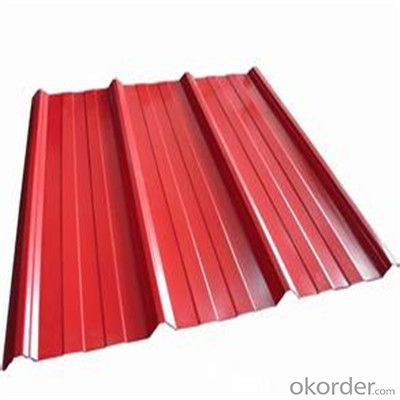
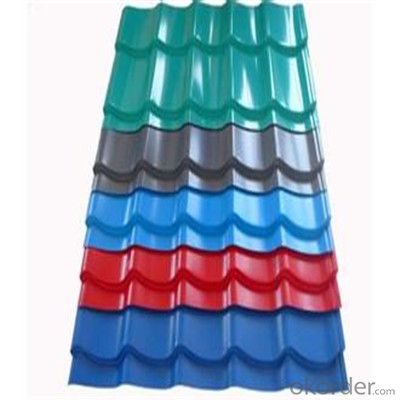
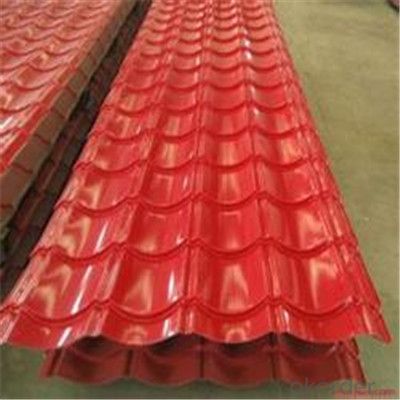
Zinc Galvanized Corrugated Steel Iron Zinc Roof Sheet
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 1000345 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
Description of Corrugated Iron Sheet:
Minimum yield strength of 550 MPa ensures required strength for roofing application
Accurate thickness, width and length gives a perfect fit for any roof
Wider valley ensures higher water discharge in case of heavy rains
Specifications of Corrugated Iron Sheet:
1) Chemical Composition: 55% Aluminum, 43.4% Zinc, 1.6% Silicon
2) Substrate: Galvalume steel sheet & Pre-painted galvalume steel sheet
3) Standard: JIS3321/ASTM A792M
4) Thickness: 0.16mm-2.0mm, all available
5) Width: 600mm-1250mm, all available
Features of Corrugated Iron Sheet:
Raw material width 762mm, after corrugated width 665mm: 9 waves.
Raw material width 914mm ,after corrugated width 800mm:11 waves.
Raw material width 1000mm, after corrugated 890mm or 900mm :12 or 14 waves. as customer requirement
Images of Corrugated Iron Sheet:

FAQ:
1. What's the Delivery port?
The main ports are Qingdao and Tianjin, we also can deliver to other ports to meet your requirements
2. How long is the lead time?
Delivery time: 45 days after order confirmed.
3. What payment term do you accept?
Payment: T/T or L/C at sight.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for fencing and gates?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for fencing and gates. Steel sheets are a durable and strong material that can provide security and protection when used for fencing or gates. They can be customized to various sizes and designs, making them suitable for different fencing and gating needs.
- Q: What are the different surface treatments for galvanized steel sheets?
- There are several surface treatments for galvanized steel sheets, including chromate passivation, oiling, painting, and powder coating. Chromate passivation is a chemical treatment that enhances the corrosion resistance of the galvanized coating. Oiling provides temporary protection against moisture and corrosion. Painting and powder coating involve applying a layer of paint or powder to the surface, providing both protection and aesthetic appeal.
- Q: How do steel sheets compare to other materials, such as aluminum or stainless steel?
- Steel sheets are generally stronger and more durable compared to aluminum or stainless steel. They offer better resistance to impact, corrosion, and extreme temperatures. Steel sheets are also more cost-effective and widely available, making them a popular choice in various industries. However, aluminum and stainless steel sheets have their own advantages, such as being lighter in weight and having better resistance to certain chemicals. Ultimately, the choice of material depends on the specific requirements of the application.
- Q: What are the different bending radius options for steel sheets?
- The bending radius options for steel sheets can vary depending on the thickness and type of steel being used. Generally, the bending radius for steel sheets ranges from 0.5 to 2 times the thickness of the sheet. For thinner sheets, such as those with a thickness of 0.5mm to 2mm, a bending radius of 0.5 to 1 times the sheet thickness is typically recommended. This allows for a tighter bend without risking cracking or deformation of the steel. For thicker sheets, such as those with a thickness of 2mm to 6mm, a bending radius of 1 to 1.5 times the sheet thickness is commonly used. This ensures that the steel retains its structural integrity and prevents any excessive stress or strain during the bending process. For even thicker sheets, typically above 6mm, a bending radius of 1.5 to 2 times the sheet thickness is often required. This larger bending radius helps to avoid any potential damage or distortion to the steel, ensuring a successful bending operation. It is important to note that these bending radius options are general guidelines and may vary depending on the specific steel grade, composition, and intended application. It is always recommended to consult the manufacturer's recommendations or seek expert advice when determining the appropriate bending radius for steel sheets.
- Q: How do steel sheets perform in impact resistance?
- Steel sheets have excellent impact resistance due to their high strength and hardness. They can effectively absorb and distribute the force of an impact, minimizing deformation and damage. Additionally, steel sheets can be further enhanced through various treatments and coatings, further improving their impact resistance.
- Q: How are steel sheets protected against rusting?
- Corrosion protection is employed to safeguard steel sheets against rusting. Several techniques are utilized for this purpose: 1. Galvanization: Zinc is applied as a coating on the steel sheets. Acting as a sacrificial anode, the zinc corrodes in lieu of the steel when exposed to moisture or oxygen. Consequently, a barrier is formed to shield the steel from rust. 2. Painting: A layer of paint is applied to the steel sheets, creating a protective barrier against moisture and oxygen. This physical barrier prevents contact between these elements and the steel, thus reducing the likelihood of rust formation. 3. Powder coating: Dry powder is spread onto the steel sheets and then heated to establish a protective layer. The powder liquefies and fuses into a smooth coating, offering remarkable resistance to rust and corrosion. 4. Electroplating: The steel sheets are immersed in a bath containing a metal coating solution, such as zinc or chromium. By passing an electric current through the bath, the metal coating bonds with the steel, serving as a safeguard against rust. 5. Phosphating: A chemical process deposits a layer of zinc or manganese phosphate onto the steel sheets. This layer enhances the adhesion of paint or other coatings, providing a surface resistant to corrosion. These techniques find widespread usage in various industries to avert the rusting of steel sheets. The selection of a specific method is contingent upon factors such as cost, durability requirements, and the intended environment for the steel sheets.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for electrical conductivity applications?
- Typically, steel sheets are not employed in electrical conductivity applications. Although steel exhibits decent heat conductivity and some electrical conductivity, it is not as efficient as specialized materials like copper or aluminum, which are specifically designed for electrical conductivity. Steel sheets find common use in domains that prioritize strength, durability, and corrosion resistance, such as construction, automotive manufacturing, and industrial equipment. In electrical conductivity applications, it is more prevalent to utilize materials with heightened conductivity, such as copper or aluminum, as they possess lower resistance and are better equipped to efficiently conduct electricity.
- Q: What are the different certification standards for steel sheets?
- Steel sheets can be certified according to various standards, each with its own specific requirements and criteria. Among the most commonly recognized certification standards for steel sheets are the following: 1. ASTM International: Cold-rolled, carbon steel sheets must meet the specifications outlined in ASTM A1008/A1008M. This standard ensures that the steel sheets possess the necessary mechanical properties, chemical composition, and dimensional requirements. 2. American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME): ASME SA240 is a specification for chromium and chromium-nickel stainless steel plates, sheets, and strips used in pressure vessels and general applications. Adhering to this certification standard guarantees the quality and safety of stainless steel sheets employed in a wide range of industrial settings. 3. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): ISO 3574 establishes the requirements for cold-reduced carbon steel sheets of commercial and drawing qualities. Certification according to ISO 3574 ensures that the steel sheets possess specific mechanical properties, surface finish, and dimensions. 4. European Committee for Standardization (CEN): EN 10025 is a European standard that addresses hot-rolled structural steel products. This certification standard covers a variety of steel sheet grades and dimensions utilized in construction and engineering applications. 5. Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS): JIS G 3141 is a Japanese standard for cold-reduced carbon steel sheets and strips. This certification standard guarantees that the steel sheets meet specific mechanical properties, chemical composition, and dimensional requirements. These examples represent just a sampling of the certification standards available for steel sheets. Depending on the intended application and geographical location, there may be additional regional or industry-specific certification standards that must be fulfilled to ensure the quality and suitability of the steel sheets.
- Q: Can the steel sheets be used for industrial machinery?
- Industrial machinery can indeed utilize steel sheets. Steel, known for its robustness, endurance, and resistance to damage, is a favored option for constructing industrial machinery. By shaping, cutting, and welding steel sheets, manufacturers can produce diverse components and parts essential for industrial machinery. The adaptability of steel empowers manufacturers to design and fabricate machinery that precisely meets specifications and demands. Furthermore, steel's capacity to endure hefty burdens, extreme temperatures, and corrosive surroundings renders it suitable for a vast array of industrial applications.
- Q: What is the price range for steel sheets?
- The price range for steel sheets can vary depending on factors such as thickness, size, quality, and the current market conditions. Generally, steel sheets can range anywhere from $20 to $200 per sheet.
Send your message to us
Zinc Galvanized Corrugated Steel Iron Zinc Roof Sheet
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 1000345 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords