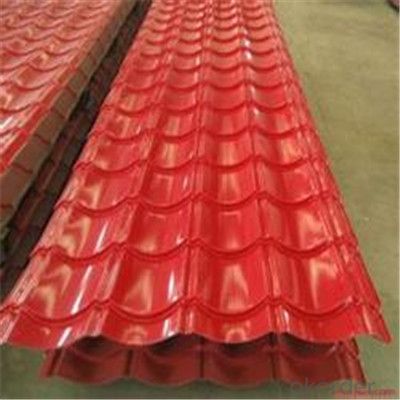
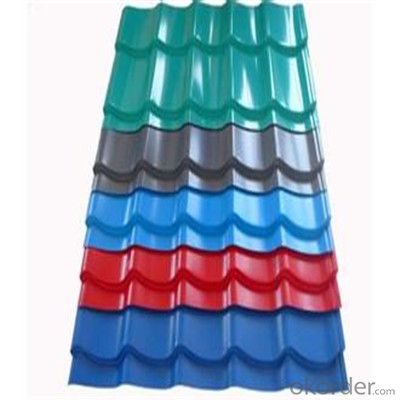
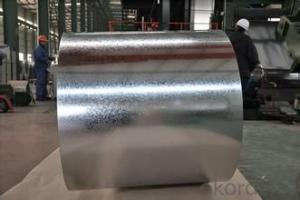
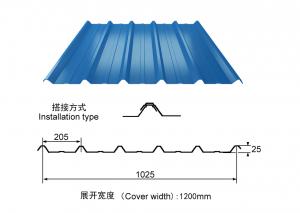
Zinc Coating Galvanized Corrugated Steel Iron Zinc Roof Sheet
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 200 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 1000000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
Description of Corrugated Iron Sheet:
1) Capacity: about 15,000 tons per month for sheet product.
2) Standard: JIS G3302 1998, ASTM A653M/A924M 2004, all according to the customer's request
3) Thickness: 0.13mm-0.5mm
4) Width: 400mm-1000mm
5) Length: We can adjust the length according to your request
6) Zinc Coating Weight: 60g/m2-275g/m2
Specifications of Corrugated Iron Sheet:
Standards: GB, JIS3312 and ASTM
Materials: SGCC, Q195-Q235B, SPCC, DC01, DX51D+Z and more
Thicknesses: 0.23-1.0MM
Widths: 600-1200mm
Zinc coating: 80 to 275g/m²
Features of Corrugated Iron Sheet:
Spangle: Regular spangle, minimized spangle and zero spangle
Hardness: Full hard, normal
Color: RAL, or other series
Surface Protection: PE, PVC, PVDF, SMP, HDP, etc.
Min trial order 10 tons each thickness, 1x20' per delivery.
Images of Corrugated Iron Sheet:

FAQ:
1. What's the Delivery port?
The main ports are Qingdao and Tianjin, we also can deliver to other ports to meet your requirements
2. How long is the lead time?
Delivery time: 45 days after order confirmed.
3. What payment term do you accept?
Payment: T/T or L/C at sight.
- Q: How do steel sheets compare to other materials, such as aluminum or copper?
- There are several advantages to using steel sheets instead of materials like aluminum or copper. Firstly, steel is known for its exceptional strength and durability, making it able to withstand heavy loads and resist impacts better than aluminum or copper. This makes steel sheets perfect for applications that require high strength and structural integrity, such as in construction or the automotive industry. Furthermore, steel sheets have a higher melting point than aluminum or copper, meaning they can withstand higher temperatures without deforming or melting. This makes steel sheets suitable for applications that involve exposure to high temperatures, like in manufacturing processes or engine components. Additionally, steel sheets have excellent corrosion resistance properties. They can be coated with protective layers like zinc or chromium to enhance their resistance to rust and corrosion. In contrast, aluminum and copper are more prone to corrosion, especially when exposed to certain environments or chemicals. This makes steel sheets the preferred choice for outdoor applications or structures that need long-term durability. Another advantage of steel sheets is their cost-effectiveness. Steel is relatively cheaper compared to aluminum or copper, especially when considering its strength and durability. This makes steel sheets a more economical choice for various applications where cost is an important factor. However, it is important to note that aluminum and copper also have their own advantages. Aluminum is lightweight and has excellent thermal conductivity, making it suitable for applications that require lightweight materials or efficient heat transfer. Copper, on the other hand, has superior electrical conductivity, making it ideal for electrical wiring or components. In conclusion, steel sheets offer exceptional strength, durability, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness compared to aluminum or copper. However, the choice of material ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as weight, thermal or electrical conductivity, and environmental factors.
- Q: What is the difference between a painted and laminated steel sheet?
- A painted steel sheet is coated with a layer of paint, while a laminated steel sheet has a layer of plastic or other material laminated onto the surface. This makes laminated steel sheets more resistant to scratches and damage, while painted steel sheets offer a wider range of color options.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used in acidic environments?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used in acidic environments, but the type of steel used and the concentration of the acid must be considered. Stainless steel or corrosion-resistant alloys are often preferred for their ability to withstand acidic conditions without corroding.
- Q: How do steel sheets handle static electricity?
- Steel sheets are generally excellent conductors of electricity, including static electricity. Due to their high electrical conductivity, steel sheets are capable of quickly dissipating any static charge that may build up on their surfaces. This ability to handle static electricity effectively is primarily attributed to the presence of free electrons within the steel's atomic structure. When a static charge is applied to a steel sheet, the free electrons readily move and redistribute themselves, neutralizing the charge and preventing any buildup or discharge of static electricity. Additionally, steel sheets are often coated with a thin layer of protective material, such as zinc or paint, which further enhances their ability to dissipate static charges. Overall, steel sheets are known for their reliable performance in handling static electricity and are commonly used in various industrial applications where electrostatic discharge can potentially cause damage or safety hazards.
- Q: What is the difference between a perforated and woven steel sheet?
- A perforated steel sheet is a metal sheet that has been punched with a pattern of holes, allowing for ventilation, drainage, or visibility. On the other hand, a woven steel sheet is a mesh-like structure created by interweaving individual steel wires, providing strength, filtration, or screening capabilities. The main difference lies in the manufacturing process and the resulting design, with perforated sheets having distinct punched holes and woven sheets having a continuous mesh pattern.
- Q: What is the difference between a smooth and corrugated stainless steel sheet?
- The distinguishing feature of a smooth stainless steel sheet is its flat and polished surface, devoid of any ridges or patterns. This type of sheet is frequently employed in situations where aesthetics and cleanliness hold significance, such as in kitchen countertops, appliances, and architectural designs. The absence of ridges makes cleaning and maintenance effortless. Conversely, a corrugated stainless steel sheet exhibits a wavy or ribbed pattern, resembling a sequence of parallel ridges or grooves. This design imparts additional strength and rigidity to the sheet, rendering it suitable for applications where structural integrity is of utmost importance. Corrugated stainless steel sheets are commonly utilized in roofing, siding, and industrial applications where durability and resistance to wear and tear are key. To summarize, the primary distinction between a smooth and corrugated stainless steel sheet lies in their surface texture and intended purpose. Smooth sheets are favored for their visual appeal and ease of upkeep, while corrugated sheets offer enhanced strength and are commonly employed in structural and industrial applications.
- Q: What's the best way to open a 10mm thick steel sheet?
- Steel plate is a kind of flat steel with big width ratio and large surface area. According to the thickness of plate Ya divided into thick and thin plates two specifications.
- Q: How do steel sheets perform in seismic zones?
- Due to their inherent strength and ductility, steel sheets exhibit excellent performance in seismic zones. The flexibility and high tensile strength of steel enable it to effectively absorb and dissipate the energy generated during seismic events, such as earthquakes. This capability helps in minimizing damage and preserving the structural integrity of buildings and other structures. In seismic design and construction, steel sheets offer several advantages, making them a commonly used material. Firstly, steel is lightweight, reducing the overall weight of the structure and enabling more efficient seismic design. Additionally, steel sheets can be easily fabricated and assembled, resulting in a faster and more cost-effective construction process. In seismic zones, steel sheets are frequently utilized as shear walls or bracing systems. These components are strategically positioned throughout the building to provide lateral stability and withstand the forces generated by earthquakes. Steel sheets can also serve as cladding material, adding an extra layer of protection against seismic forces. Furthermore, steel exhibits excellent fire resistance properties, further enhancing its performance in seismic zones. In the event of a fire, steel sheets retain their structural integrity for a longer duration compared to other materials, ensuring the safety of occupants and reducing the risk of collapse. In conclusion, steel sheets are a reliable and effective choice for construction in seismic zones. Their strength, ductility, lightweight nature, ease of fabrication, and fire resistance make them an ideal material for ensuring the safety and stability of structures during seismic events.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for elevator interiors?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for elevator interiors. Steel is a durable and versatile material that can be easily customized and shaped to fit the interior design requirements of an elevator. It provides a sleek and modern look, while also offering strength and durability to withstand daily wear and tear.
- Q: How do steel sheets perform in low-temperature environments?
- In low-temperature environments, steel sheets typically demonstrate excellent performance. The presence of low temperatures does not significantly impact the mechanical properties of steel, such as its strength and toughness. Steel possesses a low coefficient of thermal expansion, which means it does not undergo significant contraction or expansion when exposed to temperature fluctuations. This characteristic enables steel sheets to maintain their shape and structural integrity even in cold conditions. Furthermore, steel exhibits remarkable resistance to brittle fracture at low temperatures. It possesses excellent impact resistance, allowing it to absorb energy without fracturing. As a result, steel sheets are suitable for use in low-temperature environments where materials must endure heavy loads or sudden impacts, such as in cold storage facilities or offshore structures in Arctic regions. It is important to note, however, that certain types of steel, particularly those with high carbon content or low alloy steels, may experience reduced toughness and ductility at extremely low temperatures. In such cases, specific precautions may be necessary. These precautions may include utilizing steel grades specially designed for low-temperature applications or implementing appropriate insulation measures to prevent rapid temperature changes. Overall, steel sheets are generally dependable and exhibit excellent performance in low-temperature environments due to their strength, toughness, and resistance to brittle fracture. Nevertheless, the precise performance of steel in cold conditions may vary depending on the composition and quality of the steel employed.
Send your message to us
Zinc Coating Galvanized Corrugated Steel Iron Zinc Roof Sheet
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 200 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 1000000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords