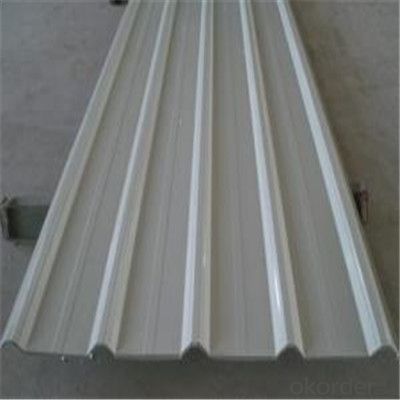
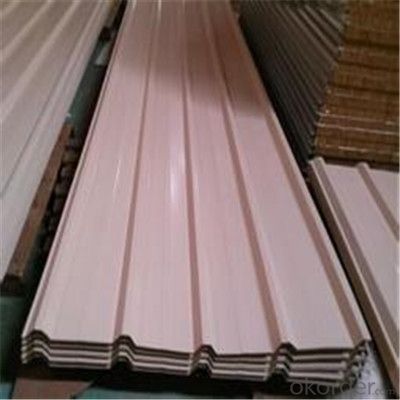
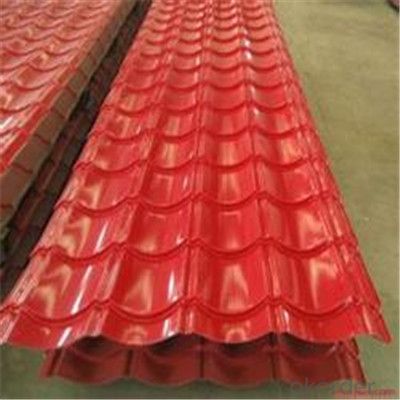
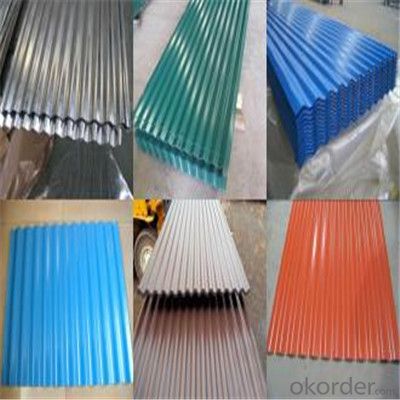
Zinc Coating Galvanized Corrugated Steel Steel Zinc Roof Sheet
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 1000000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
Description of Corrugated Iron Sheet:
China coat galvanized corrugated iron sheet for roofing:
1.Raw Material: SGCC,SGCH, Full hard
2.Thickness: 0.14-1mm
Specifications of Corrugated Iron Sheet:
Surface Finish: normal coated, embossed patterns, printed patterns
Base Metal: hot-dip zinc coated
Paint Type: Polyester, silicon modified polyesters, high-durability polyester, and polyvinylidene fluoride
Types of Top Coatings: PE, Silicon modified polyesters, High-durability polyester, Polyvinylidene fluoride
Coating surface structure: Small spangle, Zero spangle
Features of Corrugated Iron Sheet:
*Long-term resistance to atmospheric corrosion
*Bright surface
*Paintability
*Durability
*Versatility
Images of Corrugated Iron Sheet:
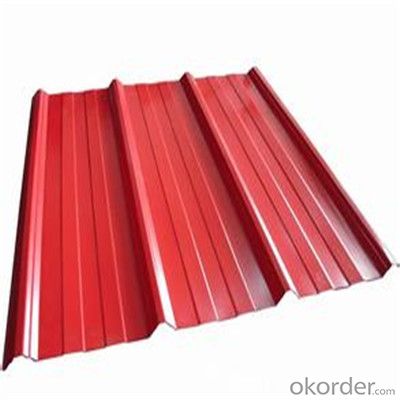

FAQ:
1. What's the Delivery port?
The main ports are Qingdao and Tianjin, we also can deliver to other ports to meet your requirements
2. How long is the lead time?
Delivery time: 45 days after order confirmed.
3. What payment term do you accept?
Payment: T/T or L/C at sight.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for interior design purposes?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for interior design purposes. They are commonly used for creating modern and industrial aesthetics in interior spaces. Steel sheets can be used for various applications such as wall paneling, room dividers, countertops, backsplashes, and decorative accents. Their durability, sleek appearance, and ability to be customized make them a popular choice for contemporary interior designs.
- Q: What is the process of polishing steel sheets?
- The process of polishing steel sheets typically involves several stages such as grinding, sanding, buffing, and finishing. Initially, the steel sheets are carefully ground to remove any imperfections or surface irregularities. Subsequently, sanding is conducted using different grits of sandpaper to refine the surface further and achieve a smoother texture. Following sanding, buffing is performed using various polishing compounds and a rotating wheel or pad to bring out a shiny, reflective finish. Finally, the steel sheets are thoroughly cleaned and inspected before being considered polished and ready for use in various applications.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for storage tanks?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for storage tanks. Steel is a strong, durable, and corrosion-resistant material, making it suitable for containing various materials and liquids in storage tanks.
- Q: What does steel plate "A3" mean?
- It can be used in all kinds of grinding tools, handles and other unimportant Abrasives parts
- Q: How are steel sheets protected during storage in warehouse facilities?
- Steel sheets are protected during storage in warehouse facilities through various measures such as applying protective coatings, using moisture-resistant packaging, implementing proper stacking and handling techniques, and maintaining controlled temperature and humidity levels to prevent corrosion and damage.
- Q: What is the typical flexural strength of a steel sheet?
- The typical flexural strength of a steel sheet can vary depending on its grade and thickness. However, most commonly used steel sheets have a flexural strength ranging from 250 to 500 megapascals (MPa).
- Q: What is the maximum thickness of a steel sheet?
- The maximum thickness of a steel sheet can vary depending on the specific type of steel being used, but it typically ranges from around 1 inch to 6 inches.
- Q: Are steel sheets suitable for agricultural applications?
- Yes, steel sheets are suitable for agricultural applications. They are durable, corrosion-resistant, and can withstand harsh weather conditions, making them ideal for various agricultural purposes such as constructing sheds, barns, fences, and storage buildings. Additionally, steel sheets can be easily fabricated and customized to meet specific agricultural needs.
- Q: What is the impact resistance of steel sheets?
- The impact resistance of steel sheets is generally high due to the material's toughness and ability to absorb and distribute energy upon impact.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for flooring or decking?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for flooring or decking. They are often used in industrial or commercial applications due to their durability, strength, and fire resistance. Steel sheets provide a sturdy and long-lasting flooring or decking option that can withstand heavy loads and harsh environments.
Send your message to us
Zinc Coating Galvanized Corrugated Steel Steel Zinc Roof Sheet
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 1000000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords