Z28 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Z28 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
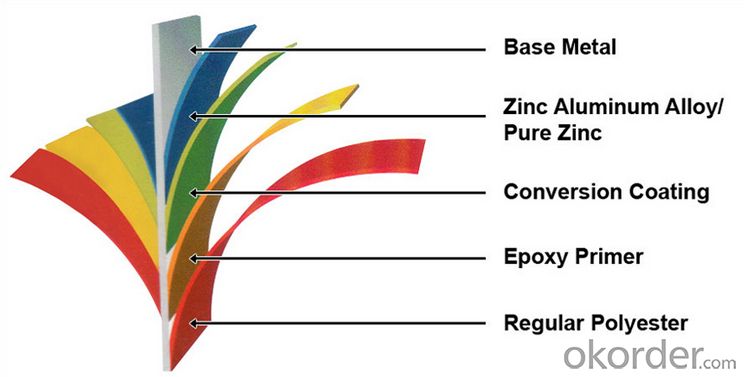
Description of Z28 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
PPGI is made by cold rolled steel sheet and galvanized steel sheets as baseplate, through the surface pretreatment (degreasing, cleaning, chemical conversion processing), coated by the method of continuous coatings (roller coating method),
and after roasting and cooling. Zinc coating: Z60, Z80, Z100, Z120, Z180, Z275, G30, G60, G90
Alu-zinc coating: AZ60, AZ80, AZ100, AZ120, AZ180, G30, G60, G90
Main Feature of Z28 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
1) Excellent corrosion resistance: The zinc layer provides a good protection of Pre-painted Galvanizeed Steel Sheet.
2) High heat resistance: The reflective surface of the material aids in efficiently reflecting the sunlight away and in turn reducing the amount of heat transmitted. The thermal reflectivity converts into energy savings.
3) Aesthetics: Pre-Painted Galvanized steel sheet is available in plethora of patterns and multiple sizes as per the requirements that given by our customers.
4) Versatility: can be used in the various areas.Standard seaworthy export packing: 3 layers of packing, inside is kraft paper, water plastic film is in the middle and outside GI steel sheet to be covered by steel strips with lock, with inner coil sleeve.
Applications of Z28 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
1. Construction and building: roofing; ventilating duct; handrail; partition panel;etc.
2. Electric appliance: refrigerator; washing machine; refrigerator; DVD;etc.
3.Transportation: oil tank; road sign; etc.
4.Agriculture:barn; etc.
5.Others:vending machine; game machine; etc.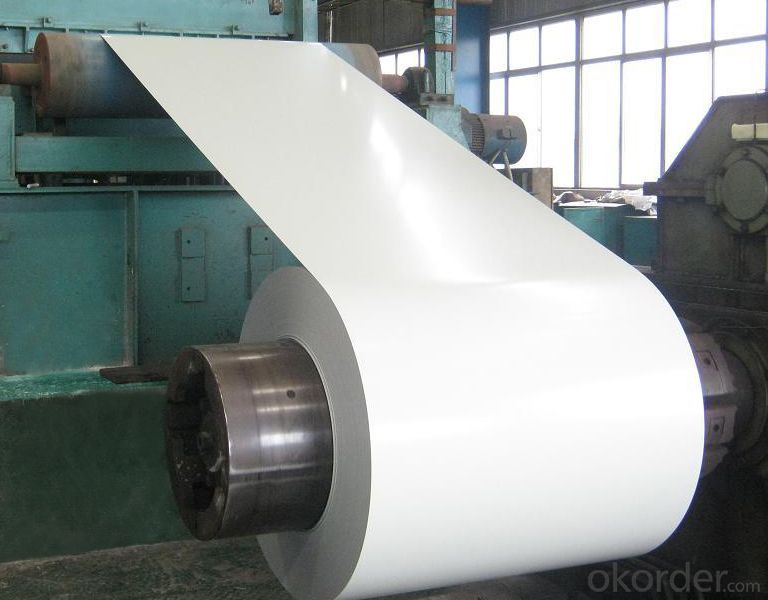 
Specifications of Z28 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
| Classified symbol | Yield Point Minimum N/mm2 | Tensile Strength Minimum | Elongation Minimum % | Application | ||||
| N/mm2 | Nominal Thickness mm (t) | |||||||
| JIS | Yogic | 0.25-0.4 | 0.4-0.6 | 0.6-1.0 | 1.0-1.6 | |||
| G3312 | specification | |||||||
| CGCC | CGCC | -205 | -270 | -20 | -21 | -24 | -24 | Commercial |
| CGCD | CGCD | --- | 270 | --- | 27 | 31 | 32 | Drawing |
| --- | CG340 | 245 | 340 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | Structural |
| CGC400 | CG400 | 295 | 400 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 18 | Structural |
| CGC440 | CG440 | 335 | 440 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 18 | Structural |
| CGC490 | CG490 | 365 | 490 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 16 | Structural |
| CGC570 | CG570 | 560 | 570 | --- | --- | --- | --- | Structural |
| ASTM Designation | Yield Point Minimum | Tensile Strength Minimum | Elongation Minimum % | Application | Q/BQB 445-2004(China standard) | ASM A653/A653M | JISG 3312 | |
| ksi(MPa) | ksi(MPa) | TDC51D+Z | (CS TYPE A+Z) | CGCC | ||||
| A653(M)-99 CS TYPE A,B,C | --- | --- | --- | Commercial | TDC52D+Z | CGCD | ||
| A653(M)-99 FS | --- | --- | --- | Lock Forming | TS250GD+Z | (G250+Z) | - | |
| A653(M)-99 DS | --- | --- | --- | Drawing | TS300GS+Z | (G300+Z) | CGC 400 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade33(230) | 33(230) | 45(310) | 20 | Structural | TS350GD+Z | (G350+Z) | CGC490 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade37(255) | 37(255) | 52(360) | 18 | Structural | TS550GD+Z | (G550+Z) | CGC570 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade40(275) | 40(275) | 55(380) | 16 | Structural | ||||
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade50(345) | 50(345) | 65(450) | 12 | Structural | ||||
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade80(550) | 80(550) | 82(570) | --- | Structural | ||||
FAQ of Z28 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1. How Can I Visit There?
Our company is located in Tianjin City, China, near Beijing. You can fly to Tianjin Airport Directly. All our clients, from home or aboard, are warmly welcome to visit us!
2. How Can I Get Some Sample?
We are honored to offer you sample.
3. Why choose CNBM?
1, ISO, BV, CE, SGS approved.
2, Competitive price and quality.
3, Efficient service team online for 24 hours.
4, Smooth production ability(50000tons/month) .
5, quick delivery and standard exporting package.
6, Flexible payment with T/T, L/C, Paypal, Kunlun bank, etc .
- Q: How is the surface condition of steel billets checked?
- The surface condition of steel billets is typically checked through visual inspection, where trained personnel examine the surface for any defects such as cracks, pitting, or surface irregularities. Additionally, non-destructive testing methods such as ultrasonic examination may also be used to detect any internal defects that may not be visible to the naked eye.
- Q: What are the main factors affecting the fatigue strength of steel billets?
- The fatigue strength of steel billets can be influenced by several key factors. 1. Material Composition: The fatigue strength of a steel billet depends on its composition, including the type and quantity of alloying elements present. Elements like carbon, manganese, and silicon have an impact on the billet's ability to resist fatigue and endure cyclic loading. 2. Surface Quality: The fatigue strength of steel billets is closely tied to their surface quality. Surface defects, such as cracks, scratches, or pits, can act as stress concentrators, leading to premature fatigue failure. Therefore, it is imperative to properly prepare and inspect the surface to ensure high fatigue resistance. 3. Heat Treatment: The fatigue strength of a steel billet can be significantly influenced by the heat treatment process used to modify its microstructure. Employing appropriate heat treatment techniques, like quenching and tempering, can enhance the billet's fatigue resistance by improving its hardness, strength, and toughness. 4. Grain Size: The fatigue strength of a steel billet is also affected by the grain size of its microstructure. Finer grains generally exhibit greater fatigue resistance due to reduced stress concentration and enhanced grain boundary strength. 5. Residual Stress: Residual stresses, which can arise from various manufacturing processes, play a crucial role in determining the fatigue strength of steel billets. Excessive residual stress can serve as a starting point for fatigue cracks, thereby diminishing the billet's fatigue life. 6. Operating Conditions: The fatigue strength of steel billets can be influenced by the conditions under which they operate. Factors such as the magnitude and frequency of applied cyclic loads, as well as the temperature, can all have a detrimental impact on the billet's fatigue life. 7. Environmental Factors: The environment in which a steel billet operates can also affect its fatigue strength. Variables like humidity, corrosive gases, and exposure to chemicals can accelerate the initiation and propagation of fatigue cracks, resulting in reduced fatigue resistance. Taking into account and comprehending these primary factors that impact the fatigue strength of steel billets is crucial when designing components and structures that can endure cyclic loading and ensure long-term reliability.
- Q: What are the different methods of hardness testing for steel billets?
- There are several methods of hardness testing for steel billets, each offering different advantages and levels of accuracy. Some of the most common methods include: 1. Rockwell hardness testing: This is one of the most widely used methods and measures the depth of indentation caused by a specific load on a steel billet's surface. It provides a hardness value based on the depth of penetration, making it convenient and relatively quick to perform. 2. Brinell hardness testing: This method involves indenting a steel billet's surface with a spherical indenter under a specific load. The diameter of the resulting impression is measured to determine the hardness value. Brinell testing is especially useful for large billets or materials with a coarse microstructure. 3. Vickers hardness testing: Vickers testing uses a pyramidal diamond indenter to create an impression on the surface of a steel billet. The diagonal length of the impression is measured, and the hardness value is calculated based on the applied load. Vickers testing is suitable for a wide range of materials, including steel billets. 4. Knoop hardness testing: Similar to Vickers testing, Knoop hardness testing also uses a pyramidal diamond indenter. However, the indentation shape is elongated and narrower, allowing for measurements on smaller or thinner samples. This method is often used for precise and microhardness testing. 5. Leeb hardness testing: Leeb testing is a portable and non-destructive method that uses an impact device to measure the rebound hardness of a steel billet. The device strikes the surface with a small ball and measures the velocity of the rebound, which is then converted into a hardness value. This method is commonly used for on-site or in-field measurements. 6. Ultrasonic hardness testing: This method uses ultrasonic waves to measure the hardness of a steel billet. The waves are transmitted through the material, and the time taken for the waves to travel through the billet is measured. This data is then converted into a hardness value. Ultrasonic testing is non-destructive and suitable for large or thick billets. It is important to note that each hardness testing method has its own limitations and considerations. The choice of method will depend on factors such as the size, shape, and surface condition of the steel billet, as well as the desired accuracy and convenience of the testing process.
- Q: What are the potential applications of steel billets in the textile industry?
- The textile industry can benefit from the wide range of potential applications offered by steel billets. One major area where steel billets prove useful is in manufacturing textile machinery components. Gears, shafts, and frames, crucial for the smooth functioning of textile machines, can be produced using steel billets. These components require high strength and durability, which steel billets provide to withstand the demanding operational conditions in the textile industry. Another application of steel billets in the textile industry is the production of molds and dies. By machining steel billets into intricate shapes, molds and dies can be created for fabricating textile products. Injection molding and extrusion processes, commonly used in textile manufacturing, rely on these molds and dies. Steel billets offer dimensional stability and resistance to wear and tear, making them ideal for producing long-lasting molds and dies. Moreover, steel billets can be employed in constructing textile production facilities. Steel, being versatile and strong, can be easily shaped and welded, making it suitable for building textile industry infrastructure. Steel billets can be used to fabricate support structures, frames, and beams for textile factories. These structures provide stability and strength to the buildings, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of textile production processes. Additionally, steel billets find applications in the packaging of textile products. Steel drums and containers, manufactured using steel billets, are commonly used for storing and transporting textiles. Steel drums offer excellent durability, protection against external factors, and resistance to damage during handling and transportation. In summary, the potential applications of steel billets in the textile industry are diverse and encompass various aspects of textile manufacturing, including machinery production, mold and die fabrication, construction, and packaging. Utilizing steel billets in these applications contributes to the efficiency, reliability, and quality of textile production processes.
- Q: How do steel billets contribute to the overall fire resistance of a structure?
- Steel billets contribute to the overall fire resistance of a structure in several ways. Firstly, steel is a non-combustible material, meaning it does not burn or contribute to the spread of fire. By using steel billets in the construction of a building, the risk of fire propagation is significantly reduced. Secondly, steel has a high melting point, typically around 1370 degrees Celsius. This means that even in the presence of intense heat, steel maintains its structural integrity and does not deform easily. Steel billets, which are solid blocks of steel, provide strength and stability to the structure, ensuring that it can withstand the impact of a fire. Additionally, steel has a low thermal conductivity, meaning it does not conduct heat easily. This property helps to slow down the transfer of heat from the fire to the surrounding areas of the structure. By acting as a barrier, steel billets prevent the temperature from rising rapidly, giving occupants more time to evacuate and firefighters more time to extinguish the fire. Moreover, steel billets are often used in the construction of fire-resistant walls or barriers within a structure. These walls are designed to compartmentalize the building, limiting the spread of fire and smoke to specific areas. By incorporating steel billets into these fire-resistant walls, the construction becomes more robust and capable of withstanding the extreme conditions of a fire. In summary, steel billets contribute to the overall fire resistance of a structure through their non-combustible nature, high melting point, low thermal conductivity, and ability to reinforce fire-resistant walls. By utilizing steel billets in the construction process, buildings can be made more resilient to fire incidents, ensuring the safety of occupants and minimizing the damage caused by fires.
- Q: What are the different surface finishes available for stainless steel billets?
- There are several surface finishes available for stainless steel billets, depending on the desired aesthetic appearance and functional requirements. Some of the most common surface finishes for stainless steel billets include: 1. Mill Finish: This is the standard finish produced by the steel mill during the manufacturing process. It has a dull appearance with visible oxidation marks and can vary in smoothness. 2. Hot Rolled: This finish is achieved by heating the stainless steel billet and then rolling it through a series of rollers. It results in a rougher surface with visible scale and a characteristic orange peel texture. 3. Cold Rolled: This finish is obtained by subjecting the stainless steel billet to cold rolling, which reduces its thickness and improves its surface smoothness. It has a slightly reflective appearance and is often used for applications requiring a smooth finish. 4. Brushed Finish: Also known as satin finish, this surface finish is achieved by mechanically brushing the stainless steel billet with abrasive materials. It creates a consistent linear pattern, giving the steel a matte appearance. 5. Polished Finish: This finish involves polishing the stainless steel billet using abrasives to create a smooth and reflective surface. The level of polish can vary from a low-gloss satin finish to a mirror-like, highly reflective finish. 6. Bead Blasted Finish: In this finish, the stainless steel billet is bombarded with tiny glass or ceramic beads under high pressure, which creates a uniform matte texture. It is commonly used for architectural and decorative applications. 7. Electropolished Finish: This surface finish is achieved by immersing the stainless steel billet in an electrolyte bath and applying an electric current. It removes a thin layer of material, resulting in a smooth, reflective surface with improved corrosion resistance. These are just a few examples of the different surface finishes available for stainless steel billets. Each finish has its own unique characteristics and is chosen based on the specific requirements of the application, such as aesthetics, corrosion resistance, and ease of cleaning.
- Q: Can steel billets be polished for improved surface finish?
- No, steel billets cannot be polished for improved surface finish as they are usually unfinished or have a rough surface due to the manufacturing process.
- Q: What are the main challenges in the marketing of steel billets?
- There are several factors that contribute to the main challenges faced in marketing steel billets. To begin with, the highly competitive nature of the steel industry is a major hurdle. The market is saturated with numerous steel manufacturers and suppliers worldwide, making it difficult for companies to stand out and maintain a strong presence. In addition, fluctuations in global demand and supply of steel pose significant challenges. Steel billets are primarily used as raw material in industries like construction, automotive, and manufacturing. Any changes in these industries' demand directly affect the demand for steel billets. Therefore, marketing strategies must be adaptable and responsive to market dynamics in order to secure a stable customer base. Pricing is also a critical challenge. Steel billets are subject to price volatility due to factors such as raw material costs, energy prices, and global economic conditions. Companies must constantly analyze these factors to set competitive prices while ensuring profitability. Furthermore, a thorough understanding of the target market's needs and preferences is necessary for effective marketing. Different industries may require specific qualities and specifications in their billets, such as size, composition, or surface finish. To meet these requirements, companies must invest in research and development and effectively communicate the advantages of their products to potential customers. Establishing and maintaining strong relationships with customers is another challenge. Steel billets are typically sold through long-term contracts, relying on trust and reliability. Consistent quality, on-time delivery, and excellent customer service are essential for building and nurturing these relationships. Lastly, environmental sustainability has emerged as a challenge in the marketing of steel billets. With increasing environmental regulations and growing consumer awareness, companies need to position themselves as environmentally responsible and promote sustainable practices throughout their value chain. To conclude, marketing steel billets presents challenges related to intense competition, demand-supply dynamics, pricing, market understanding, customer relationships, and environmental sustainability. Overcoming these challenges requires strategic planning, continuous adaptation, and a customer-centric approach.
- Q: What are the different types of steel billet surface defects?
- During the manufacturing process, various steel billet surface defects may arise. These defects have the potential to impact the steel's quality and performance, thus necessitating their identification and resolution to safeguard the final product's integrity. 1. Scale: Oxidation during heating and rolling gives rise to a widespread defect known as scale. This defect manifests as a thin layer of iron oxide on the billet's surface, which can be readily eliminated through descaling procedures. 2. Cracks: Another common defect is cracks, which can emerge on the billet's surface. These cracks can be caused by factors such as uneven cooling, excessive stress, or improper handling. Due to their ability to compromise structural integrity, cracked billets necessitate repair or disposal. 3. Pitting: Pitting is characterized by shallow depressions or pits on the billet's surface. It can arise due to impurities in the steel, inadequate cooling, or corrosion. Pitting diminishes strength and heightens susceptibility to corrosion. 4. Lamination: Lamination defects occur when the billet experiences poor bonding during manufacturing, leading to the presence of layers or separation. This defect undermines the steel's mechanical properties, potentially resulting in failure under stress. 5. Inclusions: Non-metallic substances, such as slag, oxides, or other impurities, can become trapped within the billet during manufacturing, causing inclusions. Inclusions weaken the steel and decrease its ductility, rendering it more prone to cracking or breaking. 6. Scratches: Superficial defects like scratches may arise during billet handling or transportation. While they may not significantly impact overall structural integrity, they can concentrate stress in localized areas, potentially leading to failure in specific applications. 7. Decarburization: Decarburization occurs when the billet's surface loses its carbon content during the heating process. This defect reduces hardness and strength in the affected region, impacting the steel's performance. Manufacturers and inspectors must possess knowledge of these various steel billet surface defects to ensure the production of high-quality steel products. Regular inspections, quality control measures, and appropriate corrective actions are vital in minimizing and addressing these defects, thereby guaranteeing the desired steel performance and longevity.
- Q: What does "billet" mean?
- Steelmaking and continuous casting of steel products are mainly used for steel rolling, such as round bar, wire rod, sheet metal and so on
Send your message to us
Z28 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords































