of oxides, such as alumina, magnesia, and zirconia, which have a strong affinity for oxygen and form stable compounds. This allows the refractory to form a protective oxide layer on its surface when exposed to molten metals and slag, effectively shielding it from chemical attack. Furthermore, the dense and compact structure of monolithic refractories plays a crucial role in their resistance to chemical attack. The absence of joints and seams minimizes the chances of molten metals and slag infiltrating the refractory and causing chemical reactions. This dense structure also reduces the porosity of the material, making it less permeable to aggressive substances. Moreover, manufacturers often add specialized additives to monolithic refractories to enhance their chemical resistance. These additives can include fibers, binders, and corrosion inhibitors, which further improve the refractory's ability to withstand chemical attack. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are designed to withstand chemical attack from molten metals and slag through their high melting point, chemical-resistant composition, dense structure, and specialized additives. These properties allow them to maintain their integrity and performance even in the harshest environments, making them an ideal choice for applications involving high-temperature and corrosive substances.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories help in enhancing the durability of iron and steel equipment?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in enhancing the durability of iron and steel equipment by providing high resistance to extreme temperatures, chemical attack, and mechanical wear. These refractories are composed of a single, homogeneous material, making them more robust and reliable compared to traditional brick or castable refractories. The high-temperature resistance of monolithic refractories allows them to withstand the extreme heat generated in iron and steel manufacturing processes, such as melting, casting, and forging. They can withstand temperatures exceeding 3000°F (1650°C) without losing their structural integrity, preventing premature failure of the equipment. This thermal resistance helps to maintain the shape and structure of the refractory lining, ensuring the efficient and consistent performance of the equipment. In addition to high heat resistance, monolithic refractories also exhibit excellent chemical resistance. Iron and steel equipment often comes into contact with corrosive substances, such as molten metal, slag, and various chemical compounds. The monolithic refractories' ability to resist chemical attack prevents degradation and erosion of the equipment's lining, extending its lifespan. Furthermore, monolithic refractories provide exceptional mechanical strength and wear resistance. The continuous exposure to abrasive materials, physical impacts, and mechanical stress can cause severe damage to the equipment. However, the dense and compact structure of monolithic refractories makes them highly resistant to mechanical wear, minimizing the risk of erosion and spalling. The flexibility and versatility of monolithic refractories are also advantageous in enhancing the durability of iron and steel equipment. They can be easily molded, shaped, and installed in complex geometries, ensuring a tight and precise fit. This eliminates the formation of gaps or weak points, which could lead to thermal or chemical leakage, reducing the risk of equipment failure. Overall, the use of monolithic refractories in iron and steel equipment significantly enhances its durability by providing exceptional resistance to high temperatures, chemical attack, and mechanical wear. These refractories ensure the longevity and reliability of the equipment, resulting in improved operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness in the iron and steel industry.
- Q: What are the specific requirements of monolithic refractories for ladle transfer applications?
- To ensure the effectiveness and durability of monolithic refractories used in ladle transfer applications, specific requirements must be met. These requirements are crucial for maintaining the integrity of the ladle lining and preventing any issues during the transfer process. Firstly, it is essential for monolithic refractories designed for ladle transfer applications to possess excellent thermal shock resistance. Ladles undergo extreme temperature changes during the transfer process, and the refractories must be capable of withstanding rapid heating and cooling without developing cracks or spalling. This property serves to prevent any damage to the lining and preserves the structural integrity of the ladle. Secondly, ladle transfer applications necessitate monolithic refractories that exhibit high resistance to chemical attack. Ladles often come into contact with various molten metals and slag, which can possess corrosive properties. The refractories must be able to endure these corrosive environments and maintain their physical and chemical properties over time. Another crucial requirement is good mechanical strength. Ladles can experience significant mechanical stress during the transfer process, including impacts and vibrations. Therefore, the monolithic refractories must possess sufficient strength to resist these mechanical forces and prevent any cracking or failure within the lining. Furthermore, ladle transfer applications frequently involve the use of fluxes and additives, which can possess different physical properties. The refractories used must be compatible with these fluxes and additives to ensure proper performance and avoid any adverse reactions that could impact the lining of the ladle. Lastly, monolithic refractories designed for ladle transfer applications should exhibit low porosity. Low porosity helps to minimize the penetration of molten metal and slag into the refractory lining, thereby reducing the risk of erosion and extending the service life of the refractories. In summary, the specific requirements for monolithic refractories in ladle transfer applications include excellent thermal shock resistance, high resistance to chemical attack, good mechanical strength, compatibility with fluxes and additives, and low porosity. By meeting these requirements, the refractories can effectively endure the harsh conditions of ladle transfer and ensure the longevity and performance of the ladle lining.
- Q: What are the typical properties of monolithic refractories used in iron and steel industry?
- Monolithic refractories used in the iron and steel industry typically possess high thermal conductivity, excellent resistance to thermal shock, and high mechanical strength. They are also known for their ability to withstand high temperatures and harsh chemical environments. Additionally, these refractories exhibit good erosion and abrasion resistance, low porosity, and high density, making them ideal for lining furnaces, ladles, and other equipment in the iron and steel production process.
- Q: What are the considerations for selecting monolithic refractories for reheating furnaces?
- There are several key considerations when selecting monolithic refractories for reheating furnaces. Firstly, the refractory material must have excellent thermal conductivity to efficiently transfer heat to the steel being reheated. Additionally, it should possess high resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress to withstand the rapid temperature changes and mechanical forces experienced in the furnace. The refractory should also have low porosity to prevent the penetration of gases and slag, ensuring a longer service life. Other factors to consider include the refractory's resistance to corrosive environments, ease of installation, and cost-effectiveness. Ultimately, choosing the right monolithic refractory is crucial to ensure optimal furnace performance and longevity.
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories Zirconia Slide Gate Nozzle for Iron and Steel Industry
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords