Z29 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Z29 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
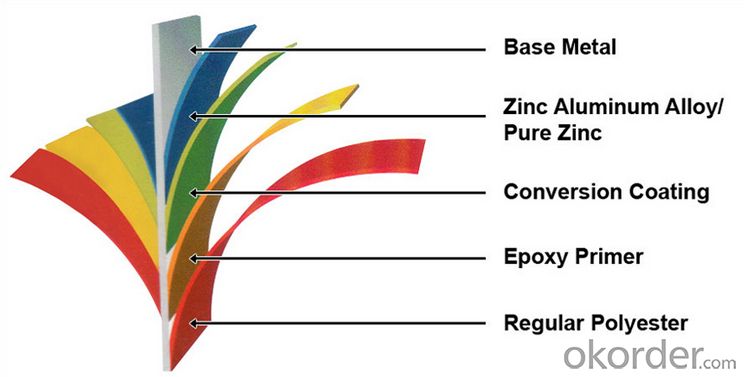
Description of Z29 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
PPGI is made by cold rolled steel sheet and galvanized steel sheets as baseplate, through the surface pretreatment (degreasing, cleaning, chemical conversion processing), coated by the method of continuous coatings (roller coating method),
and after roasting and cooling. Zinc coating: Z60, Z80, Z100, Z120, Z180, Z275, G30, G60, G90
Alu-zinc coating: AZ60, AZ80, AZ100, AZ120, AZ180, G30, G60, G90
Main Feature of Z29 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
1) Excellent corrosion resistance: The zinc layer provides a good protection of Pre-painted Galvanizeed Steel Sheet.
2) High heat resistance: The reflective surface of the material aids in efficiently reflecting the sunlight away and in turn reducing the amount of heat transmitted. The thermal reflectivity converts into energy savings.
3) Aesthetics: Pre-Painted Galvanized steel sheet is available in plethora of patterns and multiple sizes as per the requirements that given by our customers.
4) Versatility: can be used in the various areas.Standard seaworthy export packing: 3 layers of packing, inside is kraft paper, water plastic film is in the middle and outside GI steel sheet to be covered by steel strips with lock, with inner coil sleeve.
Applications of Z29 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
1. Construction and building: roofing; ventilating duct; handrail; partition panel;etc.
2. Electric appliance: refrigerator; washing machine; refrigerator; DVD;etc.
3.Transportation: oil tank; road sign; etc.
4.Agriculture:barn; etc.
5.Others:vending machine; game machine; etc.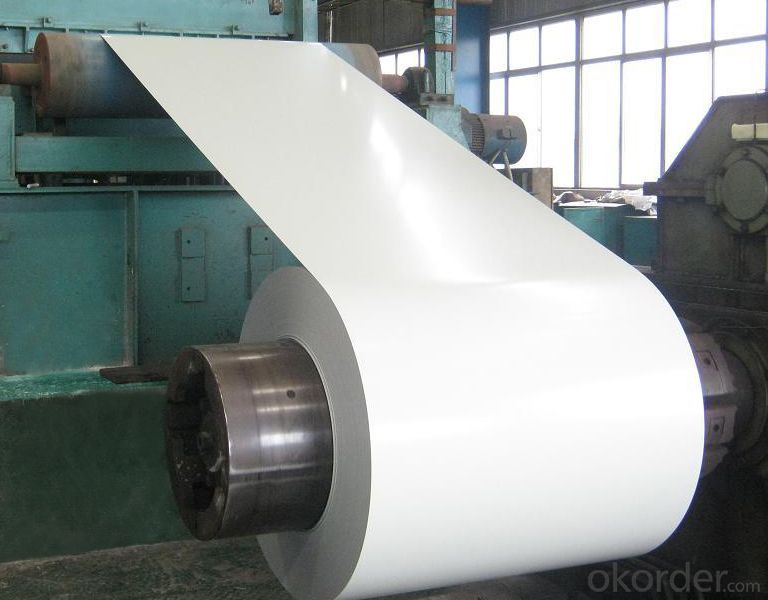 
Specifications of Z29 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
| Classified symbol | Yield Point Minimum N/mm2 | Tensile Strength Minimum | Elongation Minimum % | Application | ||||
| N/mm2 | Nominal Thickness mm (t) | |||||||
| JIS | Yogic | 0.25-0.4 | 0.4-0.6 | 0.6-1.0 | 1.0-1.6 | |||
| G3312 | specification | |||||||
| CGCC | CGCC | -205 | -270 | -20 | -21 | -24 | -24 | Commercial |
| CGCD | CGCD | --- | 270 | --- | 27 | 31 | 32 | Drawing |
| --- | CG340 | 245 | 340 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | Structural |
| CGC400 | CG400 | 295 | 400 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 18 | Structural |
| CGC440 | CG440 | 335 | 440 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 18 | Structural |
| CGC490 | CG490 | 365 | 490 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 16 | Structural |
| CGC570 | CG570 | 560 | 570 | --- | --- | --- | --- | Structural |
| ASTM Designation | Yield Point Minimum | Tensile Strength Minimum | Elongation Minimum % | Application | Q/BQB 445-2004(China standard) | ASM A653/A653M | JISG 3312 | |
| ksi(MPa) | ksi(MPa) | TDC51D+Z | (CS TYPE A+Z) | CGCC | ||||
| A653(M)-99 CS TYPE A,B,C | --- | --- | --- | Commercial | TDC52D+Z | CGCD | ||
| A653(M)-99 FS | --- | --- | --- | Lock Forming | TS250GD+Z | (G250+Z) | - | |
| A653(M)-99 DS | --- | --- | --- | Drawing | TS300GS+Z | (G300+Z) | CGC 400 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade33(230) | 33(230) | 45(310) | 20 | Structural | TS350GD+Z | (G350+Z) | CGC490 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade37(255) | 37(255) | 52(360) | 18 | Structural | TS550GD+Z | (G550+Z) | CGC570 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade40(275) | 40(275) | 55(380) | 16 | Structural | ||||
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade50(345) | 50(345) | 65(450) | 12 | Structural | ||||
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade80(550) | 80(550) | 82(570) | --- | Structural | ||||
FAQ of Z29 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1. How Can I Visit There?
Our company is located in Tianjin City, China, near Beijing. You can fly to Tianjin Airport Directly. All our clients, from home or aboard, are warmly welcome to visit us!
2. How Can I Get Some Sample?
We are honored to offer you sample.
3. Why choose CNBM?
1, ISO, BV, CE, SGS approved.
2, Competitive price and quality.
3, Efficient service team online for 24 hours.
4, Smooth production ability(50000tons/month) .
5, quick delivery and standard exporting package.
6, Flexible payment with T/T, L/C, Paypal, Kunlun bank, etc .
- Q: What is the role of steel billets in the manufacturing of construction cranes?
- In the manufacturing process of construction cranes, steel billets play a vital role as they are the raw materials used to produce various crane components. These billets are essentially partially finished steel products that are shaped and sized into rectangles or squares. A primary purpose of steel billets in crane manufacturing is the production of structural members like beams, columns, and braces. These components provide the necessary strength and stability to support the crane's weight and the loads it carries. Steel billets are chosen for their high strength and durability, enabling the crane to withstand heavy loads and adverse working conditions. Furthermore, steel billets are utilized to manufacture the crane's boom, jib, and lifting mechanisms. These parts experience significant stress and forces during crane operation, and the superior mechanical properties of steel billets make them ideal for ensuring the crane's structural integrity and longevity. Additionally, steel billets are used in the fabrication of counterweights for the crane. Counterweights are crucial for balancing the load being lifted and preventing the crane from tipping over. By using steel billets, manufacturers can create counterweights that are sufficiently heavy to counterbalance the loads without compromising the overall stability and safety of the crane. Moreover, steel billets are often employed in the production of other crane components such as pins, bolts, and connectors. These small yet essential parts contribute to the overall performance and functionality of the crane, ensuring smooth operation and structural integrity. In summary, steel billets act as the fundamental building blocks for the manufacturing of construction cranes, providing the necessary strength, durability, and stability required for these robust machines. Without steel billets, it would be nearly impossible to produce cranes capable of lifting heavy loads and withstanding the demanding conditions of construction sites.
- Q: What are the main factors affecting the cost of steel billets?
- There are several main factors that can affect the cost of steel billets. 1. Raw material costs: The cost of the raw materials used to produce steel billets, such as iron ore and scrap metal, can have a significant impact on the overall cost. Fluctuations in the prices of these raw materials in the global market can cause the cost of steel billets to rise or fall. 2. Production and processing costs: The cost of manufacturing steel billets includes various production and processing expenses, such as energy costs, labor costs, and maintenance costs. These costs can vary depending on factors such as the efficiency of production processes, the availability of skilled labor, and the cost of energy sources. 3. Supply and demand dynamics: The balance between supply and demand for steel billets in the market can heavily influence their cost. If there is a high demand for steel billets and limited supply, the prices can increase. Conversely, if there is excess supply and low demand, the prices can decrease. 4. Market competition: The level of competition among steel producers can also impact the cost of steel billets. In a competitive market, where multiple producers are vying for customers, the prices may be driven down as producers try to attract buyers. Conversely, in a less competitive market, producers may have more pricing power, leading to higher prices. 5. Trade policies and tariffs: Government policies and trade barriers, such as import tariffs and quotas, can affect the cost of steel billets. These measures can either protect domestic steel producers by making imported steel more expensive or create opportunities for cheaper imports, depending on the specific policies in place. 6. Currency exchange rates: Since steel billets are traded globally, fluctuations in currency exchange rates can impact their cost. A stronger domestic currency can make imported steel billets cheaper, while a weaker domestic currency can make them more expensive. 7. Transportation and logistics: The cost of transporting steel billets from the production facility to the end-user can also influence their overall cost. Factors such as distance, transportation mode, and fuel prices can impact the transportation expenses, which can, in turn, affect the final price of steel billets. It is important to note that these factors can interact with each other, and their impact on the cost of steel billets can vary depending on the specific market conditions and industry dynamics.
- Q: What are the challenges faced in the production of steel billets?
- There are several challenges faced in the production of steel billets. One of the main challenges is the sourcing of raw materials. Steel billets are typically produced from iron ore, which needs to be mined and processed before it can be used. The availability and quality of iron ore can vary, making it challenging to secure a consistent supply. Another challenge is the energy-intensive nature of steel production. The process of converting iron ore into steel billets requires significant amounts of energy, mainly in the form of electricity and fossil fuels. This can lead to high production costs and contribute to environmental concerns, such as greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the production of steel billets involves complex metallurgical processes. The steel needs to be heated to high temperatures and undergo various treatments to achieve the desired properties. Ensuring consistent quality and meeting specific customer requirements can be challenging, as any deviations in the production process can affect the final product's performance. Maintaining a safe working environment is also a significant challenge in steel billet production. The production process involves handling heavy machinery, molten metal, and potentially hazardous chemicals. Effective safety measures and protocols need to be implemented to protect workers and prevent accidents. Lastly, the market dynamics and competition in the steel industry pose challenges in the production of steel billets. Fluctuating demand, changes in customer preferences, and price volatility can impact production planning and profitability. Steel producers need to stay competitive by continuously improving efficiency, reducing costs, and adapting to market trends. Overall, the production of steel billets faces challenges related to raw material sourcing, energy consumption, metallurgical processes, safety, and market dynamics. Overcoming these challenges requires a combination of technological advancements, efficient operations, and strategic decision-making to ensure a sustainable and successful production process.
- Q: Billet heating furnace billet temperature reached, steel will be adhesion
- There are a lot of billet heating furnace manufacturers, not just look at the price and go blind choice, billet heating furnace selection properly, will directly affect the day after work is carried out properly, choose cost-effective equipment is the first choice for users, recommended to look at the video consultation.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of shipbuilding components?
- Steel billets are an essential raw material used in the manufacturing of shipbuilding components. These components are crucial for constructing ships, including hulls, decks, bulkheads, and other structural parts. The first step in using steel billets is to heat them in a furnace to a specific temperature, allowing them to become malleable. This process is known as hot rolling, which helps in shaping the billets into desired forms and sizes required for shipbuilding components. Hot rolling also enhances the mechanical properties of the steel, making it stronger and more durable. Once the billets are heated and shaped, they are further processed through various techniques such as forging, extrusion, or casting to create specific shipbuilding components. For example, the steel billets can be forged to create large and complex parts like ship propellers or rudders. Extrusion is used to form long and continuous shapes like shipbuilding beams or pipes. Casting is employed for intricate components such as engine parts or valves. After the initial shaping process, the steel components are then subjected to various finishing operations such as machining, welding, and surface treatment. Machining helps in achieving precise dimensions and smooth surfaces required for proper fitting and functioning of the shipbuilding components. Welding is used to join different steel components together, ensuring structural integrity and strength. Surface treatment techniques like painting or galvanizing are applied to protect the components from corrosion and increase their lifespan. Overall, steel billets play a vital role in shipbuilding as they provide the necessary raw material for manufacturing various components. Their versatility, strength, and durability make them ideal for constructing ships that can withstand the harsh marine environment. The use of steel billets, combined with advanced manufacturing techniques, ensures the production of high-quality shipbuilding components that meet stringent industry standards.
- Q: What are the different types of tests conducted on steel billets?
- There are several types of tests conducted on steel billets, including visual inspection, dimensional inspection, chemical composition analysis, mechanical testing, ultrasonic testing, and magnetic particle inspection. These tests are crucial to ensure the quality and integrity of the steel billets before they are further processed and used in various applications.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the production of gear blanks?
- Steel billets are used in the production of gear blanks as they serve as the raw material for shaping and forming the gears. The steel billets are heated and forged into the desired shape, and then machined to create the gear blanks. These gear blanks are further processed and finished to become fully functional gears, which are then used in various machinery and equipment.
- Q: Can steel billets be used for making hand tools?
- Hand tools can be made using steel billets. Steel billets are semi-finished steel products that are commonly used for further processing and shaping into different forms. Steel billets can be used to manufacture various hand tools such as wrenches, pliers, hammers, screwdrivers, and many others. Steel is a popular choice for manufacturing hand tools because of its strength, durability, and resistance to wear and tear. Steel billets can be forged, machined, or heat-treated to achieve the desired shape, size, and hardness required for hand tools. The versatility of steel allows it to be easily molded into different tool designs, providing the necessary strength and functionality. Moreover, steel hand tools offer several advantages over tools made from other materials. The high tensile strength of steel ensures that the tools can withstand significant force and pressure without breaking or deforming. Additionally, steel tools are resistant to corrosion and rust, making them suitable for both indoor and outdoor use, even in harsh environments. In conclusion, steel billets are indeed suitable for manufacturing hand tools. The strength, durability, and versatility of steel make it an excellent material for producing a wide range of hand tools that can endure heavy usage and provide long-lasting performance.
- Q: What are the different surface finishing techniques used for steel billets?
- There are several surface finishing techniques that are commonly used for steel billets. These techniques are employed to enhance the appearance, improve corrosion resistance, and provide a protective coating to the steel billets. Some of the different surface finishing techniques used for steel billets are: 1. Hot Rolling: This technique involves passing the steel billets through a series of hot rollers, which not only shapes the billets but also creates a smooth surface finish. Hot rolling is commonly used to produce steel plates, sheets, or structural shapes. 2. Cold Rolling: Cold rolling is similar to hot rolling, but it is performed at room temperature. This technique helps to achieve a smoother surface finish, increased dimensional accuracy, and improved mechanical properties of the steel billets. 3. Shot Blasting: Shot blasting is a process where steel billets are bombarded with small metallic or non-metallic particles at high velocity. This technique helps to remove scale, rust, and other contaminants from the billet's surface, resulting in a clean and uniform appearance. 4. Pickling: Pickling involves immersing the steel billets in an acid solution to remove oxides, scale, and rust from the surface. This technique helps to achieve a clean and smooth surface finish, ready for further processing or coating. 5. Galvanizing: Galvanizing is a popular surface finishing technique that involves coating the steel billets with a layer of zinc. This coating provides excellent corrosion resistance and protects the steel from environmental factors. Galvanizing can be done through hot-dip galvanizing, electro-galvanizing, or mechanical galvanizing methods. 6. Painting: Painting is often used as a surface finishing technique for steel billets. It involves applying a layer of paint or protective coating to the surface, which not only enhances the appearance but also provides protection against corrosion and weathering. 7. Passivation: Passivation is a chemical process used to remove free iron or iron oxides from the surface of steel billets. This process helps to improve the corrosion resistance of the steel and leaves a clean and passive surface. 8. Polishing: Polishing involves using abrasive materials or compounds to smoothen the surface of the steel billets. This technique is commonly used to achieve a high gloss or mirror-like finish, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of the steel. Each of these surface finishing techniques offers its own advantages and is chosen based on the specific requirements of the steel billets, such as appearance, corrosion resistance, and functionality.
- Q: What are the different types of steel billet welding processes?
- There are several types of steel billet welding processes, including submerged arc welding (SAW), gas metal arc welding (GMAW), shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), and flux-cored arc welding (FCAW). These processes differ in the type of electrode and shielding method used, as well as the specific conditions and equipment required for each process.
Send your message to us
Z29 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords































