Z27 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Z27 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
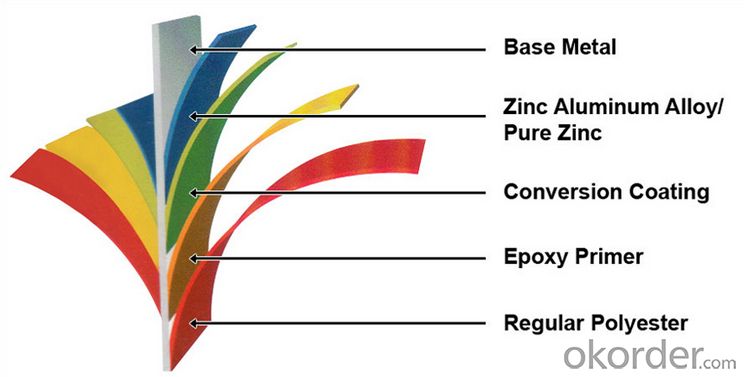
Description of Z27 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
PPGI is made by cold rolled steel sheet and galvanized steel sheets as baseplate, through the surface pretreatment (degreasing, cleaning, chemical conversion processing), coated by the method of continuous coatings (roller coating method),
and after roasting and cooling. Zinc coating: Z60, Z80, Z100, Z120, Z180, Z275, G30, G60, G90
Alu-zinc coating: AZ60, AZ80, AZ100, AZ120, AZ180, G30, G60, G90
Main Feature of Z27 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
1) Excellent corrosion resistance: The zinc layer provides a good protection of Pre-painted Galvanizeed Steel Sheet.
2) High heat resistance: The reflective surface of the material aids in efficiently reflecting the sunlight away and in turn reducing the amount of heat transmitted. The thermal reflectivity converts into energy savings.
3) Aesthetics: Pre-Painted Galvanized steel sheet is available in plethora of patterns and multiple sizes as per the requirements that given by our customers.
4) Versatility: can be used in the various areas.Standard seaworthy export packing: 3 layers of packing, inside is kraft paper, water plastic film is in the middle and outside GI steel sheet to be covered by steel strips with lock, with inner coil sleeve.
Applications of Z27 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
1. Construction and building: roofing; ventilating duct; handrail; partition panel;etc.
2. Electric appliance: refrigerator; washing machine; refrigerator; DVD;etc.
3.Transportation: oil tank; road sign; etc.
4.Agriculture:barn; etc.
5.Others:vending machine; game machine; etc. 
Specifications of Z27 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
| Classified symbol | Yield Point Minimum N/mm2 | Tensile Strength Minimum | Elongation Minimum % | Application | ||||
| N/mm2 | Nominal Thickness mm (t) | |||||||
| JIS | Yogic | 0.25-0.4 | 0.4-0.6 | 0.6-1.0 | 1.0-1.6 | |||
| G3312 | specification | |||||||
| CGCC | CGCC | -205 | -270 | -20 | -21 | -24 | -24 | Commercial |
| CGCD | CGCD | --- | 270 | --- | 27 | 31 | 32 | Drawing |
| --- | CG340 | 245 | 340 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | Structural |
| CGC400 | CG400 | 295 | 400 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 18 | Structural |
| CGC440 | CG440 | 335 | 440 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 18 | Structural |
| CGC490 | CG490 | 365 | 490 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 16 | Structural |
| CGC570 | CG570 | 560 | 570 | --- | --- | --- | --- | Structural |
| ASTM Designation | Yield Point Minimum | Tensile Strength Minimum | Elongation Minimum % | Application | Q/BQB 445-2004(China standard) | ASM A653/A653M | JISG 3312 | |
| ksi(MPa) | ksi(MPa) | TDC51D+Z | (CS TYPE A+Z) | CGCC | ||||
| A653(M)-99 CS TYPE A,B,C | --- | --- | --- | Commercial | TDC52D+Z | CGCD | ||
| A653(M)-99 FS | --- | --- | --- | Lock Forming | TS250GD+Z | (G250+Z) | - | |
| A653(M)-99 DS | --- | --- | --- | Drawing | TS300GS+Z | (G300+Z) | CGC 400 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade33(230) | 33(230) | 45(310) | 20 | Structural | TS350GD+Z | (G350+Z) | CGC490 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade37(255) | 37(255) | 52(360) | 18 | Structural | TS550GD+Z | (G550+Z) | CGC570 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade40(275) | 40(275) | 55(380) | 16 | Structural | ||||
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade50(345) | 50(345) | 65(450) | 12 | Structural | ||||
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade80(550) | 80(550) | 82(570) | --- | Structural | ||||
FAQ of Z27 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1. How Can I Visit There?
Our company is located in Tianjin City, China, near Beijing. You can fly to Tianjin Airport Directly. All our clients, from home or aboard, are warmly welcome to visit us!
2. How Can I Get Some Sample?
We are honored to offer you sample.
3. Why choose CNBM?
1, ISO, BV, CE, SGS approved.
2, Competitive price and quality.
3, Efficient service team online for 24 hours.
4, Smooth production ability(50000tons/month) .
5, quick delivery and standard exporting package.
6, Flexible payment with T/T, L/C, Paypal, Kunlun bank, etc .
- Q: What are the potential applications of steel billets in the electronics aftermarket?
- Steel billets have numerous potential applications in the electronics aftermarket. One possible application is the production of electronic enclosures or casings. Steel billets can be machined and shaped into various forms and sizes to create sturdy and reliable enclosures that protect electronic components. These enclosures provide durability and protection against environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and impact. Additionally, steel billets can be used in the manufacturing of various electronic components. For example, they can be utilized to create connectors, pins, sockets, and other small parts that are essential for electronic devices. Steel's high strength and conductivity make it an ideal material for these components, ensuring reliable performance and efficient signal transmission. Furthermore, steel billets can be employed in the production of heat sinks for electronic devices. Heat sinks are crucial in dissipating heat generated by electronic components and preventing overheating, which can lead to performance issues or even component failure. Steel's excellent thermal conductivity makes it a suitable material for heat sinks, allowing efficient heat transfer and ensuring the proper functioning of electronic devices. Moreover, steel billets can be utilized in the manufacturing of racks and cabinets used for housing and organizing electronic equipment. These structures provide a safe and secure environment for storing and accessing electronic devices in various settings, such as data centers, telecommunications facilities, or server rooms. Steel's durability and load-bearing capabilities make it an ideal choice for such applications, ensuring the protection and organization of electronic equipment. In summary, steel billets have a range of potential applications in the electronics aftermarket. Whether it is in the production of enclosures, electronic components, heat sinks, or racks and cabinets, steel's strength, conductivity, durability, and thermal properties make it a versatile material for various electronic applications.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of forgings?
- The production of forgings relies heavily on steel billets, which are a vital raw material. These semi-finished steel products serve as the starting point for shaping and forming various types of forgings. To begin the process, suitable steel billets are carefully chosen based on their chemical composition and mechanical properties. Typically made from high-quality carbon or alloy steel, these billets undergo thorough inspection to ensure their suitability for the intended end product. Once the appropriate billets are selected, they are subjected to a series of heating and shaping procedures. These billets are heated in a furnace to a specific temperature known as the forging temperature, in order to enhance their malleability. Strict temperature control is exercised to optimize plasticity and minimize potential defects. Once the forging temperature is reached, the billets are transferred to a forging press or hammer. These powerful machines exert immense pressure to mold the billets into the desired form. The force applied causes the billets to deform and conform to the shape of the die or mold being used. To achieve the final desired shape, the forged billet may undergo additional steps such as trimming, piercing, or machining. These procedures are necessary to eliminate any excess material and further refine the forged part. The quality of the steel billets throughout the manufacturing process is of utmost importance, as it directly influences the final quality of the forgings. The billets must possess consistent chemical composition, mechanical properties, and be free from defects. This ensures that the forged parts exhibit the desired strength, durability, and dimensional accuracy. In conclusion, steel billets serve as the initial material in the manufacturing of forgings. Through heating, shaping, and other processes, these billets are transformed into the final forged part. The quality of the billets directly impacts the quality of the forgings, making the selection and inspection of billets a critical step in the overall manufacturing process.
- Q: What are the different shapes and forms of steel billets?
- Depending on their intended use and manufacturing process, steel billets are available in a variety of shapes and forms. Casting is the typical process used to achieve the most common shapes, which include square, rectangular, round, and hexagonal. Square billets are widely used and are often rolled into long products such as bars, rods, and wire. Rectangular billets, with longer sides compared to their width, are also rolled into long products but are typically used for applications that require a larger cross-sectional area. Round billets, as their name suggests, are cylindrical and primarily used for producing seamless tubes, pipes, and other tubular products. The round shape is preferred in these applications as it allows for a more uniform distribution of stresses during manufacturing. Hexagonal billets, with their six sides, are commonly used for forging and machining. Their unique shape provides greater strength and stability, making them suitable for producing high-quality components like bolts, nuts, and other fasteners. In addition to these common shapes, steel billets can also be customized to meet specific requirements in terms of shape and size. Specialized molds or further processing techniques like extrusion or hot rolling can be used to achieve these custom shapes. Overall, the various shapes and forms of steel billets enable the production of a wide range of steel products, each tailored to its specific application and manufacturing process.
- Q: What are the different types of surface finishes available for steel billets?
- Steel billets have a range of surface finishes that cater to specific needs and offer distinct qualities. Some of the most commonly used surface finishes for steel billets include: 1. Hot Rolled: This is the most basic finish achieved by heating the steel billet above its recrystallization temperature and then rolling it to the desired shape and size. Hot rolled steel billets have a rough and scaled surface, suitable for applications where aesthetics are not a primary concern. 2. Cold Rolled: This finish is obtained by subjecting the hot rolled billets to a series of cold rolling processes. Cold rolled steel billets have a smoother and refined surface, with tighter tolerances and improved dimensional accuracy. 3. Pickled and Oiled: This finish involves removing rust, scale, or mill scale from the steel billets by immersing them in an acidic solution, known as pickling. After pickling, the steel billets are oiled for temporary corrosion protection. This finish is ideal for applications where cleanliness and corrosion resistance are crucial. 4. Galvanized: Galvanizing is a process that coats the steel billets with a layer of zinc for enhanced corrosion resistance. This finish is particularly suitable for outdoor applications or high humidity environments, offering protection against rust and corrosion. 5. Electroplated: Electroplating involves depositing a thin layer of metal, such as nickel or chromium, onto the steel billets through an electrochemical reaction. This finish enhances aesthetics, corrosion resistance, and can provide specific functional properties like hardness or wear resistance. 6. Powder Coated: Powder coating is a technique where dry powder is electrostatically applied to the steel billets and then cured under heat to form a durable and protective coating. This finish offers excellent corrosion resistance, impact resistance, and a wide range of color options, making it popular in architectural and decorative applications. 7. Anodized: Anodizing, commonly used for aluminum, can also be applied to steel billets. This process creates an oxide layer on the steel's surface through electrolysis. Anodized steel billets exhibit improved corrosion resistance, increased hardness, and can be dyed in various colors for aesthetic purposes. These examples illustrate the variety of surface finishes available for steel billets. The choice of finish depends on specific requirements such as aesthetics, corrosion resistance, durability, and functional properties.
- Q: What are the main factors affecting the quality of steel billets?
- There are several main factors that can significantly affect the quality of steel billets. These factors include the composition of the steel, the temperature and time of the heating process, the cooling rate, and the presence of impurities. Firstly, the composition of the steel plays a crucial role in determining its quality. The presence of certain elements such as carbon, manganese, and silicon can affect the mechanical properties of the steel, including its strength and hardness. The proper control and balance of these alloying elements are essential to ensure the desired quality of the steel billets. Secondly, the temperature and time of the heating process during the production of steel billets are critical factors. The heating process must be carefully controlled to achieve the optimal temperature for the desired transformation of the microstructure. Overheating or underheating can lead to the formation of undesirable phases or an inconsistent microstructure, which can negatively impact the quality of the billets. The cooling rate is another important factor affecting the quality of steel billets. The cooling process needs to be controlled to achieve the desired microstructure and mechanical properties. Too rapid cooling can result in the formation of brittle phases or residual stresses, while slow cooling can lead to coarse-grained structures with reduced strength. Furthermore, the presence of impurities in the steel can significantly affect its quality. Impurities such as sulfur, phosphorus, and non-metallic inclusions can decrease the mechanical properties and promote the formation of defects in the steel billets. Therefore, strict control of the raw materials and the implementation of effective refining techniques are necessary to minimize the presence of impurities. In conclusion, the main factors affecting the quality of steel billets are the composition of the steel, the temperature and time of the heating process, the cooling rate, and the presence of impurities. By carefully controlling and optimizing these factors, steel manufacturers can produce high-quality billets that meet the desired specifications and performance requirements.
- Q: Refinery carbon 3 is propane, then carbon four carbon five is what name ah?.What are they used for?
- This is isomericCarbon four is butane, n-butane and isobutaneCarbon five is pentane pentane. ISO pentane. PentaneThey are intermediates in refining
- Q: Can steel billets be used in the production of utensils and cutlery?
- Yes, steel billets can be used in the production of utensils and cutlery. Steel billets are typically processed and shaped into various forms such as sheets, bars, or rods, which can then be further manufactured into utensils and cutlery items through processes like forging, casting, or stamping.
- Q: Billet prices skyrocketing weekend, Southern China steel prices rose?
- This week, although steel prices also rose a few days, but since entering November, the price rose a week, a week plummeted, then rebounded sharply, the roller coaster trend, make steel practitioners the feeling of being alone.
- Q: How do steel billets compare to other steel products?
- Steel billets are raw steel products that are formed into a specific shape, typically a square or rectangular cross-section. They are often used as a starting material for further processing and manufacturing of various steel products. Compared to other steel products, steel billets offer flexibility in terms of size and shape, allowing manufacturers to produce a wide range of end products. Additionally, steel billets possess superior strength and durability, making them an excellent choice for structural and construction applications.
- Q: How do steel billets come out?
- Two, pig iron and scrap steel1, smelting equipmentA, BOF: top and bottom blowing, blowing, now is widely used in pure oxygen top blown converterB, open hearth:C, electric steelmaking:
Send your message to us
Z27 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords






























