Square Steel Billet Size Q235,Q255,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 20 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Square Steel Billet Size Q235,Q255,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi
Specification
Steel billet(ingot) by cogging or breakdown of semi-finished products, is the raw material of all kinds of steel mill. Billet section of square, round, flat, rectangular and abnormity of several kinds of, mainly related to the shape of rolled products.
CNBM Q235,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi Billets Steel
Hot Rolled Steel Billets/ Mild Steel Bar/ Billet Steel
Specification (see below)
Standard: GB/JIS/ASTM
Size: 50*50mm-180*180mm
Length: 3-12mtrs or Customised
Steel material: Q235,Q255,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi
Technique: Hot rolled
FOB Unit Ton Price $250-350 and Usually I will quote you CFR price.
MOQ: Usually 1000-10000MT/size
Shipment:By Container,Bulk Vessel
Packaging Details: bundles with steel strips or as customers's requirements
Delivery time: Usually within 30 days after the deposit/LC
Inspection:Third party inspection before loading.
Technical data
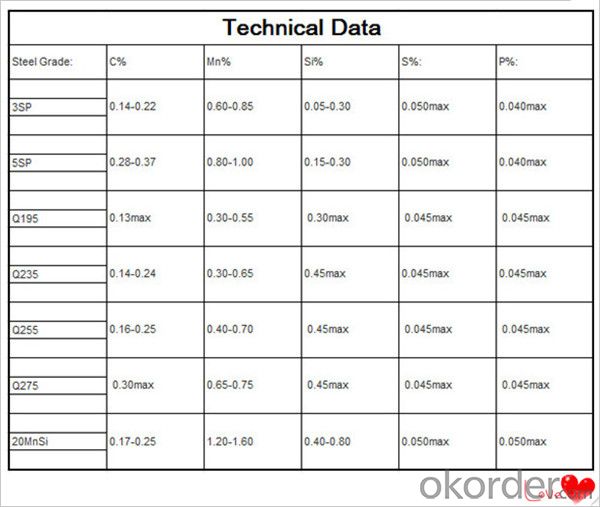
Feature Steel Billet
Rectangular billet continuous casting billet and mainly general carbon steel, low carbon low silicon cold-rolled material, high quality carbon structural steel, high strength low alloy steel, special steel, etc.
The billet is mainly divided into two kinds from the shape:
Slab: cross section width and height of the ratio of the larger, mainly used for rolling plate.
Billet: equal cross section width and height, or a huge difference, mainly used for rolling steel, wire rod. ,
Steel billets have distinct characteristics as compared with already furnished steel bars and products. Billets have a specific grain structure, which enables the metal to be processed more intricately. Steel billets are also known for their malleability and ductility, especially when exposed to varying temperatures during shaping and molding.
Packaging & Shipping
1. Packaging:
1) Small size: in bundles
2)Big size: in bulk
3)in plastic packing or as per customer requirement
2. Delivery time:
1) Normal size: within 7days send from warehouse directly
2) Special size: with 25-30days customer made for you
3. Trade terms:FOB/CFR/CIF
4. Shippment:
1) length:≤5.8m loaded in 20FT Container with 25-27tons
2) length:≤11.8m loaded in 40FT Container with 25-27tons
3) lengnth:≥12m shipped by bulk vessel, FILO terms
Steel Billet Images






Processing
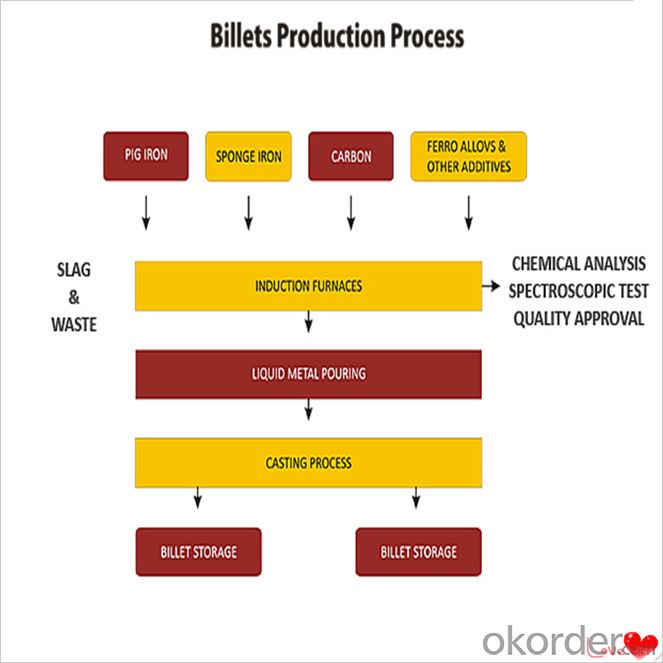
Usage-Billet Steel
Used for the plant, the bridge,shipment building high-rise building construction,lifting and transportation machinery, equipment manufracturing base building the support foundation pile manufacturing.
Billets, or ingots (as they sometimes referred to), are not of practical use until they have been formed into more functional shapes and sizes. While they have already been put in the furnace, they still require a series of shaping and molding procedures such as hot and cold working, milling and cutting before they are sold in hardware stores, or used for different applications. The unformed billets, however, can be used in striking currency such as coins and as reserves, similar to gold bars.
FAQ-Billet Steel
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1) How about your company?
A world class manufacturer & supplier of castings forging in carbon steel and alloy steel,is one of the large-scale professional investment casting production bases in China,consisting of both casting foundry forging and machining factory. Annually more than 8000 tons Precision casting and forging parts are exported to markets in Europe,America and Japan. OEM casting and forging service available according to customer’s requirements.
2) How to guarantee the quality of the products?
We have established the international advanced quality management system,every link from raw material to final product we have strict quality test;We resolutely put an end to unqualified products flowing into the market. At the same time, we will provide necessary follow-up service assurance.
3) How long can we receive the product after purchase?
In the purchase of product within three working days, We will arrange the factory delivery as soon as possible. The pecific time of receiving is related to the state and position of customers.Commonly 7 to 10 working days can be served.
4)Do you have your own QC department?
Yes, we have, our QC department will inspect the goods during the process of mass production and after completion of production.
hot sale!!! Cast Steel Grades/ mild steel bar/ billet steel
(1): High quality steel with reasonable price.
(2): Wide excellent experiences with after-sale service.
(3): Every process will be checked by responsible QC which insures every product's quality.
(4): Professional packing teams which keep every packing safely.
(5): Trial order can be done in one week.
(6): Samples can be provided as your requirements.
- Q: What are the main factors affecting the tensile strength of steel billets?
- There are several main factors that affect the tensile strength of steel billets. Firstly, the composition of the steel plays a significant role. The presence of certain elements, such as carbon, manganese, and silicon, can greatly influence the strength of the steel. Carbon, in particular, is a key element in increasing the strength of steel through its ability to form strong interatomic bonds. Secondly, the heat treatment process employed during the production of steel billets is crucial. Heat treatment, such as quenching and tempering, can significantly enhance the tensile strength of the steel by manipulating its microstructure. Quenching involves rapidly cooling the steel, which creates a hardened structure, while tempering involves reheating the steel to a specific temperature to achieve the desired balance of hardness and toughness. Additionally, the grain size of the steel also affects its tensile strength. Fine-grained steel generally exhibits higher strength due to the increased number of grain boundaries, which act as barriers to dislocation movement. On the other hand, coarse-grained steel tends to have lower strength as it allows for easier dislocation movement. Moreover, the presence of impurities or defects in the steel can weaken its tensile strength. Inclusions, such as sulfur, phosphorus, and non-metallic inclusions, can act as stress concentration points and promote crack initiation, leading to reduced strength. Similarly, the presence of voids, porosity, or other structural defects can compromise the overall strength of the steel billets. Lastly, the processing conditions during the manufacturing of steel billets can affect their tensile strength. Parameters such as rolling and forging temperatures, deformation rate, and cooling rate can influence the resulting microstructure and, consequently, the strength of the steel. In conclusion, the main factors affecting the tensile strength of steel billets include the steel composition, heat treatment process, grain size, impurities or defects, and processing conditions. Understanding and optimizing these factors are crucial for producing steel billets with the desired mechanical properties.
- Q: How are steel billets inspected for surface defects?
- Steel billets are inspected for surface defects using various methods and techniques to ensure the quality and integrity of the material. One common method is visual inspection, where trained inspectors carefully examine the surface of the billets for any visible defects such as cracks, scratches, pits, or uneven surfaces. They use proper lighting and magnification tools to thoroughly inspect the entire surface area. Another method used is dye penetrant testing. In this technique, a liquid dye is applied to the surface of the billets, which is then allowed to seep into any cracks or defects. After a specified time, excess dye is removed, and a developer is applied. The developer draws out the dye from any defects, making them clearly visible and easy to identify. Magnetic particle inspection is another widely used method. In this process, the billets are magnetized, and iron particles are applied to the surface. Any surface defects disrupt the magnetic field, causing the iron particles to gather around the defect, making them clearly visible upon inspection. This technique is particularly effective for detecting defects such as surface cracks. Ultrasonic testing is also commonly employed for inspecting steel billets. High-frequency sound waves are transmitted through the material, and any surface defects or internal flaws cause reflections or echoes. These reflections are detected and analyzed, providing information about the size, location, and type of defect present. Additionally, eddy current testing can be used to inspect steel billets for surface defects. This method involves passing an alternating current through a probe that is placed near the surface of the billet. Any defects or variations in the material's conductivity cause changes in the eddy currents, which can be detected and analyzed to identify surface defects. Overall, steel billets undergo meticulous inspection using a combination of visual, dye penetrant, magnetic particle, ultrasonic, and eddy current testing methods to ensure that any surface defects are identified and addressed, guaranteeing the quality and reliability of the final product.
- Q: What are the different methods of steel billet surface polishing?
- There are multiple techniques available for polishing the surface of steel billets, each with its own benefits and uses. These techniques consist of mechanical polishing, chemical polishing, electrochemical polishing, and abrasive blasting. Mechanical polishing is a widely employed method that employs abrasive materials to eliminate surface flaws and create a smooth outcome. It can be done manually using sandpaper or with the aid of machinery like buffing machines or belt sanders. This technique effectively removes scratches, oxidation, and other imperfections on the surface, resulting in a polished and reflective appearance. Chemical polishing is a non-mechanical approach that relies on chemical reactions to eliminate surface flaws. It involves immersing the steel billet in a chemical solution that dissolves a thin layer of the material, resulting in a smoother surface. Chemical polishing is commonly used for intricate or delicate components, as it can achieve a high level of precision and uniformity. Electrochemical polishing, also known as electropolishing, is a technique that combines chemical and electrical processes to polish the surface of the steel billet. It involves immersing the billet in an electrolyte solution and applying an electric current. The electric current removes microscopic peaks and imperfections, resulting in a smoother and brighter surface. Electrochemical polishing is frequently used for stainless steel billets due to its ability to eliminate surface contaminants and enhance corrosion resistance. Abrasive blasting, also referred to as sandblasting, is a technique that utilizes high-pressure air or water to propel abrasive materials onto the surface of the steel billet. This process effectively eliminates rust, scale, and other surface contaminants, resulting in a clean and textured finish. Abrasive blasting can be performed using various abrasive materials such as sand, steel shot, or glass beads, depending on the desired surface finish. In conclusion, the various techniques for polishing the surface of steel billets include mechanical polishing, chemical polishing, electrochemical polishing, and abrasive blasting. Each technique offers its own advantages and applications, providing a range of options to achieve the desired surface finish for steel billets.
- Q: What are the different surface defects found in stainless steel billets?
- There are several different surface defects that can be found in stainless steel billets. Some of the common surface defects include: 1. Scale: Scale is a thin layer of oxide that forms on the surface of stainless steel during the heating process. It appears as a dark, rough layer and can be easily removed by pickling or passivation. 2. Pitting: Pitting is localized corrosion that appears as small, shallow pits on the surface of the billet. It is caused by chloride ions or other aggressive chemicals and can lead to reduced corrosion resistance. 3. Scratches: Scratches can occur during handling, transportation, or processing of the billet. They are visible as linear marks on the surface and can affect the appearance and integrity of the material. 4. Lamination: Lamination defects occur as thin layers or flakes parallel to the surface of the billet. They are caused by improper rolling or inadequate bonding during the manufacturing process. 5. Inclusions: Inclusions are non-metallic particles or impurities that are embedded in the stainless steel billet. They can affect the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of the material. 6. Decarburization: Decarburization is the loss of carbon from the surface of the billet during heating. It appears as a light-colored layer and can negatively impact the material's strength and hardness. 7. Cracks: Cracks can occur due to thermal stresses, improper cooling, or mechanical damage. They can be either surface cracks or internal cracks, and can significantly weaken the billet. It is important to detect and address these surface defects to ensure the quality and performance of stainless steel billets in various applications.
- Q: What are the potential applications of steel billets in the food and beverage aftermarket?
- Steel billets have a wide range of potential applications in the food and beverage aftermarket. One potential application is in the production of food processing equipment. Steel billets can be used to manufacture machinery and equipment that is used in food processing plants, such as conveyor belts, food mixers, and cutting tools. The durability and strength of steel make it a suitable material for these applications, as it can withstand the rigors of heavy use and maintain its integrity even in harsh conditions. Another potential application of steel billets in the food and beverage aftermarket is in the construction of storage tanks and containers. Steel is known for its corrosion resistance, making it ideal for storing various food and beverage products. Steel billets can be used to manufacture tanks and containers that can safely store liquids such as water, juices, and alcoholic beverages. These steel tanks can also be insulated to ensure temperature control, which is crucial in preserving the quality of perishable products. Furthermore, steel billets can be used in the production of kitchen equipment and utensils. Steel is a hygienic material that is easy to clean and maintain, making it suitable for use in commercial kitchens and food preparation areas. Steel billets can be shaped into various kitchen utensils such as knives, pans, and cooking pots, which are essential tools in the food and beverage industry. Steel utensils are known for their durability and heat conductivity, which ensures even cooking and efficient food preparation. Overall, the potential applications of steel billets in the food and beverage aftermarket are vast. From food processing equipment to storage tanks and kitchen utensils, steel billets provide a reliable and versatile material for various industries within the food and beverage sector. Its strength, durability, and hygienic properties make it a valuable resource in ensuring the safe and efficient production, storage, and preparation of food and beverages.
- Q: What are the potential applications of steel billets in the oil and gas sector?
- Steel billets have numerous potential applications in the oil and gas sector. They can be used to manufacture various critical components such as pipes, valves, and fittings, which are essential for the transportation, processing, and storage of oil and gas. Steel billets also find use in the construction of offshore platforms and drilling equipment due to their high strength and durability. Additionally, they can be utilized in the fabrication of pressure vessels, heat exchangers, and other infrastructure required for oil refining and petrochemical processes. Overall, steel billets play a crucial role in ensuring the safety, reliability, and efficiency of operations in the oil and gas industry.
- Q: What are the different types of mechanical property testing methods for steel billets?
- Some different types of mechanical property testing methods for steel billets include tensile testing, hardness testing, impact testing, and fatigue testing. Tensile testing measures the strength and ductility of the material by applying a pulling force until it breaks. Hardness testing measures the resistance of the material to penetration or indentation. Impact testing evaluates the material's ability to absorb energy under high rates of loading. Fatigue testing assesses the material's resistance to failure under cyclic loading conditions.
- Q: What is the role of steel billets in the production of valves and fittings?
- Valves and fittings, which are crucial in industries like oil and gas, petrochemical, and water treatment, rely heavily on steel billets. These billets, derived from molten steel, serve as the starting point for producing these components. To meet specific requirements, the billets are cast into shapes like round, square, or rectangular. The usage of steel billets enables manufacturers to maintain consistent quality and performance in valves and fittings. The selection process involves considering factors such as chemical composition, mechanical properties, and microstructure to guarantee the desired characteristics in the end product. After obtaining the steel billets, they undergo various manufacturing processes like forging, machining, and heat treatment. These processes further enhance the strength, integrity, and functionality of the final valve and fitting components. One of the advantages of steel billets is their versatility in customization. They can be easily cut, shaped, and formed to create valves and fittings with different sizes, configurations, and designs. This flexibility allows them to meet the specific requirements of different applications and industries. In summary, steel billets serve as the raw material for valves and fittings, playing a vital role in their production. Their strength, durability, and customization capabilities ensure the reliability and performance of these components in various industrial settings.
- Q: What is the difference between steel billets and steel bars?
- Steel billets and steel bars, two semi-finished products made from steel, exhibit distinct dissimilarities. To begin with, steel billets possess larger dimensions compared to steel bars. Billets typically assume a square or rectangular form with a cross-sectional area ranging from 36 to 216 square inches. Their production commonly involves the continuous casting process, which entails pouring molten steel into molds, followed by cooling and solidification. Billets function as the initial material for various steel products, including bars, rods, and wire. Conversely, steel bars display smaller proportions and adhere to more standardized shapes. Their configuration can be round, square, hexagonal, or flat, contingent upon their intended application. The production of steel bars chiefly involves the hot rolling method, wherein billets undergo heating and are subsequently passed through a series of rolling mills to achieve the desired dimensions and shape. Bars frequently find use in construction, manufacturing, and other industries that prioritize strength and durability. Another disparity between steel billets and steel bars resides in their surface finish. The casting process renders steel billets with a rough mill-scale surface. In contrast, steel bars possess a smoother surface finish, achieved through hot rolling and subsequent finishing procedures such as peeling, grinding, or polishing. Moreover, steel billets primarily serve as raw materials for further processing, while steel bars represent the final product that can be directly employed in diverse applications. Steel bars commonly feature in construction projects as reinforcement for concrete structures, in machinery and tool production, as well as in the manufacturing of automotive parts, among numerous other industrial applications. In conclusion, steel billets and steel bars differ in terms of size, shape, surface finish, and purpose. Billets are larger, rougher, and act as the starting point for various steel products, whereas bars are smaller, boast a smoother surface finish, and emerge as the final product utilized across a wide array of applications.
- Q: What does "billet" mean?
- Steelmaking and continuous casting of steel products are mainly used for steel rolling, such as round bar, wire rod, sheet metal and so on
Send your message to us
Square Steel Billet Size Q235,Q255,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 20 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords

































